
How will you synthesize benzoic acid from bromobenzene.
Answer
531k+ views
Hint: Before answering this question, one should know about benzoic acid and bromobenzene. Benzoic acid is an aromatic carboxylic acid. It is found naturally in many plants Bromobenzene is an unsaturated compound that can readily undergo an addition reaction.
Complete answer:
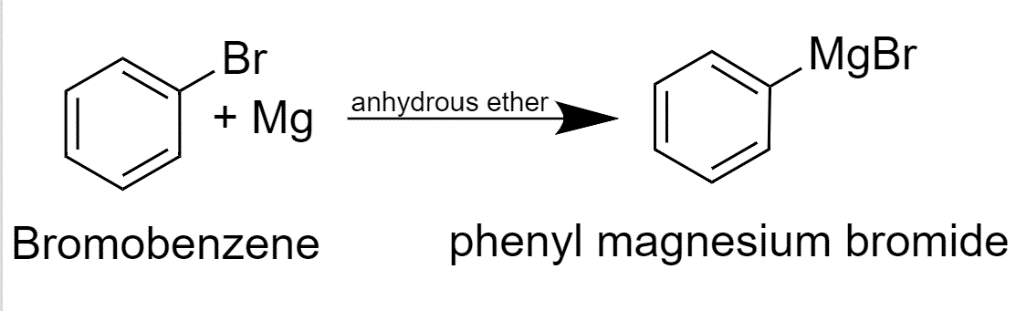
In this Grignard reagent, phenylmagnesium bromide is prepared with the help of bromobenzene and Mg metal in which diethyl ether is used as a solvent and there are some anhydrous conditions. The diethyl ether is used as a solvent to make Grignard reagents is important as the Partial positive charge on Mg in the Grignard reagent is stabilized by lone pairs of electrons on the oxygen to make sure it formed. In inert solvents, Grignard reagents are not formed. In nucleophilic addition reactions, diethyl ether or tetrahydrofuran functions well as a solvent because ether is not reactive with other reactants.
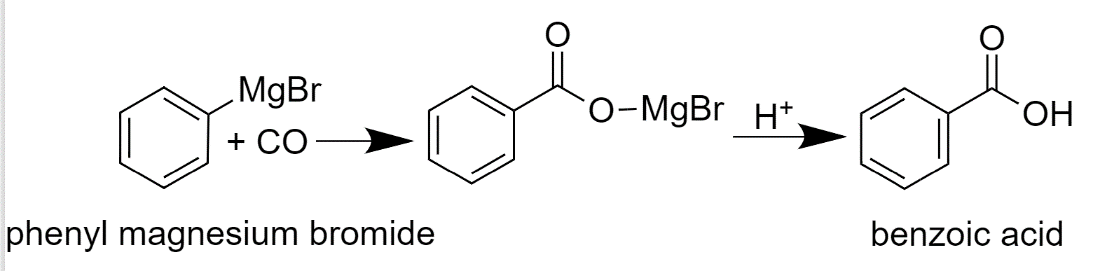
Phenyl magnesium bromide is then reacted with $C{{O}_{2}}$. After this, it will undergo hydrolysis and will give Benzoic acid.
Note:
The Carbon of the Grignard reagent shows two characteristics :
It acts as a nucleophile for the reaction with Carbon dioxide as a carbanion.
It acts as a strong base too as it reacts with acidic hydrogen atoms to give an alkane.
RMgX + HA = RH + MgAX
The structure of the Grignard reagent is represented as a partly ionic compound $\delta R...MgX\delta -+$Water, alcohols, terminal acetylenes, phenols, and carboxylic acids are some compounds that have acidic hydrogen and they will be readily donating a proton to destroy the reagent.
Complete answer:
In this Grignard reagent, phenylmagnesium bromide is prepared with the help of bromobenzene and Mg metal in which diethyl ether is used as a solvent and there are some anhydrous conditions. The diethyl ether is used as a solvent to make Grignard reagents is important as the Partial positive charge on Mg in the Grignard reagent is stabilized by lone pairs of electrons on the oxygen to make sure it formed. In inert solvents, Grignard reagents are not formed. In nucleophilic addition reactions, diethyl ether or tetrahydrofuran functions well as a solvent because ether is not reactive with other reactants.

Phenyl magnesium bromide is then reacted with $C{{O}_{2}}$. After this, it will undergo hydrolysis and will give Benzoic acid.

Note:
The Carbon of the Grignard reagent shows two characteristics :
It acts as a nucleophile for the reaction with Carbon dioxide as a carbanion.
It acts as a strong base too as it reacts with acidic hydrogen atoms to give an alkane.
RMgX + HA = RH + MgAX
The structure of the Grignard reagent is represented as a partly ionic compound $\delta R...MgX\delta -+$Water, alcohols, terminal acetylenes, phenols, and carboxylic acids are some compounds that have acidic hydrogen and they will be readily donating a proton to destroy the reagent.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




