
Strong field ligands,such as $$\mathrm{CN}^{-}$$ usually produce low spin complexes and large crystal field splitting.
If true enter 1, else enter 0.
Answer
585.9k+ views
Hint: Strong field ligands produce low spin complexes. This is due to the Crystal field theory. So, spin of a complex is directly proportional to how many electrons are unpaired in an orbital.These ligands help in pairing of the electrons.
Complete step by step answer:
Crystal field theory(CFT) was developed by H.Bethe and V.Bleck in 1935. This theory considered the bond between a metal ion and the ligand as purely electrostatic.
In coordination chemistry, a ligand is an ion or molecule that binds to a central metal atom to form a coordination complex.
CFT is based on the assumption that the metal ion and the ligands act as point charges and the interaction between them are purely electrostatic. In case of negative ligands like, Cl,CN,etc. the interaction with metal ions are ion-ion interactions. If the ligands are neutral like, CO,etc. The interaction with the metal ions are ion-dipole interactions. The name crystal field is assigned to this theory as the electrons of the central metal ion in the environment of other ions or molecules i.e.,ligands are affected by their non spherical electric field.
In this theory, we have to understand Crystal Field Stabilization Energy (CFSE) in order to answer the given question.
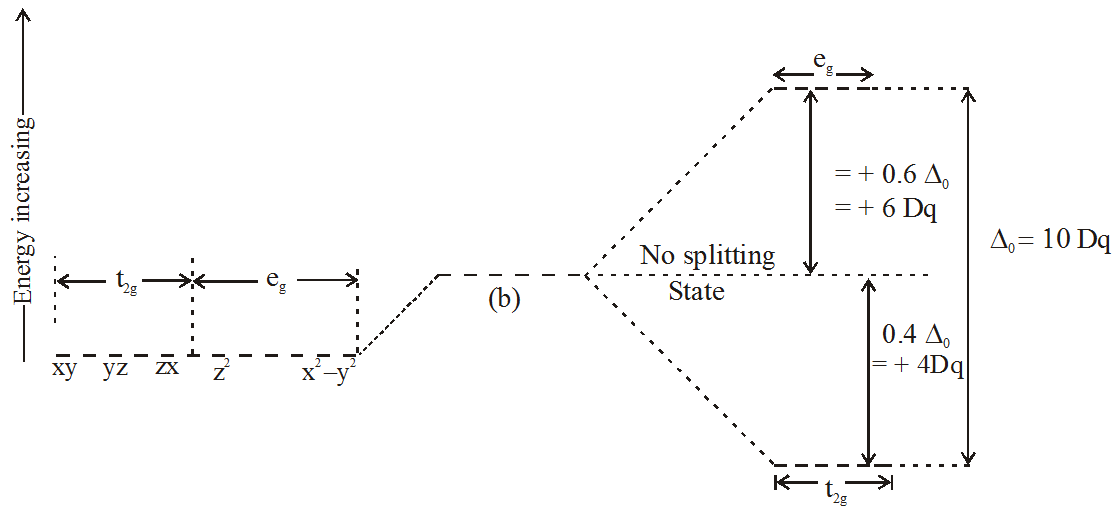
The phenomenon of crystal field splitting in an octahedral complex is illustrated here. The energy difference between two sets of d-orbitals; $$\mathrm{t}_{2 \mathrm{g}} \text { and } \mathrm{e}_{\mathrm{g}}$$ is called crystal field splitting energy and is symbolically represented as $$\Delta_{0}$$.
Now,in order to solve the given question we have to know about CFSE.
Crystal field stabilization energy(CFSE) is the amount of stabilization provided by splitting of the d-orbitals into two levels.
