
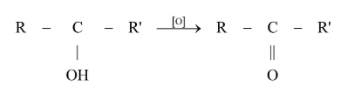
How will you obtained:
Acetone from propene
Answer
523.5k+ views
Hint: The alkene can be converted into the ketone. The reaction of conversion involves two-step: Hydration followed by oxidation. The hydration involves the addition of water molecules across the double bond to form oxonium ions which on the attack with base converted into the corresponding secondary alcohol. On oxidation, secondary alcohol generated ketones.
Complete step by step answer:
Propene is converted into the corresponding ketone that is acetone (or propanone ). The reaction of the conversion of the alkene to the ketone involves two steps :
1) Hydration
2) Oxidation
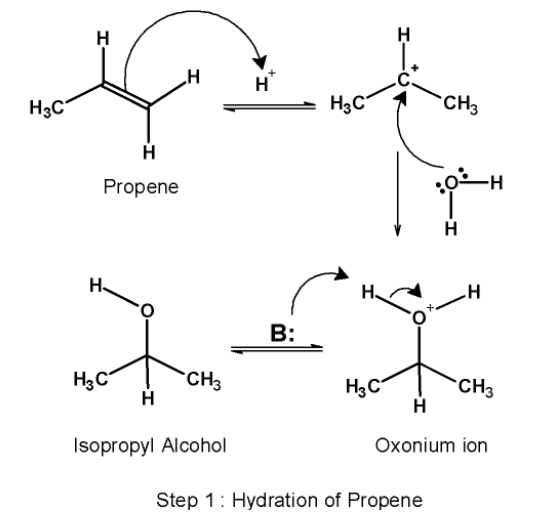
Step 1) Hydration:
The first step involves the acid-catalyzed hydration of the alkene i.e.propene.it converts the alkene into corresponding alcohol. Here, propene on hydration forms isopropyl alcohol. This step itself comprises three sub-steps. Those are as follows:
a) This step involves the attack of the proton on the propene. The highly electronegative double bond attack on the hydrogen ion. The protonation of the alkene generates a carbocation at the carbon atom. Here, the p electrons (i.e. double-bonded electrons) acts as a Lewis base. They donate their electrons to the hydrogen ion.
b) The water molecule acts as a nucleophile and attacks on the electrophilic carbocation formed earlier. The nucleophilic attack results in the formation of oxonium ions.
c) In the next step, the oxonium ion is deprotonated by a base. The deprotonation results in the formation of alcohol and regenerates the acid catalyst.
The conversion of propene to isopropyl alcohol is as shown below,
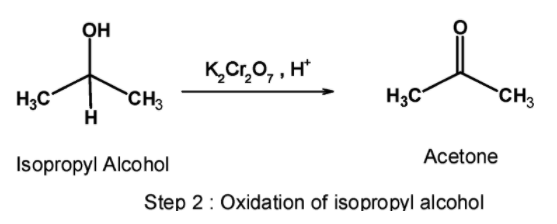
Step 2) Oxidation:
In the second step, the isopropyl alcohol obtained is oxidized using a suitable oxidizing agent. Here, acidified potassium dichromate is used to convert the isopropyl alcohol to acetone. The reaction is as shown below,
Here, we have converted propene into acetone.
Note: Note that, instead of potassium dichromate in an acidic medium we can use Pyridinium chlorochromate (PCC) as the oxidizing agent.it is a milder version of the chromic acid. It converts primary alcohols to aldehydes and secondary alcohol to a ketone. Further oxidation to carboxylic acid is not feasible by PCC.

Complete step by step answer:
Propene is converted into the corresponding ketone that is acetone (or propanone ). The reaction of the conversion of the alkene to the ketone involves two steps :
1) Hydration
2) Oxidation
Step 1) Hydration:
The first step involves the acid-catalyzed hydration of the alkene i.e.propene.it converts the alkene into corresponding alcohol. Here, propene on hydration forms isopropyl alcohol. This step itself comprises three sub-steps. Those are as follows:
a) This step involves the attack of the proton on the propene. The highly electronegative double bond attack on the hydrogen ion. The protonation of the alkene generates a carbocation at the carbon atom. Here, the p electrons (i.e. double-bonded electrons) acts as a Lewis base. They donate their electrons to the hydrogen ion.
b) The water molecule acts as a nucleophile and attacks on the electrophilic carbocation formed earlier. The nucleophilic attack results in the formation of oxonium ions.
c) In the next step, the oxonium ion is deprotonated by a base. The deprotonation results in the formation of alcohol and regenerates the acid catalyst.
The conversion of propene to isopropyl alcohol is as shown below,

Step 2) Oxidation:
In the second step, the isopropyl alcohol obtained is oxidized using a suitable oxidizing agent. Here, acidified potassium dichromate is used to convert the isopropyl alcohol to acetone. The reaction is as shown below,

Here, we have converted propene into acetone.
Note: Note that, instead of potassium dichromate in an acidic medium we can use Pyridinium chlorochromate (PCC) as the oxidizing agent.it is a milder version of the chromic acid. It converts primary alcohols to aldehydes and secondary alcohol to a ketone. Further oxidation to carboxylic acid is not feasible by PCC.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




