
What is the peculiarity of the DNA structure?
Answer
570k+ views
Hint: The molecule that holds the genetic code of species is DNA, short for deoxyribonucleic acid. Animals, fungi, protists, archaea, and bacteria are involved in this. DNA is in the organism in each cell and tells cells what proteins to make.
Complete answer:
The abbreviated form of Deoxyribonucleic acid is DNA. It is in the form of chromosomes that are present. Chromosomes are located in the nucleus of every cell. DNA is transferred from the parental generation by gametes to the offspring. A double-helical structure containing nucleotides is DNA.
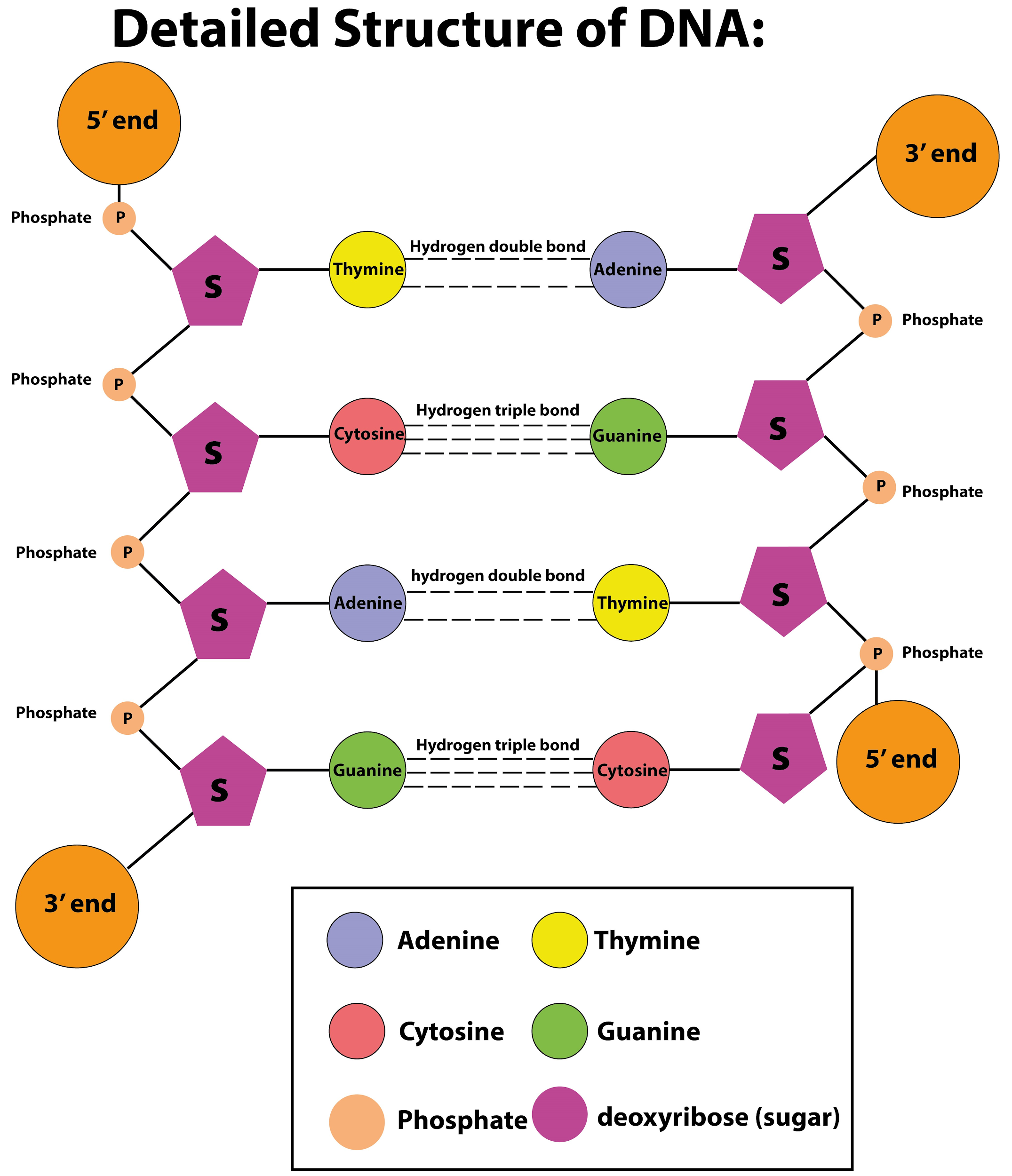
These nucleotides, such as adenine thymine, cytosine, and guanine, are made of deoxyribose sugar, phosphoric acid, and nitrogen bases. The DNA molecule's double helix or spiral staircase structure was suggested by James D. Waston and Francis Crick in 1953. The Nobel Prize for this discovery was awarded to them.
Additional information: The nucleic acid is DNA and ribonucleic acid (RNA). Nucleic acids are one of the four main types of macromolecules, alongside proteins, lipids, and complex carbohydrates (polysaccharides) that are important for all known forms of life.
As they are made of simpler monomeric units called nucleotides, the two DNA strands are known as polynucleotides. Every nucleotide consists of one of four nucleobases containing nitrogen (cytosine [C], guanine [G], adenine [A], or thymine [T]), deoxyribose-called sugar, and a phosphate group. Covalent bonds between the sugar of one nucleotide and the phosphate of the next, resulting in an alternating sugar-phosphate backbone, link the nucleotides to each other in a chain.
Note: The same biological knowledge is processed by both strands of double-stranded DNA. As and when the two strands split, this information is repeated. Non-coding is a major part of DNA (more than $98\%$ for humans), which means that these parts do not function as patterns for protein sequences. The two DNA strands run in opposite directions and are thus anti-parallel to each other.
Complete answer:
The abbreviated form of Deoxyribonucleic acid is DNA. It is in the form of chromosomes that are present. Chromosomes are located in the nucleus of every cell. DNA is transferred from the parental generation by gametes to the offspring. A double-helical structure containing nucleotides is DNA.

These nucleotides, such as adenine thymine, cytosine, and guanine, are made of deoxyribose sugar, phosphoric acid, and nitrogen bases. The DNA molecule's double helix or spiral staircase structure was suggested by James D. Waston and Francis Crick in 1953. The Nobel Prize for this discovery was awarded to them.
Additional information: The nucleic acid is DNA and ribonucleic acid (RNA). Nucleic acids are one of the four main types of macromolecules, alongside proteins, lipids, and complex carbohydrates (polysaccharides) that are important for all known forms of life.
As they are made of simpler monomeric units called nucleotides, the two DNA strands are known as polynucleotides. Every nucleotide consists of one of four nucleobases containing nitrogen (cytosine [C], guanine [G], adenine [A], or thymine [T]), deoxyribose-called sugar, and a phosphate group. Covalent bonds between the sugar of one nucleotide and the phosphate of the next, resulting in an alternating sugar-phosphate backbone, link the nucleotides to each other in a chain.
Note: The same biological knowledge is processed by both strands of double-stranded DNA. As and when the two strands split, this information is repeated. Non-coding is a major part of DNA (more than $98\%$ for humans), which means that these parts do not function as patterns for protein sequences. The two DNA strands run in opposite directions and are thus anti-parallel to each other.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




