
Show the formation of \[MgO\] by transfer of electrons between combining atoms.
Answer
533.7k+ views
Hint: Magnesium oxide is an inorganic compound that occurs in nature as the mineral periclase. Aqueous media combines quickly with water to form magnesium hydroxide. It is used as an antacid and mild laxative and has many non medicinal uses.
Complete step by step answer:
The atomic number of Magnesium is\[12\].
The electronic configuration of magnesium is
\[Mg\left( {Z = 12} \right){\text{ }} = {\text{ }}1{s^2}2{s^2}2{p^6}3{s^2}\]
In order to obtain an octet configuration, it will lose two electrons.
The atomic number of oxygen is\[8\].
The electronic configuration of oxygen is
\[O\left( {Z{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}8} \right){\text{ }} = {\text{ }}1{s^2}2{s^2}2{p^4}\]
In order to obtain an octet configuration, it has to gain two electrons.
When magnesium reacts with oxygen, the magnesium atom transfers its two outermost electrons to an oxygen atom. By losing two electrons, the magnesium atoms form a magnesium ion (\[M{g^{2 + }}\]) and by gaining two electrons, the oxygen atom forms an oxide ion (\[{O^{2 - }}\]).
\[Mg:{\text{ }} + {\text{ }}O{\text{ }} \to {\text{ }}MgO\]
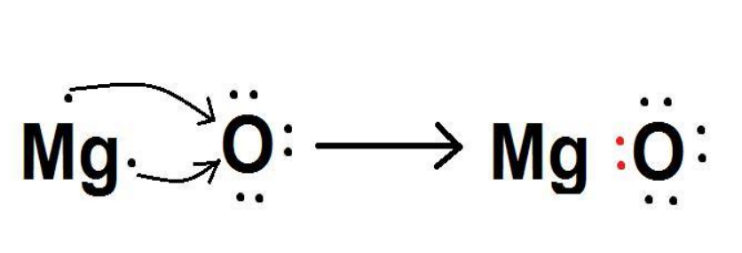
Note: Magnesium oxide nanoparticles can be prepared using the hydroxide precipitation process, which is followed by the thermal decomposition of the hydroxide. \[MgO\] Can be characterized by X-ray powder diffraction and scanning electron microscopes.
Magnesium oxide nanoparticles can be applied in electronics, catalysis, ceramics, petrochemical products, coatings, and many other fields. Magnesium oxide nanoparticles can be used along with wood chips and shavings to make materials such as sound-proof, light-weight, heat-insulating, and refractory fiberboard and metallic ceramics.
Magnesia (magnesium oxide,\[MgO\]) is mainly produced from the calcination of magnesite in a process similar to the production of lime from limestone. A smaller proportion of the world's \[MgO\] production comes from seawater and brine sources.
Complete step by step answer:
The atomic number of Magnesium is\[12\].
The electronic configuration of magnesium is
\[Mg\left( {Z = 12} \right){\text{ }} = {\text{ }}1{s^2}2{s^2}2{p^6}3{s^2}\]
In order to obtain an octet configuration, it will lose two electrons.
The atomic number of oxygen is\[8\].
The electronic configuration of oxygen is
\[O\left( {Z{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}8} \right){\text{ }} = {\text{ }}1{s^2}2{s^2}2{p^4}\]
In order to obtain an octet configuration, it has to gain two electrons.
When magnesium reacts with oxygen, the magnesium atom transfers its two outermost electrons to an oxygen atom. By losing two electrons, the magnesium atoms form a magnesium ion (\[M{g^{2 + }}\]) and by gaining two electrons, the oxygen atom forms an oxide ion (\[{O^{2 - }}\]).
\[Mg:{\text{ }} + {\text{ }}O{\text{ }} \to {\text{ }}MgO\]
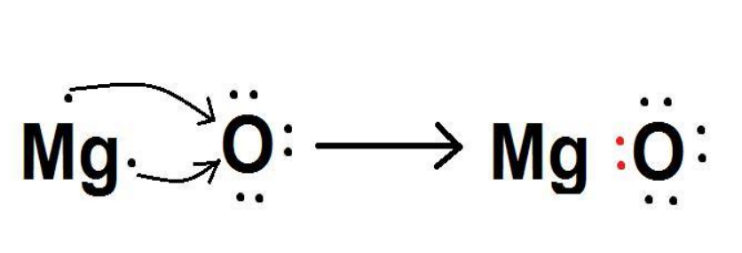
Note: Magnesium oxide nanoparticles can be prepared using the hydroxide precipitation process, which is followed by the thermal decomposition of the hydroxide. \[MgO\] Can be characterized by X-ray powder diffraction and scanning electron microscopes.
Magnesium oxide nanoparticles can be applied in electronics, catalysis, ceramics, petrochemical products, coatings, and many other fields. Magnesium oxide nanoparticles can be used along with wood chips and shavings to make materials such as sound-proof, light-weight, heat-insulating, and refractory fiberboard and metallic ceramics.
Magnesia (magnesium oxide,\[MgO\]) is mainly produced from the calcination of magnesite in a process similar to the production of lime from limestone. A smaller proportion of the world's \[MgO\] production comes from seawater and brine sources.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




