
Out of the following four nets there are two correct nets to make a tetrahedron. Identify them.
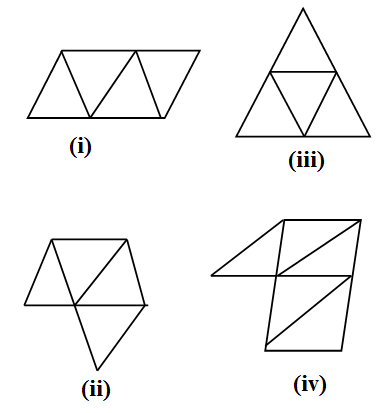
Answer
546.3k+ views
Hint: We recall the shape of tetrahedron and nets of a polyhedron. Since we have only four triangular faces in the tetrahedron we have four triangles in the net. We try to fold the polygons of the nets along the common sides and attempt to make a tetrahedron. \[\]
Complete step by step solution:
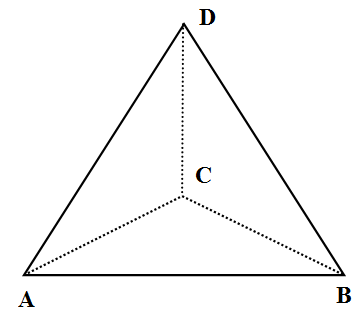
We know that a tetrahedron is a convex polyhedron with 4 triangular faces, 4 vertices and 6 straight edges. It is also called a triangular pyramid because it is a polyhedron with a flat polygon (triangular ) base and triangular faces connecting the base to a common point. We call that the common point as apex. We have drawn the tetrahedron with apex $D$ and triangular base ABC below with other faces DCA, DCB, DAB. \[\]
We also know that a net of a polyhedron is an arrangement of non-overlapping edge-joined polygons in the plane which can be folded (along edges) to become the faces of the polyhedron. \[\]
(i) We denote the vertices of the triangles in the net as shown in the below figure. \[\]
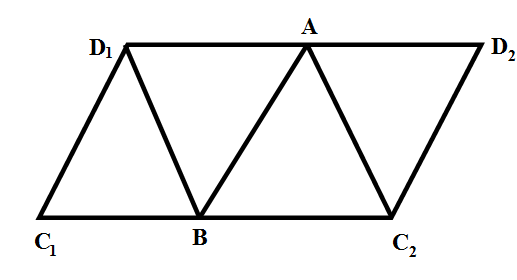
We fold the triangle $A{{D}_{1}}{{C}_{2}}$ upward along $A{{C}_{2}}$ and we fold the triangle $A{{D}_{1}}B$ upward along AB. The vertices ${{D}_{1}}$ and ${{D}_{2}}$ are going to coincide and we name the vertex as D. When we fold the triangle $A{{D}_{1}}B$ , the triangle $B{{D}_{1}}{{C}_{1}}$ will also be folded and the vertices ${{C}_{2}},{{C}_{1}}$ will coincide and we name that vertex as C. We have now D as the apex and ABC as the base for the tetrahedron as ABCD. \[\]
(ii) We denote the vertices of the triangles in the net as shown in the below figure.
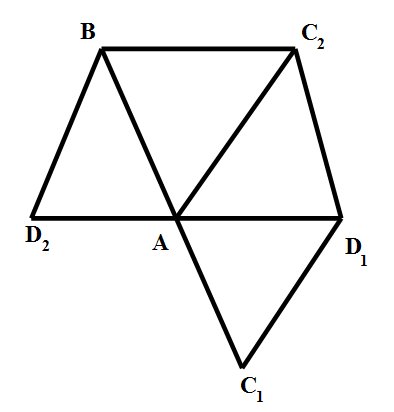
We cannot get a tetrahedron by folding along the sides. We may fold triangle $A{{D}_{1}}{{C}_{2}}$ and $A{{D}_{2}}B$ where ${{D}_{1}}$ and ${{D}_{2}}$ will coincide but the triangle $A{{C}_{1}}{{D}_{1}}$ will remain unused. We may also fold triangles $A{{D}_{1}}{{C}_{2}}$ and $A{{D}_{1}}{{C}_{1}}$ where ${{C}_{1}},{{C}_{2}}$ will coincide but triangle $A{{D}_{2}}B$ remain unused. So we cannot make tetrahedra here. \[\]
(iii) We denote the vertices of the triangles in the net as shown in the below figure. \[\]
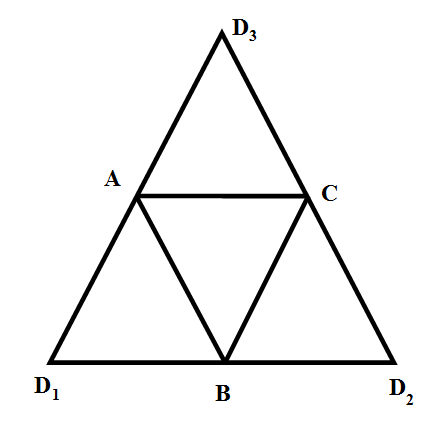
We fold the triangle $A{{D}_{1}}B$ along AB, the triangle $B{{D}_{2}}C$ along BC and the triangle $A{{D}_{3}}C$ along AC. The vertices ${{D}_{1}},{{D}_{2}},{{D}_{3}}$ will coincide and we name the that vertex as D. So we have the tetrahedron with apex D and triangular base ABC. \[\]
(iv) We see in the figure there 5 triangles in the net but tetrahedron as 4 triangular faces. Hence we cannot make a tetrahedron with the net in (iv). \[\]
Note: We note that the word coincides means meeting or merging at one point. We note that tetrahedron has all edges of equal length and hence the polygons in the net of regular tetrahedron are equilateral triangles. The total surface area of tetrahedron is $\sqrt{3}\times {{a}^{2}}$ where $a$ is the length of any edge.
Complete step by step solution:
We know that a tetrahedron is a convex polyhedron with 4 triangular faces, 4 vertices and 6 straight edges. It is also called a triangular pyramid because it is a polyhedron with a flat polygon (triangular ) base and triangular faces connecting the base to a common point. We call that the common point as apex. We have drawn the tetrahedron with apex $D$ and triangular base ABC below with other faces DCA, DCB, DAB. \[\]

