
Ortho-nitrophenol is less soluble in water than para-nitrophenols because:
(A) o-nitrophenol is more volatile in steam than those of m- and p- isomers.
(B) o-nitrophenol shows intramolecular H-bonding
(C) o-nitrophenol shows intermolecular H-bonding
(D) None of these
Answer
577.5k+ views
Hint: The organic compounds can form H-bonding with water and dissolves in water. Here, one of the isomers is not able to form H-bonds with water molecules which is the reason why it has low solubility.
Complete step by step solution:
We are given the fact that which isomer of nitrophenol is less soluble in water and we need to give the reason why this happens.
- The tendency of dissolution of any organic compounds in water is dependent on forming hydrogen bonding with the solvent molecules which are water molecules. So, let’s see if there will be any difference in H-bonding of nitrophenol isomers with water or not.
i) p-nitrophenol
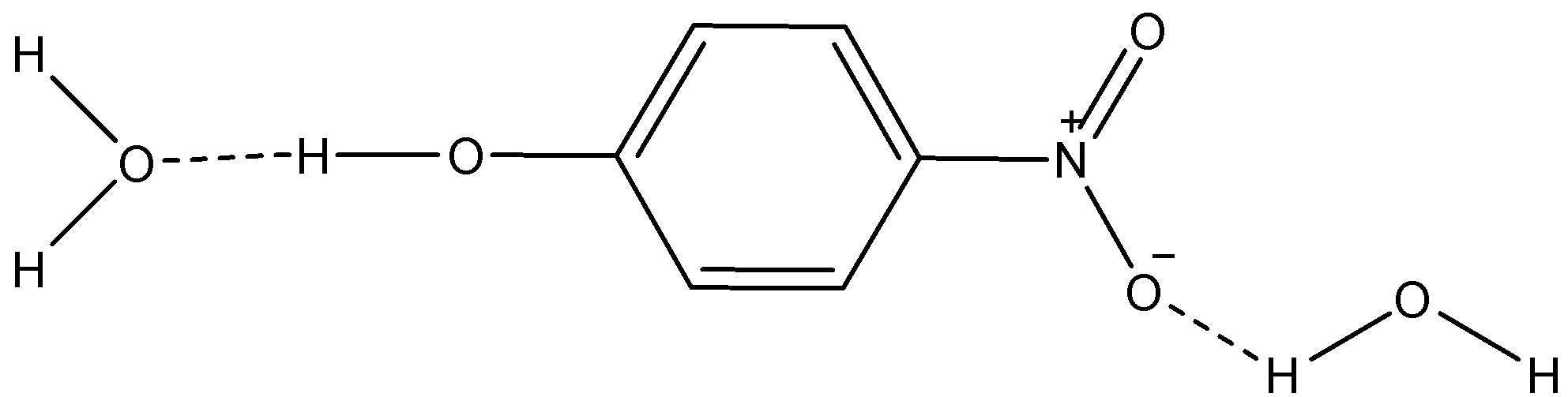
Here, we can see that the dotted lines show H-bonding between the molecules of water and p-nitrophenol. So, this increases the solubility of p-nitrophenol in water.
