
State Newton’s third law of motion.
Answer
591.9k+ views
Hint: Forces are applied on objects or bodies and the effects of these forces are studied in this law. Force is a push or a pull applied on one body by the other body when two bodies interact with each other.
Complete step by step solution:
Step I:
As per Newton’s third law of motion:
“To every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction”.
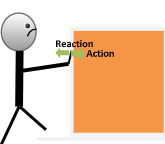
Step II:
Suppose there are two bodies A and B. They both are made to interact with each other. Now if object A applies some force on object B, then object B will also apply the same amount of force on object A but in the opposite direction.
Step III:
From the above explanation, it is clear that whenever two bodies interact with each other, then there are two forces ‘action-reaction’ acts on the objects. These forces always occur in pairs. They can be equal in magnitude but their direction will always be the opposite.
Step IV:
It can be explained using the example of an airplane flying. Two pairs of forces act oppositely to each other and make the airplane fly efficiently. The wings of the airplane are designed in a way that they push the air downwards by applying the action force. Air, in turn, applies the same amount of reaction force in the opposite direction and pushes up the wings. This makes the airplane fly.
Note:
In order to find the number of net forces acting on a system, it is important to know the total external forces acting on the system. Newton’s third law of motion is used in evaluating the external forces acting on a system as it has three points to be considered:
The action and reaction forces must act on two different objects or two bodies.
The forces should be equal in magnitudes.
The direction in which these forces are acting should be in the opposite direction.
Complete step by step solution:
Step I:
As per Newton’s third law of motion:
“To every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction”.

Step II:
Suppose there are two bodies A and B. They both are made to interact with each other. Now if object A applies some force on object B, then object B will also apply the same amount of force on object A but in the opposite direction.
Step III:
From the above explanation, it is clear that whenever two bodies interact with each other, then there are two forces ‘action-reaction’ acts on the objects. These forces always occur in pairs. They can be equal in magnitude but their direction will always be the opposite.
Step IV:
It can be explained using the example of an airplane flying. Two pairs of forces act oppositely to each other and make the airplane fly efficiently. The wings of the airplane are designed in a way that they push the air downwards by applying the action force. Air, in turn, applies the same amount of reaction force in the opposite direction and pushes up the wings. This makes the airplane fly.
Note:
In order to find the number of net forces acting on a system, it is important to know the total external forces acting on the system. Newton’s third law of motion is used in evaluating the external forces acting on a system as it has three points to be considered:
The action and reaction forces must act on two different objects or two bodies.
The forces should be equal in magnitudes.
The direction in which these forces are acting should be in the opposite direction.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 9 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Who is eligible for RTE class 9 social science CBSE

Which places in India experience sunrise first and class 9 social science CBSE

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it

Name 10 Living and Non living things class 9 biology CBSE