We also know that a net of a polyhedron is an arrangement of non-overlapping edge-joined polygons in the plane which can be folded (along edges) to become the faces of the polyhedron. \[\]
(i) We denote the vertices of the triangles in the net as shown in the below figure. \[\]

We fold the triangle $A{{D}_{1}}{{C}_{2}}$ upward along $A{{C}_{2}}$ and we fold the triangle $A{{D}_{1}}B$ upward along AB. The vertices ${{D}_{1}}$ and ${{D}_{2}}$ are going to coincide and we name the vertex as D. When we fold the triangle $A{{D}_{1}}B$ , the triangle $B{{D}_{1}}{{C}_{1}}$ will also be folded and the vertices ${{C}_{2}},{{C}_{1}}$ will coincide and we name that vertex as C. We have now D as the apex and ABC as the base for the tetrahedron as ABCD. \[\]
(ii) We denote the vertices of the triangles in the net as shown in the below figure.

We cannot get a tetrahedron by folding along the sides. We may fold triangle $A{{D}_{1}}{{C}_{2}}$ and $A{{D}_{2}}B$ where ${{D}_{1}}$ and ${{D}_{2}}$ will coincide but the triangle $A{{C}_{1}}{{D}_{1}}$ will remain unused. We may also fold triangles $A{{D}_{1}}{{C}_{2}}$ and $A{{D}_{1}}{{C}_{1}}$ where ${{C}_{1}},{{C}_{2}}$ will coincide but triangle $A{{D}_{2}}B$ remain unused. So we cannot make tetrahedra here. \[\]
(iii) We denote the vertices of the triangles in the net as shown in the below figure. \[\]

We fold the triangle $A{{D}_{1}}B$ along AB, the triangle $B{{D}_{2}}C$ along BC and the triangle $A{{D}_{3}}C$ along AC. The vertices ${{D}_{1}},{{D}_{2}},{{D}_{3}}$ will coincide and we name the that vertex as D. So we have the tetrahedron with apex D and triangular base ABC. \[\]
(iv) We see in the figure there 5 triangles in the net but tetrahedron as 4 triangular faces. Hence we cannot make a tetrahedron with the net in (iv). \[\]
Note: We note that the word coincides means meeting or merging at one point. We note that tetrahedron has all edges of equal length and hence the polygons in the net of regular tetrahedron are equilateral triangles. The total surface area of tetrahedron is $\sqrt{3}\times {{a}^{2}}$ where $a$ is the length of any edge.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 9 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Who is eligible for RTE class 9 social science CBSE

Which places in India experience sunrise first and class 9 social science CBSE

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it

Name 10 Living and Non living things class 9 biology CBSE




