
What is spermiogenesis? Demonstrate diagrammatically the process of spermiogenesis.
Answer
544.5k+ views
Hint: The stage of spermatogenesis in which the spermatids differentiate into mature spermatozoa is spermiogenesis. The germ cells go through a series of cellular divisions before this point, particularly mitosis (spermatocytogenesis) and meiosis (spermatidogenesis).
Complete answer:
The final stage of spermatogenesis is spermiogenesis, in which the maturation of spermatozoa into mature, motile spermatozoa takes place. The spermatid is a circular cell comprising the nucleus, the centriole, the mitochondria and the Golgi apparatus. Traditionally, the spermatogenesis process is divided into four phases: the Golgi phase, the cap phase, the development of a tail, and the stage of maturation.
Spermatogenesis- Male gamete formation process, i.e. spermatozoa. In the male gonads, called testes, the spermatogenesis process takes place. Every testis has seminiferous tubules called germinal epithelium that are lined with cuboidal epithelium. Germinal epithelium cells undergo spermatogenesis in order to produce sperm.
Among germinal cells, there are Sertoli cells or nurse cells that provide sperm nutrition. Germ cells are known as main germ cells or primordial germ cells in the testes.
Three stages pass through the primordial cell, namely,
1) multiplication phase
2) growth phase
3) maturation phase
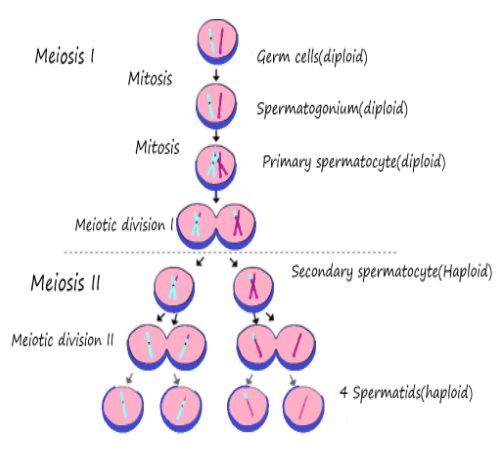
Multiplication phase: To create a large number of spermatogonia, primordial cells undergo repeated mitotic divisions. Every diploid spermatogonia is (2n).
Growth phase: The spermatogonium cell gathers food and grows in size. It is also considered the largest spermatocyte.
Maturation phase: First meiotic or maturation division occurs in the primary spermatocyte. The chromosomes that are homologous start pairing. Each chromosome that is homologous splits longitudinally. The creation of Chiasma results in an exchange of genetic material.
Two haploid, secondary spermatocytes are produced at the end of meiotic division I.
Each secondary spermatocyte is subjected to II meiotic division and spermatids are formed. Each spermatogonium produces four haploid spermatids at the end of the maturation stage.
Spermatid is non-motile, so to become a functional, motile male gamete, i.e. spermatozoan, it must undergo spermatogenesis. Many spermatid changes occur, such as sperm length increases, centrioles are separated into proximal and distal centrioles, distal centriole gives rise to the axial filament, mitochondria are spirally coiled, and acrosome types of the Golgi complex.
Note: The mature spermatozoa are released into the lumen of the seminiferous tubule from the protective Sertoli cells and a process called spermiation then takes place, eliminating the remaining unwanted cytoplasm and organelles. The spermatozoa that result are now mature but lack motility, making them sterile.
Complete answer:
The final stage of spermatogenesis is spermiogenesis, in which the maturation of spermatozoa into mature, motile spermatozoa takes place. The spermatid is a circular cell comprising the nucleus, the centriole, the mitochondria and the Golgi apparatus. Traditionally, the spermatogenesis process is divided into four phases: the Golgi phase, the cap phase, the development of a tail, and the stage of maturation.
Spermatogenesis- Male gamete formation process, i.e. spermatozoa. In the male gonads, called testes, the spermatogenesis process takes place. Every testis has seminiferous tubules called germinal epithelium that are lined with cuboidal epithelium. Germinal epithelium cells undergo spermatogenesis in order to produce sperm.
Among germinal cells, there are Sertoli cells or nurse cells that provide sperm nutrition. Germ cells are known as main germ cells or primordial germ cells in the testes.
Three stages pass through the primordial cell, namely,
1) multiplication phase
2) growth phase
3) maturation phase
Multiplication phase: To create a large number of spermatogonia, primordial cells undergo repeated mitotic divisions. Every diploid spermatogonia is (2n).
Growth phase: The spermatogonium cell gathers food and grows in size. It is also considered the largest spermatocyte.
Maturation phase: First meiotic or maturation division occurs in the primary spermatocyte. The chromosomes that are homologous start pairing. Each chromosome that is homologous splits longitudinally. The creation of Chiasma results in an exchange of genetic material.
Two haploid, secondary spermatocytes are produced at the end of meiotic division I.
Each secondary spermatocyte is subjected to II meiotic division and spermatids are formed. Each spermatogonium produces four haploid spermatids at the end of the maturation stage.
Spermatid is non-motile, so to become a functional, motile male gamete, i.e. spermatozoan, it must undergo spermatogenesis. Many spermatid changes occur, such as sperm length increases, centrioles are separated into proximal and distal centrioles, distal centriole gives rise to the axial filament, mitochondria are spirally coiled, and acrosome types of the Golgi complex.

Note: The mature spermatozoa are released into the lumen of the seminiferous tubule from the protective Sertoli cells and a process called spermiation then takes place, eliminating the remaining unwanted cytoplasm and organelles. The spermatozoa that result are now mature but lack motility, making them sterile.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




