
Osazone formation involves only 2 carbon atoms of glucose because of:
A.Oxidation
B.Chelation
C.Reduction
D.Hydrolysis
Answer
577.5k+ views
Hint:Glucose reacts with one molecule of phenyl hydrazine to form glucose phenylhydrazine and the second molecule of phenyl hydrazine oxidises second Carbon atom to form keto group, the third molecule of phenyl hydrazine then reacts with this Carbon atom.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us discuss Osazone formation in a detailed manner:
-Osazones are a class of carbohydrate derivatives which are formed when a reducing sugar reacts with 3 equivalents of phenyl hydrazine at boiling temperatures.
- To understand the formation of Osazone let us look into its mechanism:
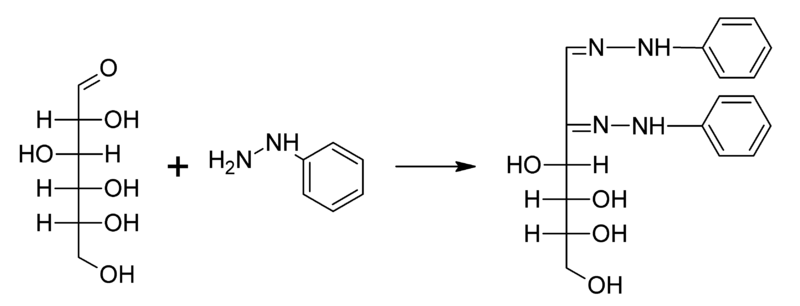
-So as you can see the first molecule of phenyl gets attached to the sugar molecule, second will bring about the oxidation of the 2nd Carbon atom and converts it into the keto group and finally the third one will get attached to the carbon atom.
-Thus, from here we can conclude that Osazone formation involves only 2 carbon atoms of glucose molecules because of oxidation.
Hence, option A is the correct answer.
Additional information:
Only reducing sugar forms an Osazone derivative. Non-reducing ones are not able to form it because they don’t have an OH group attached to the anomeric carbon and hence are not able to reduce other compounds.
-Closely related sugars or carbohydrates (which differ from one another only at carbon number 1 and 2) give identical Osazone derivatives. For example, glucose, fructose and mannose form identical Osazones at carbon number 1 and 2 and Osazone formation involves only these carbon molecules.
-This reaction was developed by German chemist Emil Fischer.
Note:
It is important to note that Osazone formation reaction is used as a test to identify monosaccharides who differ in stereochemistry of each other only by one chiral carbon. It also finds importance in identifying the type of carbohydrates because Osazone derivatives all sugars have a definite boiling and are highly crystalline in nature.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us discuss Osazone formation in a detailed manner:
-Osazones are a class of carbohydrate derivatives which are formed when a reducing sugar reacts with 3 equivalents of phenyl hydrazine at boiling temperatures.
- To understand the formation of Osazone let us look into its mechanism:

-So as you can see the first molecule of phenyl gets attached to the sugar molecule, second will bring about the oxidation of the 2nd Carbon atom and converts it into the keto group and finally the third one will get attached to the carbon atom.
-Thus, from here we can conclude that Osazone formation involves only 2 carbon atoms of glucose molecules because of oxidation.
Hence, option A is the correct answer.
Additional information:
Only reducing sugar forms an Osazone derivative. Non-reducing ones are not able to form it because they don’t have an OH group attached to the anomeric carbon and hence are not able to reduce other compounds.
-Closely related sugars or carbohydrates (which differ from one another only at carbon number 1 and 2) give identical Osazone derivatives. For example, glucose, fructose and mannose form identical Osazones at carbon number 1 and 2 and Osazone formation involves only these carbon molecules.
-This reaction was developed by German chemist Emil Fischer.
Note:
It is important to note that Osazone formation reaction is used as a test to identify monosaccharides who differ in stereochemistry of each other only by one chiral carbon. It also finds importance in identifying the type of carbohydrates because Osazone derivatives all sugars have a definite boiling and are highly crystalline in nature.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




