
State with reason, how the linear width of central maximum will be affected if
(i) Monochromatic yellow light is replaced with red light, and
(ii) Distance between the slit and the screen is increased.
Answer
590.4k+ views
Hint: In a single slit diffraction, the light bends around the edge of the obstacles to form a diffraction pattern which consists of maxima and minima. Maxima are those with bright spots and minima are those with dark spots. Here central maximum is the central bright spot or the first bright spot in the pattern.
Formula used:
Linear width of central maximum, \[{{\beta }_{0}}=\dfrac{2\lambda D}{a}\]
Complete answer:
Diffraction is a phenomenon which shows the wave nature of light, as we know that light has dual nature of particle and wave, when the light source faces an obstacles in path it bends around the corners of the obstacles. We can observe this in our daily life too, for example the shadow made by any object.
In a single slit diffraction, the light source is passed through the slit whose width is nearly the order of the wavelength of the light source. So, when light is passed through a slit, we get a diffraction pattern on a screen, which is kept at a few cm or m away from the slit. The diffraction pattern and the arrangement can be understood by the given diagram
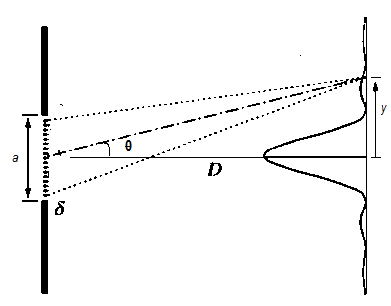
From the diagram we can derive,
\[a\sin \theta =\lambda \] and \[\tan \theta =\dfrac{y}{D}\]
Where λ, is the wavelength of the light source. As θ is very small nearly order of the wavelength
\[\theta =\dfrac{\lambda }{a}\] and \[\theta =\dfrac{y}{D}\]
We can equate the both equation, therefore it becomes
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{y}{D}=\dfrac{\lambda }{a} \\
& \Rightarrow y=\dfrac{\lambda D}{a} \\
\end{align}\]
Linear width of central maximum is the twice of y we can also observe from the diagram,
\[\Rightarrow {{\beta }_{0}}=2y\]
Where, \[{{\beta }_{0}}\]is the linear width of the central maximum.
\[\Rightarrow {{\beta }_{0}}=\dfrac{2\lambda D}{a}\]
From the above equation we can conclude that the linear width of central maximum is directly proportional to the wavelength and the distance between the slit and the screen.
Therefore, (i) the linear width will increase if the monochromatic yellow light is replaced with red light because red light has a larger wavelength than yellow. (ii) Similarly with the increase of distance between the screen and the slit the linear width of the central maximum will increase.
Note:
The wavelength of the red light is greater than yellow light and its frequency is less than the yellow light, many of us get confused by it and can make mistakes. Similarly one can get confused between angular width and the linear width. Angular width is given as 2θ and linear width is 2y.
Formula used:
Linear width of central maximum, \[{{\beta }_{0}}=\dfrac{2\lambda D}{a}\]
Complete answer:
Diffraction is a phenomenon which shows the wave nature of light, as we know that light has dual nature of particle and wave, when the light source faces an obstacles in path it bends around the corners of the obstacles. We can observe this in our daily life too, for example the shadow made by any object.
In a single slit diffraction, the light source is passed through the slit whose width is nearly the order of the wavelength of the light source. So, when light is passed through a slit, we get a diffraction pattern on a screen, which is kept at a few cm or m away from the slit. The diffraction pattern and the arrangement can be understood by the given diagram

From the diagram we can derive,
\[a\sin \theta =\lambda \] and \[\tan \theta =\dfrac{y}{D}\]
Where λ, is the wavelength of the light source. As θ is very small nearly order of the wavelength
\[\theta =\dfrac{\lambda }{a}\] and \[\theta =\dfrac{y}{D}\]
We can equate the both equation, therefore it becomes
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{y}{D}=\dfrac{\lambda }{a} \\
& \Rightarrow y=\dfrac{\lambda D}{a} \\
\end{align}\]
Linear width of central maximum is the twice of y we can also observe from the diagram,
\[\Rightarrow {{\beta }_{0}}=2y\]
Where, \[{{\beta }_{0}}\]is the linear width of the central maximum.
\[\Rightarrow {{\beta }_{0}}=\dfrac{2\lambda D}{a}\]
From the above equation we can conclude that the linear width of central maximum is directly proportional to the wavelength and the distance between the slit and the screen.
Therefore, (i) the linear width will increase if the monochromatic yellow light is replaced with red light because red light has a larger wavelength than yellow. (ii) Similarly with the increase of distance between the screen and the slit the linear width of the central maximum will increase.
Note:
The wavelength of the red light is greater than yellow light and its frequency is less than the yellow light, many of us get confused by it and can make mistakes. Similarly one can get confused between angular width and the linear width. Angular width is given as 2θ and linear width is 2y.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




