
State and explain Kirchhoff’s Laws in the current electricity.
Answer
522.4k+ views
Hint: Junction is any point in the circuit where the current can split. Use sign concentrations to find KVL and KCL. First law deals with the sum of current coming and leaving at a junction. Second law deals with the sum of potential differences plus the algebraic sum of e.m.f is equal to zero.
Complete step-by-step answer:
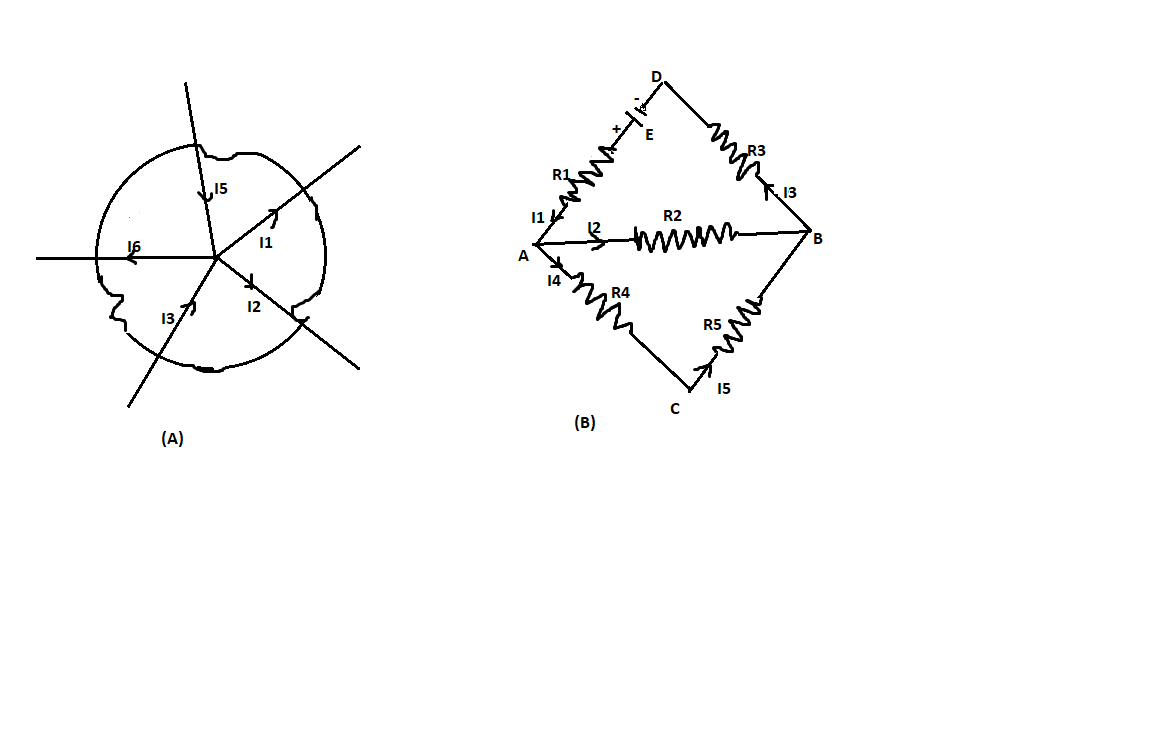
Kirchhoff’s laws are generally used to analyse the electrical circuit that is to calculate the current and resistance in the network. Kirchhoff's law Voltage law and current law are derived on the basis of principle of conservation of energy. Kirchhoff’s law is of two type:
1. Kirchhoff’s Current Law(KCL)
Statement: The algebraic sum of current entering and leaving at any junction in a circuit is zero.
$i.e.\sum\limits_{{}}^{{}}{i=0}$
Consider a surface as containing the conductor meeting at a point P as shown in figure (a). Now, taking the current flowing away from the junction as positive and current flowing towards the junction as negative, then
\[\begin{array}{*{35}{l}}
{{I}_{1}}-{{I}_{2}}+{{I}_{3}}-{{I}_{4}}+{{I}_{5}}=0 \\
{{I}_{1}}+{{I}_{3}}={{I}_{2}}+{{I}_{4}}-{{I}_{5}} \\
\end{array}\]
2. Kirchhoff’s Current Law(KVL)
Statement: The sum of voltage of sources and all potential drop (IR drop) in any closed loop of a network is zero.
While applying KVL, positive value of current is taken when we are travelling in the direction of current and e.m.f is taken negative when we travel from negative to positive electrode of source.
In ABDA loop,
${{I}_{1}}{{R}_{1}}+{{I}_{2}}{{R}_{2}}+{{I}_{3}}{{R}_{3}}=E$
In ABCA loop,
$\begin{align}
& {{I}_{2}}{{R}_{2}}-{{I}_{5}}{{R}_{5}}-{{I}_{4}}{{R}_{4}}=0 \\
& {{I}_{2}}{{R}_{2}}={{I}_{5}}{{R}_{5}}-{{I}_{4}}{{R}_{4}} \\
\end{align}$
Note: Do not get confused between ohm's law and Kirchhoff’ law. Kirchhoff’s laws are used to determine currents and potential difference in the complicated circuit. Ohms law is valid only for graphs passing through origin. Current is the rate of flow of electric charge. Steady state current is electric current which does not depend upon time.
Complete step-by-step answer:

Kirchhoff’s laws are generally used to analyse the electrical circuit that is to calculate the current and resistance in the network. Kirchhoff's law Voltage law and current law are derived on the basis of principle of conservation of energy. Kirchhoff’s law is of two type:
1. Kirchhoff’s Current Law(KCL)
Statement: The algebraic sum of current entering and leaving at any junction in a circuit is zero.
$i.e.\sum\limits_{{}}^{{}}{i=0}$
Consider a surface as containing the conductor meeting at a point P as shown in figure (a). Now, taking the current flowing away from the junction as positive and current flowing towards the junction as negative, then
\[\begin{array}{*{35}{l}}
{{I}_{1}}-{{I}_{2}}+{{I}_{3}}-{{I}_{4}}+{{I}_{5}}=0 \\
{{I}_{1}}+{{I}_{3}}={{I}_{2}}+{{I}_{4}}-{{I}_{5}} \\
\end{array}\]
2. Kirchhoff’s Current Law(KVL)
Statement: The sum of voltage of sources and all potential drop (IR drop) in any closed loop of a network is zero.
While applying KVL, positive value of current is taken when we are travelling in the direction of current and e.m.f is taken negative when we travel from negative to positive electrode of source.
In ABDA loop,
${{I}_{1}}{{R}_{1}}+{{I}_{2}}{{R}_{2}}+{{I}_{3}}{{R}_{3}}=E$
In ABCA loop,
$\begin{align}
& {{I}_{2}}{{R}_{2}}-{{I}_{5}}{{R}_{5}}-{{I}_{4}}{{R}_{4}}=0 \\
& {{I}_{2}}{{R}_{2}}={{I}_{5}}{{R}_{5}}-{{I}_{4}}{{R}_{4}} \\
\end{align}$
Note: Do not get confused between ohm's law and Kirchhoff’ law. Kirchhoff’s laws are used to determine currents and potential difference in the complicated circuit. Ohms law is valid only for graphs passing through origin. Current is the rate of flow of electric charge. Steady state current is electric current which does not depend upon time.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




