
Prepare a chart showing different modes of reproduction with suitable examples each:
Answer
571.5k+ views
Hint: Reproduction is a biological process through which an organism produces organisms that are similar to it. Reproduction can take place with or without gametes. Based on this reproduction is divided into two categories; sexual and asexual reproduction.
Complete answer: Reproduction is an important biological process that ensures the continuity of the species. It is divided into two major categories based on the model used by organisms to produce a similar organism.
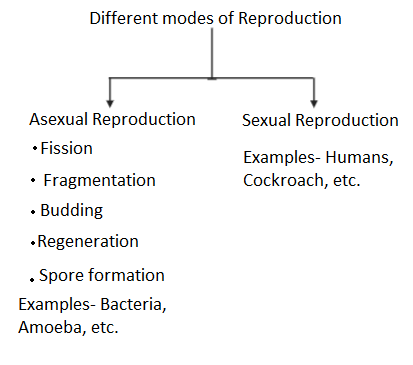
A. Asexual reproduction: It is a type of reproduction involving only one or a single parent. The resulting organisms are exact copies of their parents. Cell division is usually by mitosis. It is usually seen in primitive type organisms like bacteria. It is further than five types.
i. Fission: In this type of asexual reproduction, the parent body splits into two or more cells called the daughter cells. Amoeba shows the binary type fission in which it divides into two daughter cells.
ii. Fragmentation: In this type of asexual reproduction, the parent body breaks into fragments. These fragments then individually grow into whole organisms. This is seen in Spirogyra.
iii. Budding: In this, the parent body forms an outgrowth called a bud. This bud remains to attach to the parent body for some time. When this bud detaches it grows to become a whole organism. Yeast reproduces by Budding.
iv. Regeneration: It is a special type of reproduction in which any cut part of the parent can form a whole organism. This is evident in Planaria.
v. Spore formation: In this type of reproduction, the parent body forms the spores. These are small circular cells that carry gametes. These spores blow off from the parent body and grow into individuals when suitable conditions are required.
B. Sexual Reproduction: It is a type of reproduction involving the fusion of gametes for the production of offspring. Two parents are involved in this type of reproduction that is of opposite sexes. Meiosis is the prevalent cell division type in sexual reproduction. One of the parents is male and the other is female. The male produces the male gamete usually called sperm and the female produces the female gamete called an egg. These gametes fuse in the process of fertilization. Fertilization results in the formation of zygote. This zygote grows and divides to form a whole organism. It is usually evident in higher or complex organisms like humans, and other animals and plants.
Note: Sexual reproduction is a much complex process as compared to asexual reproduction. As sexual reproduction consists of the fusion of gametes from two different parents, it results in variations. Moreover, the gametes formed are haploid meaning that they have only half a set of chromosomes. When they fuse they make a diploid zygote with a full set of chromosomes. This results in the recombination of genes and variations.
Complete answer: Reproduction is an important biological process that ensures the continuity of the species. It is divided into two major categories based on the model used by organisms to produce a similar organism.

A. Asexual reproduction: It is a type of reproduction involving only one or a single parent. The resulting organisms are exact copies of their parents. Cell division is usually by mitosis. It is usually seen in primitive type organisms like bacteria. It is further than five types.
i. Fission: In this type of asexual reproduction, the parent body splits into two or more cells called the daughter cells. Amoeba shows the binary type fission in which it divides into two daughter cells.
ii. Fragmentation: In this type of asexual reproduction, the parent body breaks into fragments. These fragments then individually grow into whole organisms. This is seen in Spirogyra.
iii. Budding: In this, the parent body forms an outgrowth called a bud. This bud remains to attach to the parent body for some time. When this bud detaches it grows to become a whole organism. Yeast reproduces by Budding.
iv. Regeneration: It is a special type of reproduction in which any cut part of the parent can form a whole organism. This is evident in Planaria.
v. Spore formation: In this type of reproduction, the parent body forms the spores. These are small circular cells that carry gametes. These spores blow off from the parent body and grow into individuals when suitable conditions are required.
B. Sexual Reproduction: It is a type of reproduction involving the fusion of gametes for the production of offspring. Two parents are involved in this type of reproduction that is of opposite sexes. Meiosis is the prevalent cell division type in sexual reproduction. One of the parents is male and the other is female. The male produces the male gamete usually called sperm and the female produces the female gamete called an egg. These gametes fuse in the process of fertilization. Fertilization results in the formation of zygote. This zygote grows and divides to form a whole organism. It is usually evident in higher or complex organisms like humans, and other animals and plants.
Note: Sexual reproduction is a much complex process as compared to asexual reproduction. As sexual reproduction consists of the fusion of gametes from two different parents, it results in variations. Moreover, the gametes formed are haploid meaning that they have only half a set of chromosomes. When they fuse they make a diploid zygote with a full set of chromosomes. This results in the recombination of genes and variations.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




