
State molecular and structural formula of benzene:
Answer
533.7k+ views
Hint: At first we will look into what is given in the question. Then we will write the structural formula then we will write the molecular formula of benzene. Then we will look deep into the benzene.
Complete step by step answer:
Step1. We are given a compound called benzene. We need to write its chemical and molecular formula.
Step2. Benzene is an organic chemical compound. It contains six carbons and six hydrogens. It is a hydrocarbon since it consists of only hydrogen and carbon. It contains three pi bonds. It is cyclic in nature. The pi bonds are continuous. It is aromatic in nature. It is colorless and highly flammable. It is a cyclic compound
Step3. The molecular formula is ${C_6}{H_6}$ . The Carbon is connected with two carbons; single bonded with one and double bonded with another. That carbon is also connected with single bonded hydrogen.
Step4. Its structure is given below.
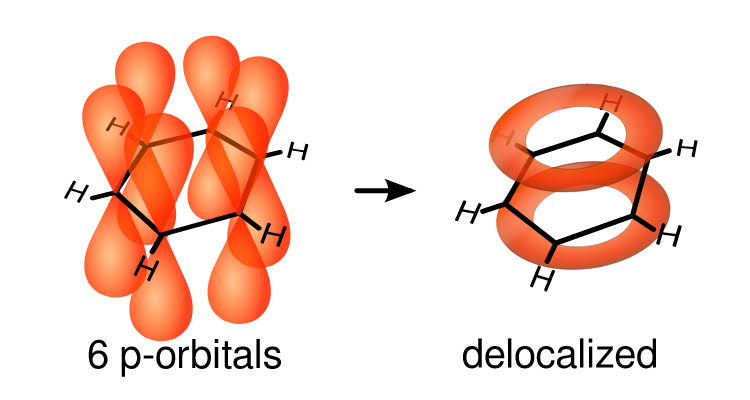
It is an aromatic cyclic compound. It is a hexagonal ring. Ortho, meta, para are used to differentiate the position when a substitute is attached to it. All six carbon compounds are of the same length. It is a planar molecule.
Note: A lot of important chemical compounds can be formed by adding one or more functional groups at benzene. Toluene, phenol, aniline are one of the most famous examples. It is most commonly used as an intermediate to form other chemicals. It is also an additive of the petrol. It reduces the knocking.
Complete step by step answer:
Step1. We are given a compound called benzene. We need to write its chemical and molecular formula.
Step2. Benzene is an organic chemical compound. It contains six carbons and six hydrogens. It is a hydrocarbon since it consists of only hydrogen and carbon. It contains three pi bonds. It is cyclic in nature. The pi bonds are continuous. It is aromatic in nature. It is colorless and highly flammable. It is a cyclic compound
Step3. The molecular formula is ${C_6}{H_6}$ . The Carbon is connected with two carbons; single bonded with one and double bonded with another. That carbon is also connected with single bonded hydrogen.
Step4. Its structure is given below.

It is an aromatic cyclic compound. It is a hexagonal ring. Ortho, meta, para are used to differentiate the position when a substitute is attached to it. All six carbon compounds are of the same length. It is a planar molecule.
Note: A lot of important chemical compounds can be formed by adding one or more functional groups at benzene. Toluene, phenol, aniline are one of the most famous examples. It is most commonly used as an intermediate to form other chemicals. It is also an additive of the petrol. It reduces the knocking.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




