
Show that the points $\left( -2,3 \right),\left( 8,3 \right)$ and $\left( 6,7 \right)$
are the vertices of a right triangle.
Answer
622.5k+ views
Hint: Use the basic rule of Pythagoras theorem to prove it.
Let us roughly draw a triangle with the given vertices:
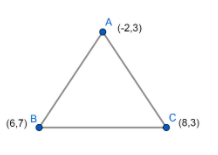
Now, let us calculate distances between the points of triangle:
As we have the distance formula for two vertices in $2-D$ as
If two points $X\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)\And Y\left( {{x}_{2}}{{y}_{2}} \right)$ are given
then
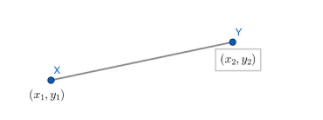
$xy=\sqrt{{{\left( {{x}_{1}}-{{x}_{2}} \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( {{y}_{1}}-{{y}_{2}} \right)}^{2}}}$
By using above formula now let’s calculate $AB,BC,AC:$
$AB=\sqrt{{{\left( -2-6 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( 3-7 \right)}^{2}}}\text{ }\left( \text{as }A=\left( -
2,3 \right)B=\left( 6,7 \right) \right)$
\[\begin{align}
& AB=\sqrt{64+16} \\
& AB=\sqrt{80}=\sqrt{4\times 4\times 5}.................\left( 1 \right) \\
& AB=4\sqrt{5} \\
\end{align}\]
Now, Let’s calculate $BC\text{ }\left( \text{as }B=\left( 6,7 \right)C=\left( 8,3 \right) \right)$
\[\begin{align}
& BC=\sqrt{{{\left( 6-8 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( 7-3 \right)}^{2}}} \\
& BC=\sqrt{4+16} \\
& BC=\sqrt{20}=\sqrt{2\times 2\times 5}................\left( 2 \right) \\
& BC=2\sqrt{5} \\
\end{align}\]
Now,
$\begin{align}
& AC=\sqrt{{{\left( -2-8 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( 3-3 \right)}^{2}}} \\
& AC=\sqrt{100}=10...........\left( 3 \right) \\
\end{align}$
Hence we can observe that $AC$ has the highest length in $AB,BC\And AC$ .
Therefore if $ABC$ will represent a right angle triangle then it will show or follow Pythagoras
property and $AC$ will be the Hypotenuse length.
As Pythagoras property can be expressed as following:
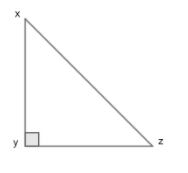
$x{{y}^{2}}+y{{z}^{2}}=x{{z}^{2}}$
Where $xz$ is Hypotenuse and biggest in length among the three sides.
Hence, if $ABC$ will represent right angle triangle then:
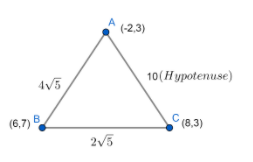
It will follow
\[\begin{align}
& A{{B}^{2}}+B{{C}^{2}}=A{{C}^{2}} \\
& {{\left( 4\sqrt{5} \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( 2\sqrt{5} \right)}^{2}}={{\left( 10
\right)}^{2}}=100 \\
\end{align}\]
Let LHS (Left Hand Side):
$\begin{align}
& {{\left( 4\sqrt{5} \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( 2\sqrt{5} \right)}^{2}}=80+20 \\
& =100=RHS \\
\end{align}$
Hence, It is proved that $ABC$ is a right angled triangle at $B$ with $AC$ as Hypotenuse.
Note: In straight line we learn concept of calculating slope of a line and property of
perpendicular lines as well which is “If two lines are perpendicular then; $Slope\left( Line1
\right)\times Slope\left(Line2 \right)=-1.........\left( 1 \right)$
As right angle triangle will have 3 lines and all have slope, and if two of them will follow
equation $\left( 1 \right)$ then the triangle will be a right angled triangle. This proving is
more advanced than the provided solution.
We have formula of slope as
$m=\dfrac{{{y}_{2}}-{{y}_{1}}}{{{x}_{2}}-{{x}_{1}}}$ with a line of two points given as $\left(
{{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)\And \left( {{x}_{2}}{{y}_{2}} \right)$ .
Now in given triangle
\[\begin{align}
& {{m}_{AB}}=\dfrac{{{y}_{2}}-{{y}_{1}}}{{{x}_{2}}-{{x}_{1}}}=\dfrac{3-7}{-2-6}=\dfrac{-4}{-
8}=\dfrac{1}{2} \\
& {{m}_{BC}}=\dfrac{7-3}{6-8}=\dfrac{-4}{2}=-2 \\
& \text{As }{{\text{m}}_{AB}}\times {{m}_{BC}}=-1 \\
\end{align}\]
Hence, $ABC$ have $B$ angle as $90{}^\circ $.
Therefore $ABC$is a right angle triangle.
We can calculate angle between the lines by using formula
$\tan \theta =\left| \dfrac{{{m}_{1}}-{{m}_{2}}}{1+{{m}_{1}}{{m}_{2}}} \right|$ where
${{m}_{1}}\And {{m}_{2}}$ are slopes of two lines between which we need to find angle and
slopes can be calculated by formula $m=\dfrac{{{y}_{2}}-{{y}_{1}}}{{{x}_{2}}-{{x}_{1}}}$ .
Hence; this can be the angel approach as well but it may be lengthy than the above two discussed problems.
Let us roughly draw a triangle with the given vertices:

