
Pisum sativum is a
(a) Climber
(b) Tree
(c) Shrub
(d) Heterotroph
Answer
577.5k+ views
Hint: Pisum sativum has a weak stem that requires support for upright growth. It has a soft green pliable stem that is provided with an ample support system when cultivated in farms. Money plants, grapevine, jasmine, and beans are other examples that come under this category.
Complete step by step answer:
Pisum sativum is the botanical name of the pea plant. It is a climber that uses tendrils created for climbing at the apex of a compound leaf. A branched tendril is produced by these modified terminal leaflets. It has a very poor stem and cannot stand on its own, so they either climb on another plant, wall, or just stick to it by holding it.
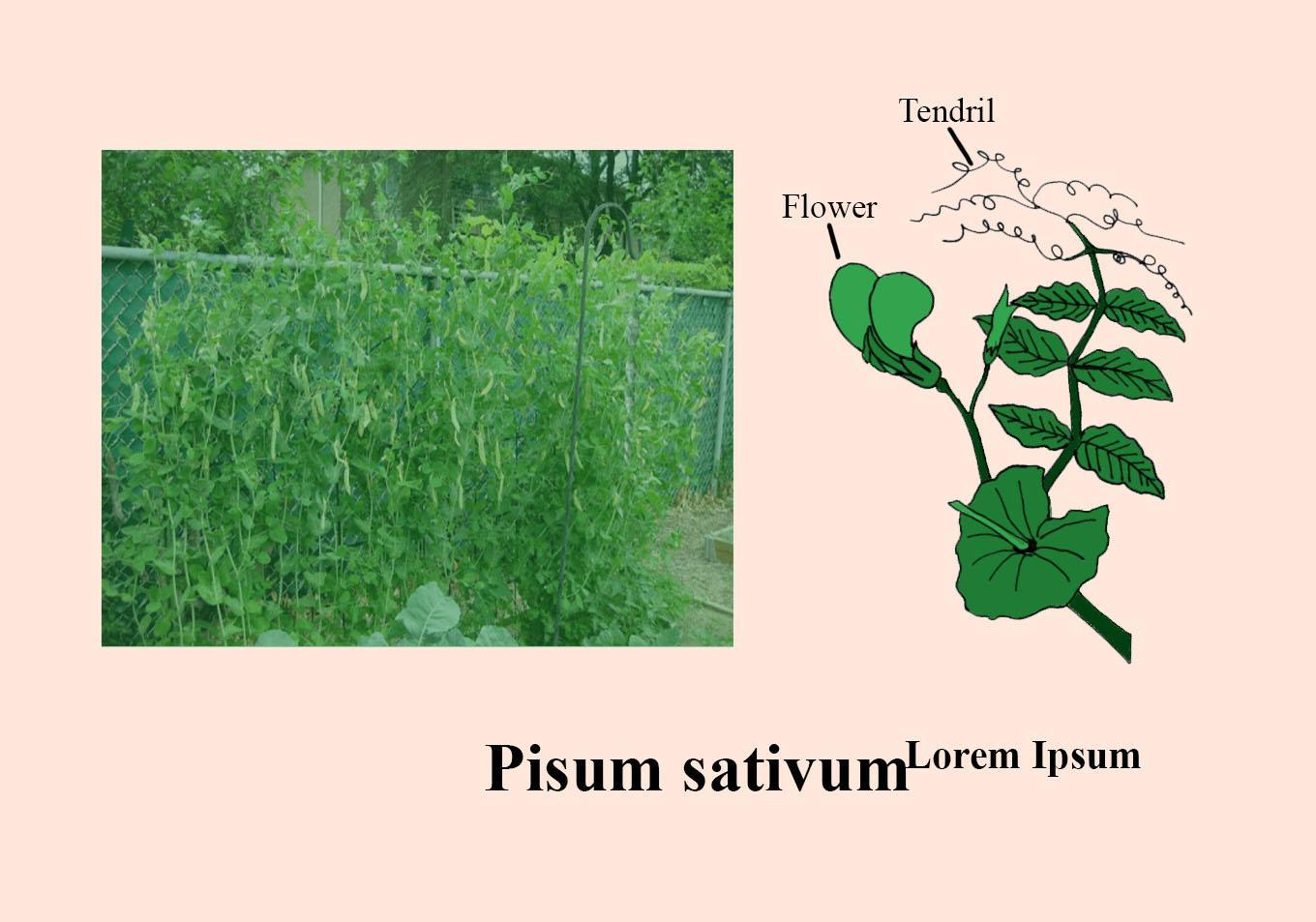
Pisum sativum is an annual plant that has 15 to 300 cm long erect or ascending stems. With several lateral roots, it has a well- developed taproot, up to 120 cm long.
So, the correct answer is, '(a) Climber'.
Additional information:
- A tree is a perennial plant. It has an elongated stem or trunk which supports branches and leaves. The definition of a tree can be narrower in other applications, including only woody plants with secondary growth, plants that can be used as wood or plants above a specified height.
- The small to medium- sized perennial woody plant is a shrub or bush. Shrubs have persistent woody stems above the field, unlike herbaceous plants. Shrubs may be evergreen or deciduous.
- A heterotroph is an organism that, through carbon fixation, is unable to produce its own food and therefore derives its nutritional intake from other sources of organic carbon, primarily plant or animal matter.
Note: The small spherical seed or the seed- pod of the pod fruit constitutes the pea. There are many peas in every pod, which can be green or yellow. Botanically, the peapod contains seeds and grows from the ovary of a (pea) flower. So they are considered as fruit. From the Fabaceae other edible seeds, such as pigeon pea (Cajanus cajan) , cowpea (Vigna unguiculata) , and seeds from several species of Lathyrus, are present.
Complete step by step answer:
Pisum sativum is the botanical name of the pea plant. It is a climber that uses tendrils created for climbing at the apex of a compound leaf. A branched tendril is produced by these modified terminal leaflets. It has a very poor stem and cannot stand on its own, so they either climb on another plant, wall, or just stick to it by holding it.

Pisum sativum is an annual plant that has 15 to 300 cm long erect or ascending stems. With several lateral roots, it has a well- developed taproot, up to 120 cm long.
So, the correct answer is, '(a) Climber'.
Additional information:
- A tree is a perennial plant. It has an elongated stem or trunk which supports branches and leaves. The definition of a tree can be narrower in other applications, including only woody plants with secondary growth, plants that can be used as wood or plants above a specified height.
- The small to medium- sized perennial woody plant is a shrub or bush. Shrubs have persistent woody stems above the field, unlike herbaceous plants. Shrubs may be evergreen or deciduous.
- A heterotroph is an organism that, through carbon fixation, is unable to produce its own food and therefore derives its nutritional intake from other sources of organic carbon, primarily plant or animal matter.
Note: The small spherical seed or the seed- pod of the pod fruit constitutes the pea. There are many peas in every pod, which can be green or yellow. Botanically, the peapod contains seeds and grows from the ovary of a (pea) flower. So they are considered as fruit. From the Fabaceae other edible seeds, such as pigeon pea (Cajanus cajan) , cowpea (Vigna unguiculata) , and seeds from several species of Lathyrus, are present.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




