
What is rectification? With relevant circuit diagrams and waveforms explain the working of P-N junction diodes as a full wave rectifier.
Answer
590.7k+ views
Hint: A rectifier is an electronic device whose function is to convert the alternating current to direct current. This process of conversion of current is known as rectification, since it actually straightens the direction of the electric current. In half-wave rectification of a single-phase supply, either the positive half or the negative half of the alternating sine wave is passed, while the other half of the wave is blocked by the rectifier. On the other hand, a full-wave rectifier converts the whole of the input waveform to a single waveform of constant polarity at its output.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Rectification is defined as the process of conversion of alternating current to direct current. Rectification is carried out by a diode that allows current to flow in one direction but not in the opposite direction. Direct current that has undergone the rectification process has various changes in the voltage (ripples) lingering from the alternating current. Capacitors are used to smooth and straighten the input electric current and make the output even.
A rectifier is an electrical device whose function is to convert the input alternating current (AC), which periodically and continuously reverses its direction, to the output in the form of direct current (DC), which flows in a single direction in a circuit.
The two types of rectification processes are as followed:-
- Half-Wave Rectification:
In Half-Wave Rectification, when AC supply is applied at the input, a positive half cycle appears across the load, whereas the negative half cycle is suppressed by the rectifier. This can be achieved by using the semiconductor PN junction diode. The diode allows the electric current to flow only in one direction in the circuit. Thus, it can convert the AC voltage into DC voltage.
- Full-Wave Rectification:
In Full-Wave Rectification, when the AC input is supplied, during both the half cycles of the waveform, that is the positive as well as the negative cycle, current flows through the load in the same direction. This can be done with the help of two crystal diodes. The two diodes conduct the electric current alternately.
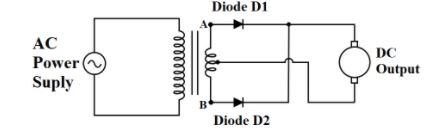
The PN junction diode is used as a full wave rectifier as shown in the figure.
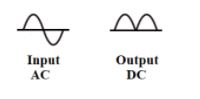
Waveform for a full wave rectifier:
An AC input is given to the primary of the transformer in the first half cycle of the AC. End A of the secondary centre taping transformer is positive and end B is negative. Diode D1 is in forward biased mode and thus, the current flows but diode D2 is in reverse biased mode and thus, the current does not flow through it. In the next half cycle of AC, end A of secondary centre taping transformer is negative and end B is positive. Diode D1 is in reverse biased mode and thus, the current does not flow but diode D2 is in forward biased mode and thus, the current flows through it. This process continues and the output DC signal is obtained across the load resistance.
Note: Physically, rectifiers can take a number of forms, like the vacuum tube diodes, the mercury arc valves, the stacks of copper and selenium oxide plates, the wet chemical cells, the semiconductor diodes, the silicon-controlled rectifiers and the other silicon-based semiconductor switches.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Rectification is defined as the process of conversion of alternating current to direct current. Rectification is carried out by a diode that allows current to flow in one direction but not in the opposite direction. Direct current that has undergone the rectification process has various changes in the voltage (ripples) lingering from the alternating current. Capacitors are used to smooth and straighten the input electric current and make the output even.
A rectifier is an electrical device whose function is to convert the input alternating current (AC), which periodically and continuously reverses its direction, to the output in the form of direct current (DC), which flows in a single direction in a circuit.
The two types of rectification processes are as followed:-
- Half-Wave Rectification:
In Half-Wave Rectification, when AC supply is applied at the input, a positive half cycle appears across the load, whereas the negative half cycle is suppressed by the rectifier. This can be achieved by using the semiconductor PN junction diode. The diode allows the electric current to flow only in one direction in the circuit. Thus, it can convert the AC voltage into DC voltage.
- Full-Wave Rectification:
In Full-Wave Rectification, when the AC input is supplied, during both the half cycles of the waveform, that is the positive as well as the negative cycle, current flows through the load in the same direction. This can be done with the help of two crystal diodes. The two diodes conduct the electric current alternately.
The PN junction diode is used as a full wave rectifier as shown in the figure.

Waveform for a full wave rectifier:

An AC input is given to the primary of the transformer in the first half cycle of the AC. End A of the secondary centre taping transformer is positive and end B is negative. Diode D1 is in forward biased mode and thus, the current flows but diode D2 is in reverse biased mode and thus, the current does not flow through it. In the next half cycle of AC, end A of secondary centre taping transformer is negative and end B is positive. Diode D1 is in reverse biased mode and thus, the current does not flow but diode D2 is in forward biased mode and thus, the current flows through it. This process continues and the output DC signal is obtained across the load resistance.
Note: Physically, rectifiers can take a number of forms, like the vacuum tube diodes, the mercury arc valves, the stacks of copper and selenium oxide plates, the wet chemical cells, the semiconductor diodes, the silicon-controlled rectifiers and the other silicon-based semiconductor switches.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