Now, let us calculate distances between the points of triangle:
As we have the distance formula for two vertices in $2-D$ as
If two points $X\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)\And Y\left( {{x}_{2}}{{y}_{2}} \right)$ are given
then

$xy=\sqrt{{{\left( {{x}_{1}}-{{x}_{2}} \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( {{y}_{1}}-{{y}_{2}} \right)}^{2}}}$
By using above formula now let’s calculate $AB,BC,AC:$
$AB=\sqrt{{{\left( -2-6 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( 3-7 \right)}^{2}}}\text{ }\left( \text{as }A=\left( -
2,3 \right)B=\left( 6,7 \right) \right)$
\[\begin{align}
& AB=\sqrt{64+16} \\
& AB=\sqrt{80}=\sqrt{4\times 4\times 5}.................\left( 1 \right) \\
& AB=4\sqrt{5} \\
\end{align}\]
Now, Let’s calculate $BC\text{ }\left( \text{as }B=\left( 6,7 \right)C=\left( 8,3 \right) \right)$
\[\begin{align}
& BC=\sqrt{{{\left( 6-8 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( 7-3 \right)}^{2}}} \\
& BC=\sqrt{4+16} \\
& BC=\sqrt{20}=\sqrt{2\times 2\times 5}................\left( 2 \right) \\
& BC=2\sqrt{5} \\
\end{align}\]
Now,
$\begin{align}
& AC=\sqrt{{{\left( -2-8 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( 3-3 \right)}^{2}}} \\
& AC=\sqrt{100}=10...........\left( 3 \right) \\
\end{align}$
Hence we can observe that $AC$ has the highest length in $AB,BC\And AC$ .
Therefore if $ABC$ will represent a right angle triangle then it will show or follow Pythagoras
property and $AC$ will be the Hypotenuse length.
As Pythagoras property can be expressed as following:

$x{{y}^{2}}+y{{z}^{2}}=x{{z}^{2}}$
Where $xz$ is Hypotenuse and biggest in length among the three sides.
Hence, if $ABC$ will represent right angle triangle then:

It will follow
\[\begin{align}
& A{{B}^{2}}+B{{C}^{2}}=A{{C}^{2}} \\
& {{\left( 4\sqrt{5} \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( 2\sqrt{5} \right)}^{2}}={{\left( 10
\right)}^{2}}=100 \\
\end{align}\]
Let LHS (Left Hand Side):
$\begin{align}
& {{\left( 4\sqrt{5} \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( 2\sqrt{5} \right)}^{2}}=80+20 \\
& =100=RHS \\
\end{align}$
Hence, It is proved that $ABC$ is a right angled triangle at $B$ with $AC$ as Hypotenuse.
Note: In straight line we learn concept of calculating slope of a line and property of
perpendicular lines as well which is “If two lines are perpendicular then; $Slope\left( Line1
\right)\times Slope\left(Line2 \right)=-1.........\left( 1 \right)$
As right angle triangle will have 3 lines and all have slope, and if two of them will follow
equation $\left( 1 \right)$ then the triangle will be a right angled triangle. This proving is
more advanced than the provided solution.
We have formula of slope as
$m=\dfrac{{{y}_{2}}-{{y}_{1}}}{{{x}_{2}}-{{x}_{1}}}$ with a line of two points given as $\left(
{{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)\And \left( {{x}_{2}}{{y}_{2}} \right)$ .
Now in given triangle
\[\begin{align}
& {{m}_{AB}}=\dfrac{{{y}_{2}}-{{y}_{1}}}{{{x}_{2}}-{{x}_{1}}}=\dfrac{3-7}{-2-6}=\dfrac{-4}{-
8}=\dfrac{1}{2} \\
& {{m}_{BC}}=\dfrac{7-3}{6-8}=\dfrac{-4}{2}=-2 \\
& \text{As }{{\text{m}}_{AB}}\times {{m}_{BC}}=-1 \\
\end{align}\]
Hence, $ABC$ have $B$ angle as $90{}^\circ $.
Therefore $ABC$is a right angle triangle.
We can calculate angle between the lines by using formula
$\tan \theta =\left| \dfrac{{{m}_{1}}-{{m}_{2}}}{1+{{m}_{1}}{{m}_{2}}} \right|$ where
${{m}_{1}}\And {{m}_{2}}$ are slopes of two lines between which we need to find angle and
slopes can be calculated by formula $m=\dfrac{{{y}_{2}}-{{y}_{1}}}{{{x}_{2}}-{{x}_{1}}}$ .
Hence; this can be the angel approach as well but it may be lengthy than the above two discussed problems.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 9 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Who is eligible for RTE class 9 social science CBSE

Which places in India experience sunrise first and class 9 social science CBSE

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it

Name 10 Living and Non living things class 9 biology CBSE




