
Sketch and label V.S of mature anatropous ovule.
Answer
561.6k+ views
Hint: The ovule is typically made up of a nucleus, it is the largest organelle present in the ovule. The integuments which are found at the very centre are said to form the female gametophyte and the tough exterior layer which generally protect the ovule. The ovules turn out to be entirely reversed in the duration of the development in Anatropous so that the micropyle lies close to the hilum. We can say that the helium is a scar which scripts the point where the seed was attached to the wall of fruit by the funicle.
Complete answer:
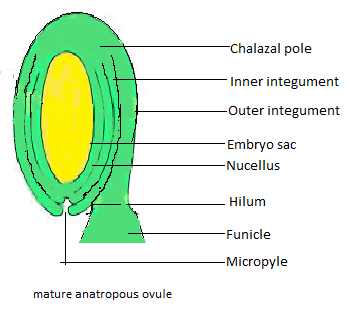
Chalazal pole:
The top parts are called chalazae poles. It is green in colour. One can define chalaza as a pair of spring-like structures. The chalazae function is to protect the egg. Covers the egg and has a thickness.
Integuments:
In the given figure, the nucleus of the anatropous ovule. The organ which forms the seeds of flowering plants is known as ovules. It is stood in the ovary of the flower and is made up of nucellus and protected by integuments.
Embryo sac:
The structure that gives rise to and stores the female reproductive cells of the flower is called the ovule. It is the reason that the ovules are called as an embryo sac in flowering plants. That develops in seed after fertilization in the plant.
Nucellus:
Nucellus is a tissue. The tissue that makes up the more area of the ovule of seed plants. It includes the embryo sac and nutritive tissue. It is enclosed by the instruments.
Funicle:
It is an insect antennae. Funicle is attaches the ovule to the placenta in the flowering plant.The funicle is the segment connecting the club with the base.
Micropyle:
Typically, the nucleus is closed by the integument which leaves a small gap, which is called the micropyle.
Note: A mature anatropous ovule has the typical features of wind-pollinated flowers. The pollen grains of the flower which contain mature anatropous ovules are light, dry and non-stick. They produce large amounts of pollen grains. These flowers have a large and feathery stigma. The flowers are exposed so that the pollen can easily dispersed toward the stamen.
Complete answer:

Chalazal pole:
The top parts are called chalazae poles. It is green in colour. One can define chalaza as a pair of spring-like structures. The chalazae function is to protect the egg. Covers the egg and has a thickness.
Integuments:
In the given figure, the nucleus of the anatropous ovule. The organ which forms the seeds of flowering plants is known as ovules. It is stood in the ovary of the flower and is made up of nucellus and protected by integuments.
Embryo sac:
The structure that gives rise to and stores the female reproductive cells of the flower is called the ovule. It is the reason that the ovules are called as an embryo sac in flowering plants. That develops in seed after fertilization in the plant.
Nucellus:
Nucellus is a tissue. The tissue that makes up the more area of the ovule of seed plants. It includes the embryo sac and nutritive tissue. It is enclosed by the instruments.
Funicle:
It is an insect antennae. Funicle is attaches the ovule to the placenta in the flowering plant.The funicle is the segment connecting the club with the base.
Micropyle:
Typically, the nucleus is closed by the integument which leaves a small gap, which is called the micropyle.
Note: A mature anatropous ovule has the typical features of wind-pollinated flowers. The pollen grains of the flower which contain mature anatropous ovules are light, dry and non-stick. They produce large amounts of pollen grains. These flowers have a large and feathery stigma. The flowers are exposed so that the pollen can easily dispersed toward the stamen.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




