
How primary amine is prepared by Hoffmann bromamide degradation reaction? Write the equation.
Answer
595.2k+ views
Hint: The primary amine is made from a compound that contains nitrogen with the carbonyl group. This reaction is used to make one carbon less than the original reactant taken. This reaction can be used in both aliphatic and aromatic compounds.
Complete step by step answer:
Hoffmann bromamide reaction: when a primary amide is treated with an aqueous or ethanolic solution of potassium hydroxide and bromine ( or potassium hypobromite,), it gives a primary amine which has one carbon less than the original amide.
The general reaction can be written as:
\[R-CON{{H}_{2}}+B{{r}_{2}}+4KOH\to R-N{{H}_{2}}+{{K}_{2}}C{{O}_{3}}+2KBr+2{{H}_{2}}O\]
Let us take an example: for preparing ethylamine from propionamide:
\[C{{H}_{3}}C{{H}_{2}}CON{{H}_{2}}+B{{r}_{2}}+4KOH\to C{{H}_{3}}C{{H}_{2}}N{{H}_{2}}+{{K}_{2}}C{{O}_{3}}+2KBr+2{{H}_{2}}O\]
This was an example of the aliphatic chain.
The same product can be obtained with an aromatic compound also:
\[{{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}CON{{H}_{2}}+B{{r}_{2}}+4KOH\to {{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}N{{H}_{2}}+{{K}_{2}}C{{O}_{3}}+2KBr+2{{H}_{2}}O\]
In this reaction, Aniline is prepared from Benzamide.
This reaction is widely used for stepping down or descent of homologous series.
Mechanism: Hoffmann bromamide reaction is believed to occur by the following mechanism through the formation of an intermediate acylnitrene(II).
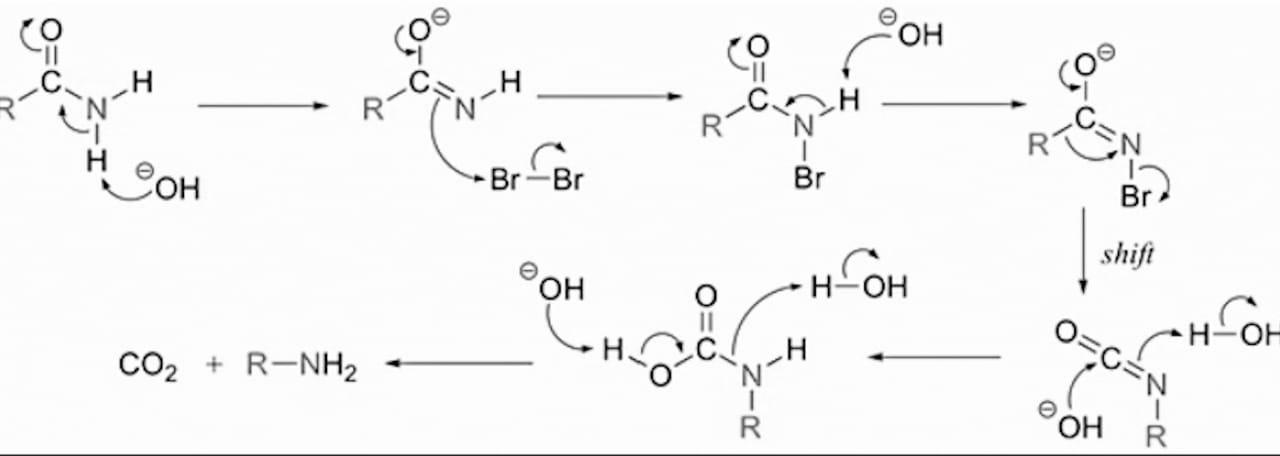
The formation of isocyanate as an intermediate in the above reaction is supported by the observation that when the reaction is carried out with methanolic \[C{{H}_{3}}ONa\] instead of aqueous \[NaOH\], a methyl carbonate or urethane is obtained instead of the amine.
For example,
\[C{{H}_{3}}CON{{H}_{2}}\text{ }\to \text{ }C{{H}_{3}}N{{H}_{2}}\] (catalyst is bromine and sodium hydroxide)
\[C{{H}_{3}}CON{{H}_{2}}\text{ }\to \text{ }C{{H}_{3}}NH-CO-OC{{H}_{3}}\] (catalyst is methanolic and methanol)
\[C{{H}_{3}}NH-CO-OC{{H}_{3}}\] is a urethane.
Note: This is the type of reaction in which the product has one carbon less than reactant, so while writing this reaction it should be taken care of. The catalyst should also be taken care of because different catalysts would yield different products.
Complete step by step answer:
Hoffmann bromamide reaction: when a primary amide is treated with an aqueous or ethanolic solution of potassium hydroxide and bromine ( or potassium hypobromite,), it gives a primary amine which has one carbon less than the original amide.
The general reaction can be written as:
\[R-CON{{H}_{2}}+B{{r}_{2}}+4KOH\to R-N{{H}_{2}}+{{K}_{2}}C{{O}_{3}}+2KBr+2{{H}_{2}}O\]
Let us take an example: for preparing ethylamine from propionamide:
\[C{{H}_{3}}C{{H}_{2}}CON{{H}_{2}}+B{{r}_{2}}+4KOH\to C{{H}_{3}}C{{H}_{2}}N{{H}_{2}}+{{K}_{2}}C{{O}_{3}}+2KBr+2{{H}_{2}}O\]
This was an example of the aliphatic chain.
The same product can be obtained with an aromatic compound also:
\[{{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}CON{{H}_{2}}+B{{r}_{2}}+4KOH\to {{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}N{{H}_{2}}+{{K}_{2}}C{{O}_{3}}+2KBr+2{{H}_{2}}O\]
In this reaction, Aniline is prepared from Benzamide.
This reaction is widely used for stepping down or descent of homologous series.
Mechanism: Hoffmann bromamide reaction is believed to occur by the following mechanism through the formation of an intermediate acylnitrene(II).

The formation of isocyanate as an intermediate in the above reaction is supported by the observation that when the reaction is carried out with methanolic \[C{{H}_{3}}ONa\] instead of aqueous \[NaOH\], a methyl carbonate or urethane is obtained instead of the amine.
For example,
\[C{{H}_{3}}CON{{H}_{2}}\text{ }\to \text{ }C{{H}_{3}}N{{H}_{2}}\] (catalyst is bromine and sodium hydroxide)
\[C{{H}_{3}}CON{{H}_{2}}\text{ }\to \text{ }C{{H}_{3}}NH-CO-OC{{H}_{3}}\] (catalyst is methanolic and methanol)
\[C{{H}_{3}}NH-CO-OC{{H}_{3}}\] is a urethane.
Note: This is the type of reaction in which the product has one carbon less than reactant, so while writing this reaction it should be taken care of. The catalyst should also be taken care of because different catalysts would yield different products.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




