
What is the shape of T.M.V.? What is its genetic material?
Answer
542.1k+ views
Hint: Viruses are microscopic parasites and contagious sellers with residing and non-living characteristics. These viruses can infect plants, animals, and different microorganisms.
Complete answer:
Viruses are non-cellular, microscopic, and infectious marketers that stay by way of relying upon the host cell They incorporate genetic material as RNA or DNA and proteins; they invade and reproduce through using organisms, plants, and animal cell organelles as they lack the required cell material.
The TMV was the first pathogen recognized as a virus. The tobacco mosaic virus (TMV) is a single stranded RNA virus that belongs to the Tobamovirus genus, which is recognised to infect a huge range of plants, particularly the tobacco plant and other contributors of the Solanaceae family. This virus motives an contamination that has a characteristic mosaic-like molting pattern.
This mosaic-like sample is additionally formed with the aid of the discoloration of the leaves and consequently it acquires its name the Tobacco mosaic virus. Like different plant viruses, TMV has a very large variety of plant hosts which it can infect and has specific signs depending on the host. The tobacco mosaic virus has been known to motivate a production loss for flue-cured tobacco.
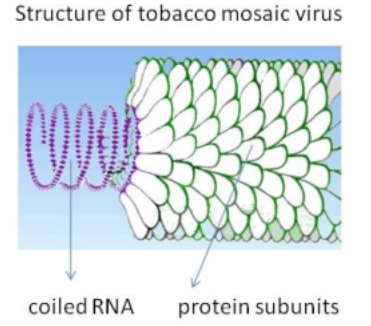
Structure of TMV:
- TMV possesses a rod-like appearance. Its capsid is made from 2130 molecules of lined proteins called capsomeres and one molecule of genomic single stranded RNA.
- All the capsomeres (coat protein) are organized and are developed into a rod-like helical structure. It consists of 6.3 - 6.5 kb single stranded RNA genomes.
- The 3'-terminus of the genome of this virus has tRNA (transfer ribonucleic acid) like look and 5'- terminus of the genome of this virus has a methylated nucleotide cap.
Note: Bacteriophage replicates and also multiplies inside the bacterial cell with the help of a cycle either a lytic or lysogenic cycle. These Bacteriophages are highly specific for their target bacteria, and it is essential against multi-resistant pathogens.
Complete answer:
Viruses are non-cellular, microscopic, and infectious marketers that stay by way of relying upon the host cell They incorporate genetic material as RNA or DNA and proteins; they invade and reproduce through using organisms, plants, and animal cell organelles as they lack the required cell material.
The TMV was the first pathogen recognized as a virus. The tobacco mosaic virus (TMV) is a single stranded RNA virus that belongs to the Tobamovirus genus, which is recognised to infect a huge range of plants, particularly the tobacco plant and other contributors of the Solanaceae family. This virus motives an contamination that has a characteristic mosaic-like molting pattern.
This mosaic-like sample is additionally formed with the aid of the discoloration of the leaves and consequently it acquires its name the Tobacco mosaic virus. Like different plant viruses, TMV has a very large variety of plant hosts which it can infect and has specific signs depending on the host. The tobacco mosaic virus has been known to motivate a production loss for flue-cured tobacco.

Structure of TMV:
- TMV possesses a rod-like appearance. Its capsid is made from 2130 molecules of lined proteins called capsomeres and one molecule of genomic single stranded RNA.
- All the capsomeres (coat protein) are organized and are developed into a rod-like helical structure. It consists of 6.3 - 6.5 kb single stranded RNA genomes.
- The 3'-terminus of the genome of this virus has tRNA (transfer ribonucleic acid) like look and 5'- terminus of the genome of this virus has a methylated nucleotide cap.
Note: Bacteriophage replicates and also multiplies inside the bacterial cell with the help of a cycle either a lytic or lysogenic cycle. These Bacteriophages are highly specific for their target bacteria, and it is essential against multi-resistant pathogens.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