ii) o-nitrophenol:
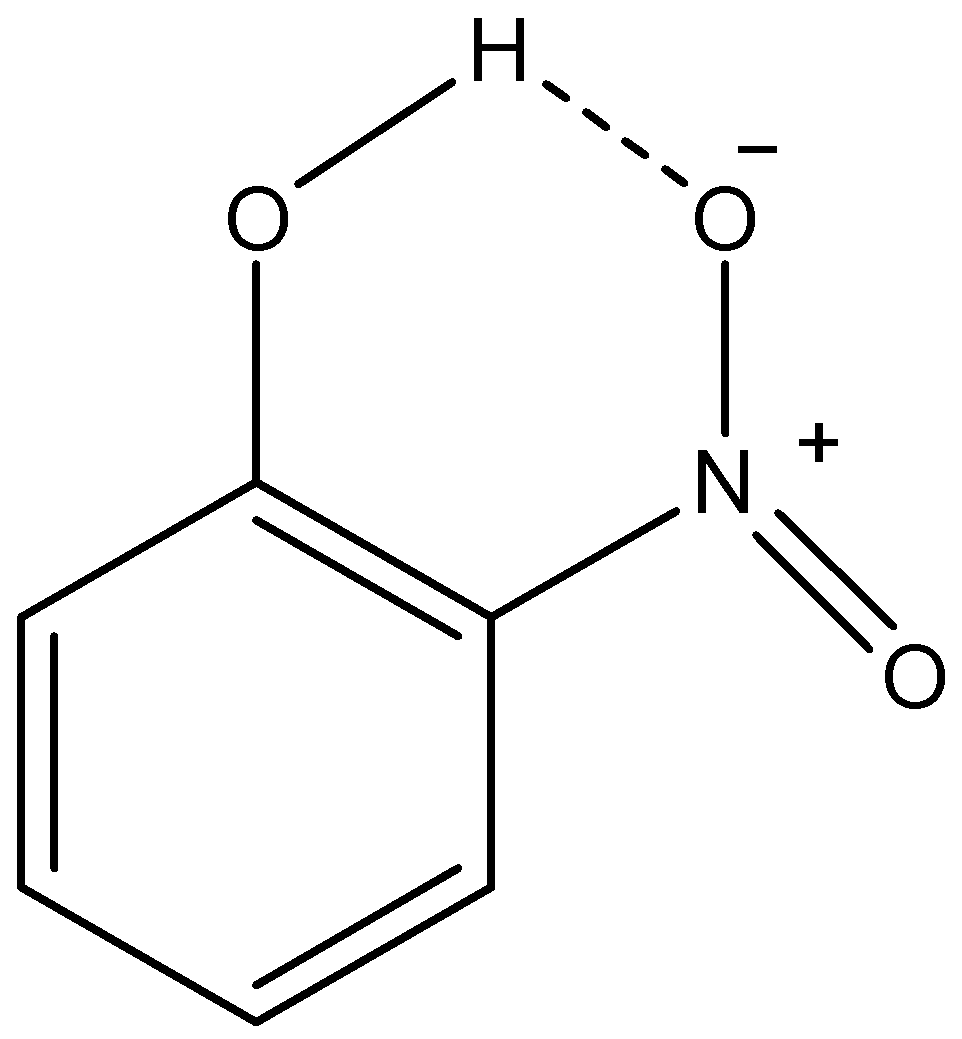
Here, we can see that as the oxygen atom of nitro group and the hydrogen atom of phenolic –OH group is in vicinity, they make H-bond. This H-bonding between two functional groups in the same molecule is called intramolecular H-bonding. Due to this H-bonding, the o-isomer of nitrophenol is not able to form H-bonds with solvent molecules. This makes it less soluble in water in comparison with p-nitrophenol. Therefore, we can conclude that o-nitrophenol forms intramolecular H-bonding which is the reason for its low solubility.
So, the correct answer to this question is (B).
Note: Remember that however p-nitrophenol can make intermolecular H-bonding. That means it can make H-bonds with other molecules of p-nitrophenol but this does not alter its solubility in water.
Complete step by step solution:
We are given the fact that which isomer of nitrophenol is less soluble in water and we need to give the reason why this happens.
- The tendency of dissolution of any organic compounds in water is dependent on forming hydrogen bonding with the solvent molecules which are water molecules. So, let’s see if there will be any difference in H-bonding of nitrophenol isomers with water or not.
i) p-nitrophenol

Here, we can see that the dotted lines show H-bonding between the molecules of water and p-nitrophenol. So, this increases the solubility of p-nitrophenol in water.
ii) o-nitrophenol:

Here, we can see that as the oxygen atom of nitro group and the hydrogen atom of phenolic –OH group is in vicinity, they make H-bond. This H-bonding between two functional groups in the same molecule is called intramolecular H-bonding. Due to this H-bonding, the o-isomer of nitrophenol is not able to form H-bonds with solvent molecules. This makes it less soluble in water in comparison with p-nitrophenol. Therefore, we can conclude that o-nitrophenol forms intramolecular H-bonding which is the reason for its low solubility.
So, the correct answer to this question is (B).
Note: Remember that however p-nitrophenol can make intermolecular H-bonding. That means it can make H-bonds with other molecules of p-nitrophenol but this does not alter its solubility in water.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




