
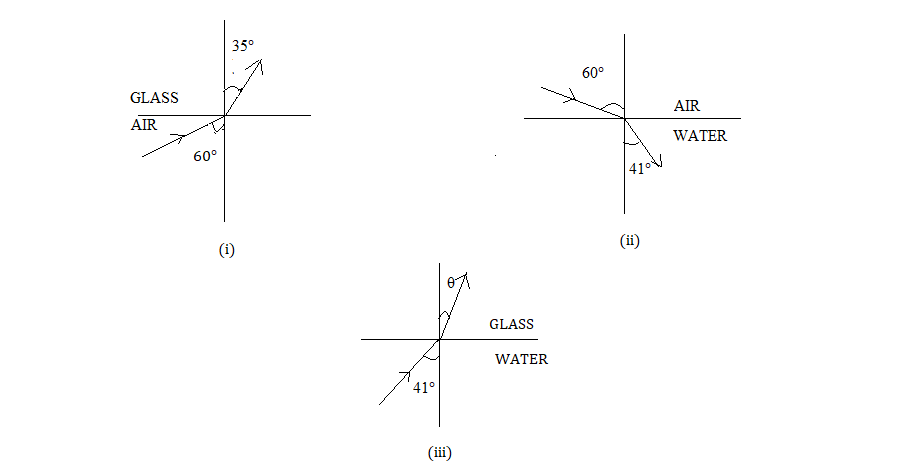
Refraction of light from air to glass and from air to water are shown in figure (i) and figure (ii) below. The value of the angle θ in the case of refraction as shown in figure (iii) will be
A. 30°
B. 35°
C. 60°
D. 41°

Answer
591k+ views
Hint: When angle of incidence and angle of refraction is given, Snell’s Law is used to solve the problem.
Formula used:
\[_{1}{{\mu }^{2}}=\dfrac{\sin i}{\sin r}\] here, the first medium is represented by 1 and the second medium is represented by 2 and \[_{1}{{\mu }^{2}}\] is the refractive index of medium 2 with respect to 1. [Snell’s Law].
Complete step by step solution:
When light falls on the boundary it divides the two media which is called interface and depending upon the relative refractive indices of the two media the light will either be refracted to a lesser angle, or at a greater angle. These angles are measured with respect to the normal line which is perpendicular to the boundary. In the case of light traveling from air to water, light would refract towards the normal line, because the speed of light is less in water than in air; light traveling from water to air would refract away from the normal line.
The equations for the given diagram according to Snell’s law are:-
\[\begin{align}
& ~~\text{From the given figure (i)} \\
& _{a}{{\mu }^{g}}=\dfrac{\sin i}{\sin r}=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{g}}}{{{\mu }_{a}}}=\dfrac{\sin {{60}^{\circ }}}{\sin {{35}^{\circ }}}..........(i) \\
& ~~\text{From the given figure (ii)} \\
& _{a}{{\mu }^{w}}=\dfrac{\sin i}{\sin r}=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{w}}}{{{\mu }_{a}}}=\dfrac{\sin {{60}^{\circ }}}{\sin {{41}^{\circ }}}..........(ii) \\
& ~~\text{From the given figure (iii)} \\
& _{w}{{\mu }^{g}}=\dfrac{\sin i}{\sin r}=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{g}}}{{{\mu }_{w}}}=\dfrac{\sin {{41}^{\circ }}}{\sin {{\theta }^{\circ }}}..........(iii) \\
\end{align}\]
[where, sin i= sin of angle of incident and sin r = the sin of angle of refraction of light]
Now, let us divide equation (i) by (ii) and then the whole by (iii) i.e., Equation[ (i)/(ii)] / (iii) we get,
\[\begin{align}
& \dfrac{\sin {{60}^{\circ }}}{\sin {{35}^{\circ }}}\times\dfrac{\sin {{41}^{\circ }}}{\sin {{60}^{\circ }}}\times\dfrac{\sin {{\theta }^{\circ }}}{\sin {{41}^{\circ }}}=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{g}}}{{{\mu }_{a}}}\times\dfrac{{{\mu }_{a}}}{{{\mu }_{w}}}\times\dfrac{{{\mu }_{w}}}{{{\mu }_{g}}} \\
& \dfrac{\sin {{\theta }^{\circ }}}{\sin {{35}^{\circ }}}=1 \\
& {{\theta }^{\circ }}={{35}^{\circ }} \\
\end{align}\]
Therefore, the answer is 35° which is option B.
