
Out of 64 codons, 61 codons code for 20 types of amino acids. What is it called?
(a) Wobbling of codon
(b) Overlapping of genes
(c) University of codons
(d) Degeneracy of genetic code
Answer
566.4k+ views
Hint: This is the concept in which a single amino acid is coded by more than one genetic codon. These genetic codes are the relationship between the sequence of nucleotides and the amino acids.
Complete answer:
Out of 64 codons, 61 codons code for 20 sorts of amino alkanoic acid, this is often called degeneracy of ordering. Genetic code is a set of rules by which a linear sequence of nucleotides specifies the linear sequence of the polypeptide. This means that they specify how the nucleotide sequence of a messenger RNA is translated into an amino alkanoic acid sequence of the polypeptide.
Additional Information:
- There are 64 different genetic codes each of which codes for one out of 20 amino acids.
- These codes have degenerated which means the same amino acid is coded by more than one base triplet.
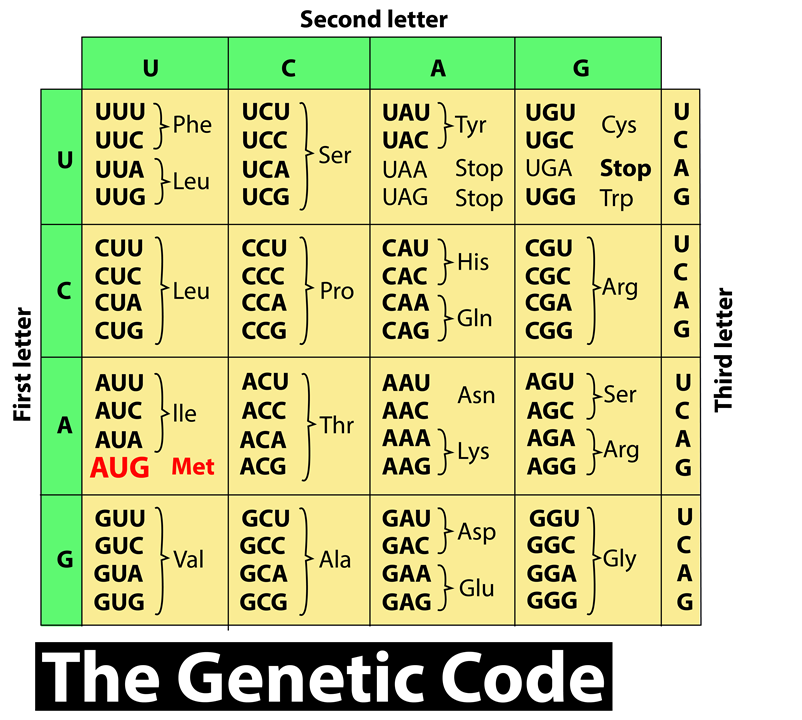
- Lack of specificity in protein synthesis is not implied by degeneracy.
- This means that a particular amino acid can be directed to its place in the polypeptide chain by more than one base triplet. For example, the three amino acids arginine, alanine, and leucine each are having 6 similar codons.
- The degeneracy of genetic code is basically of two types: partial and complete.
- Partial degeneracy: In this type the first two nucleotides are identical but the third nucleotides of the degenerate codon are different. For example, leucine is coded by CUU and CUC both.
- Complete degeneracy: in this type any of the four bases can take the third position and still code for the same amino acid. For example, serine is coded by UCU, UCC, UCA, and UCG.
- The genetic codon never overlapping this means a base in messenger RNA is not shared by two different codons. If the overlapping will be possible then 6 bases could code for four amino acids which are not true.
- Wobbling of a codon is loose base pairing between the first base of the anticodon and the third base of the codon on mRNA.
So, the correct answer is, ’(d) Degeneracy of genetic code’.
Note:
- Degeneracy of genetic code means the same amino acid is coded by more than one base triplet.
- A codon consists of three nucleotide bases called triplets.
- The degeneracy of genetic code is basically of two types: partial and complete.
- In partial degeneracy, the first two nucleotides are the same but the third one is different.
- In complete degeneracy, any of the four bases can take the third position.
Complete answer:
Out of 64 codons, 61 codons code for 20 sorts of amino alkanoic acid, this is often called degeneracy of ordering. Genetic code is a set of rules by which a linear sequence of nucleotides specifies the linear sequence of the polypeptide. This means that they specify how the nucleotide sequence of a messenger RNA is translated into an amino alkanoic acid sequence of the polypeptide.
Additional Information:
- There are 64 different genetic codes each of which codes for one out of 20 amino acids.
- These codes have degenerated which means the same amino acid is coded by more than one base triplet.

- Lack of specificity in protein synthesis is not implied by degeneracy.
- This means that a particular amino acid can be directed to its place in the polypeptide chain by more than one base triplet. For example, the three amino acids arginine, alanine, and leucine each are having 6 similar codons.
- The degeneracy of genetic code is basically of two types: partial and complete.
- Partial degeneracy: In this type the first two nucleotides are identical but the third nucleotides of the degenerate codon are different. For example, leucine is coded by CUU and CUC both.
- Complete degeneracy: in this type any of the four bases can take the third position and still code for the same amino acid. For example, serine is coded by UCU, UCC, UCA, and UCG.
- The genetic codon never overlapping this means a base in messenger RNA is not shared by two different codons. If the overlapping will be possible then 6 bases could code for four amino acids which are not true.
- Wobbling of a codon is loose base pairing between the first base of the anticodon and the third base of the codon on mRNA.
So, the correct answer is, ’(d) Degeneracy of genetic code’.
Note:
- Degeneracy of genetic code means the same amino acid is coded by more than one base triplet.
- A codon consists of three nucleotide bases called triplets.
- The degeneracy of genetic code is basically of two types: partial and complete.
- In partial degeneracy, the first two nucleotides are the same but the third one is different.
- In complete degeneracy, any of the four bases can take the third position.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




