
Reimer- Tiemann reaction involves as intermediate:
(A) Carbocation
(B)Carbanion
(C)Free radical
(D)Carbene
Answer
564.9k+ views
Hint: In an electrophilic substitution reaction electrophile is formed as a reaction intermediate.
- Reaction intermediates are highly reactive organic compounds which are formed for a short period of time in the middle stage of a reaction. An intermediate could be electron deficiency or excess of electron or having vacant orbital. Carbocation, Carbanion, free radical, nitrene, or Carbene are different types of reaction intermediates which are formed in a reaction.
Complete Solution :
Reamer-Tiemann reaction is an electrophilic substitution reaction which involves the treatment of phenol with chloroform in aqueous sodium hydroxide solution followed by the acid hydrolysis, which leads to the formation of salicylaldehyde (ortho-hydroxybenzaldehyde) as a chief product of the reaction.
- In this reaction chloroform first reacts with sodium hydroxide to produce dichlorocarbene which is the intermediate of this reaction.
This reaction is represented through following reaction –
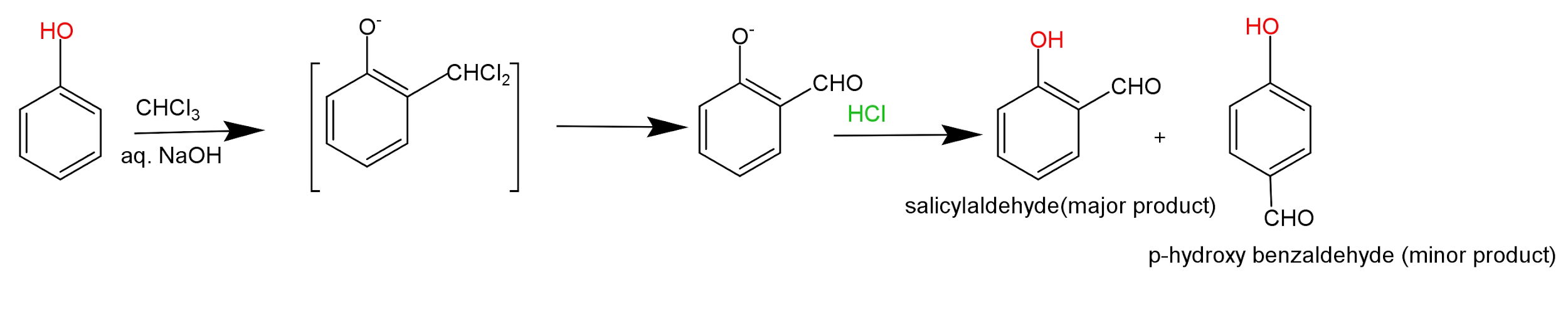
Carbene is an electron deficient neutral species which contains six electrons in their outermost shell. These are uncharged reactive intermediates which contains a divalent carbon atom which is hybridised and contains perpendicular vacant p-orbitals. There are two types of carbene formed in a chemical reaction; singlet carbene (which contains a pair of two non-bonding electrons) and triplet carbene (it contains two nonbonding electrons which are unpaired).
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note: Carbocation and Carbanion are intermediates which are formed in electrophilic and nucleophilic substitution and addition reaction.
- Free radicals are formed in that reaction in which homolytic breakdown of chemical reaction takes place, while carbocation and Carbanion are formed in those reactions in which heterolytic breakdown of chemical bond takes place.
- Reaction intermediates are highly reactive organic compounds which are formed for a short period of time in the middle stage of a reaction. An intermediate could be electron deficiency or excess of electron or having vacant orbital. Carbocation, Carbanion, free radical, nitrene, or Carbene are different types of reaction intermediates which are formed in a reaction.
Complete Solution :
Reamer-Tiemann reaction is an electrophilic substitution reaction which involves the treatment of phenol with chloroform in aqueous sodium hydroxide solution followed by the acid hydrolysis, which leads to the formation of salicylaldehyde (ortho-hydroxybenzaldehyde) as a chief product of the reaction.
- In this reaction chloroform first reacts with sodium hydroxide to produce dichlorocarbene which is the intermediate of this reaction.
This reaction is represented through following reaction –

Carbene is an electron deficient neutral species which contains six electrons in their outermost shell. These are uncharged reactive intermediates which contains a divalent carbon atom which is hybridised and contains perpendicular vacant p-orbitals. There are two types of carbene formed in a chemical reaction; singlet carbene (which contains a pair of two non-bonding electrons) and triplet carbene (it contains two nonbonding electrons which are unpaired).
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note: Carbocation and Carbanion are intermediates which are formed in electrophilic and nucleophilic substitution and addition reaction.
- Free radicals are formed in that reaction in which homolytic breakdown of chemical reaction takes place, while carbocation and Carbanion are formed in those reactions in which heterolytic breakdown of chemical bond takes place.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