Additional information:
Snell’s law is used to determine the direction of rays of light through refractive media with varying indices of refraction. The indices of refraction of the media is to be labelled as n1, n2 and so on, which should be used to represent the factor by which the speed of light rays decreases when traveling through a refractive medium, such as glass or water, as opposed to its velocity in a vacuum.
Note: Application of Snell’s laws - Refraction allows lenses, magnifiers, prisms and rainbows. Even our eyes depend on the curvature of light. Without refraction, light cannot not be focussed on our retina.
Formula used:
\[_{1}{{\mu }^{2}}=\dfrac{\sin i}{\sin r}\] here, the first medium is represented by 1 and the second medium is represented by 2 and \[_{1}{{\mu }^{2}}\] is the refractive index of medium 2 with respect to 1. [Snell’s Law].
Complete step by step solution:
When light falls on the boundary it divides the two media which is called interface and depending upon the relative refractive indices of the two media the light will either be refracted to a lesser angle, or at a greater angle. These angles are measured with respect to the normal line which is perpendicular to the boundary. In the case of light traveling from air to water, light would refract towards the normal line, because the speed of light is less in water than in air; light traveling from water to air would refract away from the normal line.
The equations for the given diagram according to Snell’s law are:-
\[\begin{align}
& ~~\text{From the given figure (i)} \\
& _{a}{{\mu }^{g}}=\dfrac{\sin i}{\sin r}=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{g}}}{{{\mu }_{a}}}=\dfrac{\sin {{60}^{\circ }}}{\sin {{35}^{\circ }}}..........(i) \\
& ~~\text{From the given figure (ii)} \\
& _{a}{{\mu }^{w}}=\dfrac{\sin i}{\sin r}=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{w}}}{{{\mu }_{a}}}=\dfrac{\sin {{60}^{\circ }}}{\sin {{41}^{\circ }}}..........(ii) \\
& ~~\text{From the given figure (iii)} \\
& _{w}{{\mu }^{g}}=\dfrac{\sin i}{\sin r}=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{g}}}{{{\mu }_{w}}}=\dfrac{\sin {{41}^{\circ }}}{\sin {{\theta }^{\circ }}}..........(iii) \\
\end{align}\]
[where, sin i= sin of angle of incident and sin r = the sin of angle of refraction of light]
Now, let us divide equation (i) by (ii) and then the whole by (iii) i.e., Equation[ (i)/(ii)] / (iii) we get,
\[\begin{align}
& \dfrac{\sin {{60}^{\circ }}}{\sin {{35}^{\circ }}}\times\dfrac{\sin {{41}^{\circ }}}{\sin {{60}^{\circ }}}\times\dfrac{\sin {{\theta }^{\circ }}}{\sin {{41}^{\circ }}}=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{g}}}{{{\mu }_{a}}}\times\dfrac{{{\mu }_{a}}}{{{\mu }_{w}}}\times\dfrac{{{\mu }_{w}}}{{{\mu }_{g}}} \\
& \dfrac{\sin {{\theta }^{\circ }}}{\sin {{35}^{\circ }}}=1 \\
& {{\theta }^{\circ }}={{35}^{\circ }} \\
\end{align}\]
Therefore, the answer is 35° which is option B.
Additional information:
Snell’s law is used to determine the direction of rays of light through refractive media with varying indices of refraction. The indices of refraction of the media is to be labelled as n1, n2 and so on, which should be used to represent the factor by which the speed of light rays decreases when traveling through a refractive medium, such as glass or water, as opposed to its velocity in a vacuum.
Note: Application of Snell’s laws - Refraction allows lenses, magnifiers, prisms and rainbows. Even our eyes depend on the curvature of light. Without refraction, light cannot not be focussed on our retina.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




