
One turn of the helix in a B-form DNA is approximately
A. \[3.4\text{ }nm\]
B. \[2\text{ }nm\]
C. \[20\text{ }nm\]
D. \[0.34\text{ }nm\]
Answer
571.2k+ views
Hint: The famous DNA model is the Watson-Crick model. The model says that DNA exists as a double helix. The two polynucleotide chain strands are antiparallel, which is to say that they pass in opposite directions. The sugar-phosphate-sugar chain forms the backbone. The nitrogenous bases are expected, but face within, more or less perpendicular to this backbone. Adenine and guanine from one strand are obligatory base pairs on another strand of thymine and cytosine, respectively.
Complete answer: Each ascending stage is described by a pair of bases. One complete turn of the helical line requires 10 moves or 10 base pairs. This gap is known as the pitch. The pitch would be \[3.4\text{ }nm\] and the increase per base pair would be \[0.34\text{ }nm\]. As a consequence, there are about 10 pairs per switch. The intertwined strands form two grooves of different widths, referred to as the main groove and the small groove, which may facilitate binding to specific proteins.
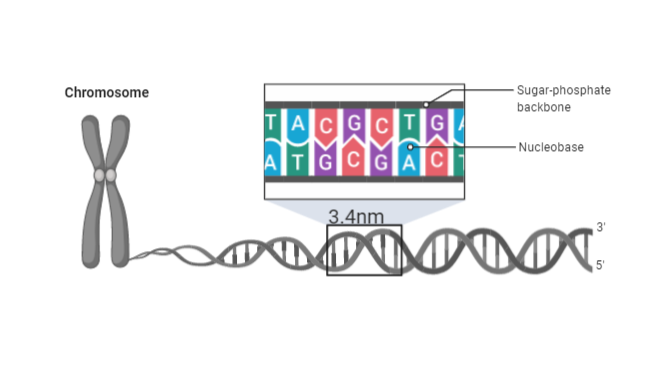
The correct answer is A.
Note: The DNA mentioned above is a type B-DNA. -Three major types of DNA are double-stranded and interlinked between complementary base pairs. These are the concepts A-form, B-form, and Z-form. There are two types of DNA in the cell: autosomal DNA and mitochondrial DNA. Autosomal DNA (also known as nuclear DNA) is packaged into 22 paired chromosomes. One was inherited from the mother in each pair of autosomes, and one was inherited from the father. Z-DNA is a type of DNA that has a different structure from the more common form of B-DNA. It is a left-hand double helix in which the sugar-phosphate backbone has a zigzag pattern due to the alternating stacking of bases in anti-conformation and syn-conformation.
Complete answer: Each ascending stage is described by a pair of bases. One complete turn of the helical line requires 10 moves or 10 base pairs. This gap is known as the pitch. The pitch would be \[3.4\text{ }nm\] and the increase per base pair would be \[0.34\text{ }nm\]. As a consequence, there are about 10 pairs per switch. The intertwined strands form two grooves of different widths, referred to as the main groove and the small groove, which may facilitate binding to specific proteins.

The correct answer is A.
Note: The DNA mentioned above is a type B-DNA. -Three major types of DNA are double-stranded and interlinked between complementary base pairs. These are the concepts A-form, B-form, and Z-form. There are two types of DNA in the cell: autosomal DNA and mitochondrial DNA. Autosomal DNA (also known as nuclear DNA) is packaged into 22 paired chromosomes. One was inherited from the mother in each pair of autosomes, and one was inherited from the father. Z-DNA is a type of DNA that has a different structure from the more common form of B-DNA. It is a left-hand double helix in which the sugar-phosphate backbone has a zigzag pattern due to the alternating stacking of bases in anti-conformation and syn-conformation.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers