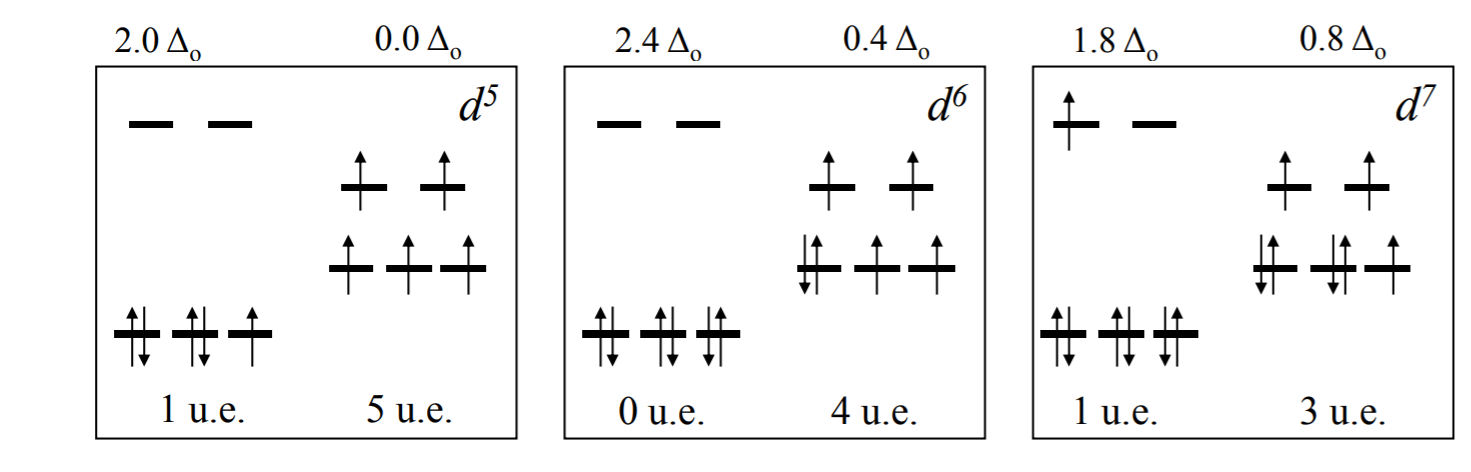
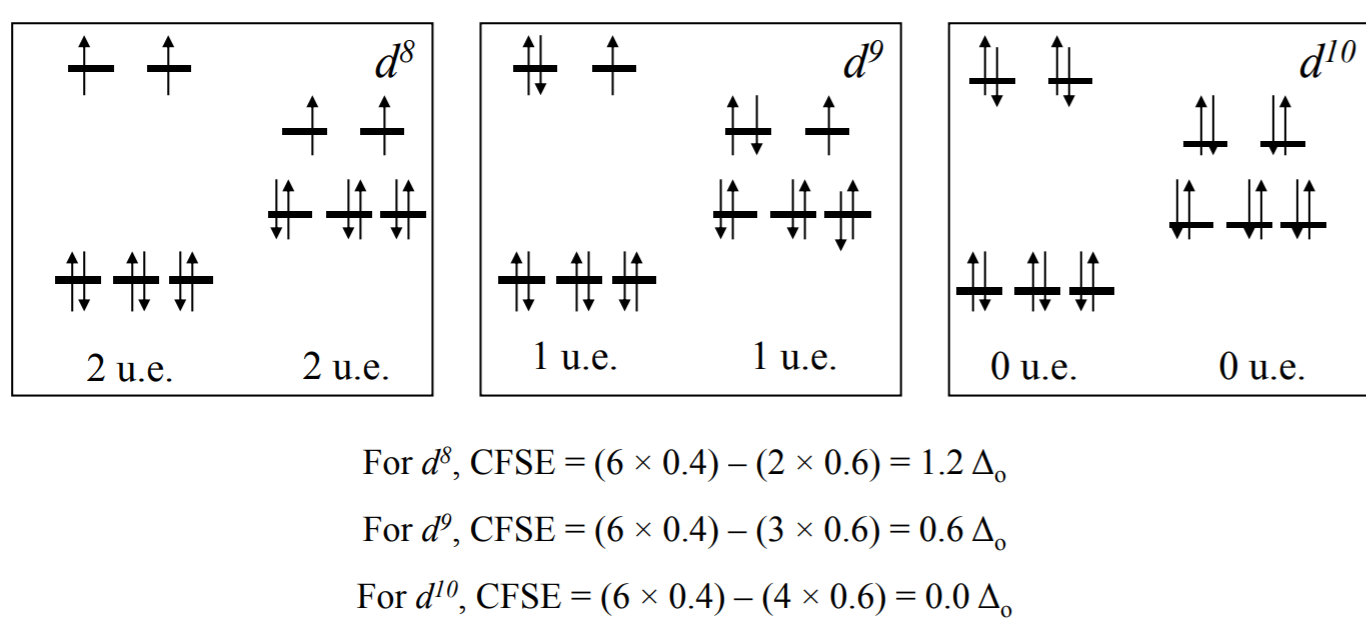
There are two possibilities for metal ions having $$\mathrm{d}^{4}-\mathrm{d}^{7}$$ electronic configuration. Depending on the nature of the ligands and the metal they could be high-spin or low 2 spin complexes. For the $$\mathrm{d}^{4}$$ system, CFSE = For high-spin, (3 × 0.4 ) – (1 × 0.6 ) = 0.6$$\Delta_{0}$$ and for low-spin, 4 × 0.4 = 1.6$$\Delta_{0}$$.
Metal ions with 4 to 7 electrons in the d orbital can exist as high spin or low spin complexes. Weaker ligands tend to give high-spin complexes, whereas stronger ligands tend to give low-spin complexes.
So, the correct answer is “1”.
Note: In case of strong field complexes, the complex has less number of unpaired electrons due to large crystal field splitting. These are called low spin complexes. Now coming to spin, when there are electrons unpaired in an orbital after making the complex which generally happens in case of weak field ligands(there are some exceptions too) the complex is of high spin which means spin of a complex depends on the number of unpaired electrons in an orbital. On the other hand when all the electrons are paired up generally happens in case of strong field ligands (There are exceptions also) the complex is of low spin.
Complete step by step answer:
Crystal field theory(CFT) was developed by H.Bethe and V.Bleck in 1935. This theory considered the bond between a metal ion and the ligand as purely electrostatic.
In coordination chemistry, a ligand is an ion or molecule that binds to a central metal atom to form a coordination complex.
CFT is based on the assumption that the metal ion and the ligands act as point charges and the interaction between them are purely electrostatic. In case of negative ligands like, Cl,CN,etc. the interaction with metal ions are ion-ion interactions. If the ligands are neutral like, CO,etc. The interaction with the metal ions are ion-dipole interactions. The name crystal field is assigned to this theory as the electrons of the central metal ion in the environment of other ions or molecules i.e.,ligands are affected by their non spherical electric field.
In this theory, we have to understand Crystal Field Stabilization Energy (CFSE) in order to answer the given question.

The phenomenon of crystal field splitting in an octahedral complex is illustrated here. The energy difference between two sets of d-orbitals; $$\mathrm{t}_{2 \mathrm{g}} \text { and } \mathrm{e}_{\mathrm{g}}$$ is called crystal field splitting energy and is symbolically represented as $$\Delta_{0}$$.
Now,in order to solve the given question we have to know about CFSE.
Crystal field stabilization energy(CFSE) is the amount of stabilization provided by splitting of the d-orbitals into two levels.
There are two possibilities for metal ions having $$\mathrm{d}^{4}-\mathrm{d}^{7}$$ electronic configuration. Depending on the nature of the ligands and the metal they could be high-spin or low 2 spin complexes. For the $$\mathrm{d}^{4}$$ system, CFSE = For high-spin, (3 × 0.4 ) – (1 × 0.6 ) = 0.6$$\Delta_{0}$$ and for low-spin, 4 × 0.4 = 1.6$$\Delta_{0}$$.
Metal ions with 4 to 7 electrons in the d orbital can exist as high spin or low spin complexes. Weaker ligands tend to give high-spin complexes, whereas stronger ligands tend to give low-spin complexes.


So, the correct answer is “1”.
Note: In case of strong field complexes, the complex has less number of unpaired electrons due to large crystal field splitting. These are called low spin complexes. Now coming to spin, when there are electrons unpaired in an orbital after making the complex which generally happens in case of weak field ligands(there are some exceptions too) the complex is of high spin which means spin of a complex depends on the number of unpaired electrons in an orbital. On the other hand when all the electrons are paired up generally happens in case of strong field ligands (There are exceptions also) the complex is of low spin.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




