
Take the z=axis as vertical and the x-y plane as horizontal. A particle ‘A’ is projected with velocity $4\sqrt 2 m{s^{ - 1}}$ making an angle $45^\circ $ to the horizontal. Particle B is projected at $5m{s^{ - 1}}$ an angle $\theta = {\tan ^{ - 1}}\left( {\dfrac{1}{3}} \right)$ to y axis in y-z plane then velocity of B wrt A.
A) Has its initial magnitude$5m{s^{ - 1}}$.
B) Magnitude will change with time.
C) Lies in the xy plane.
D) Will initially make an angle$\left( {\theta + \dfrac{\pi }{2}} \right)$.
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: The x,y and z are the three directions which are mutually perpendicular to each other, the particle A is in plane x-z and the particle B is in the plane y-z. The relative velocity is the difference between the velocities of the two bodies.
Formula used:
The relative velocity of the two particles is given by,
$ \Rightarrow {v_B} - {v_A}$
Where the velocity of particle B is ${v_B}$ and the velocity of particle A is${v_A}$.
Complete step by step solution:
In this problem it is given that a particle ‘A’ is projected with velocity $4\sqrt 2 m{s^{ - 1}}$ making an angle $45^\circ $ to the horizontal. Particle B is projected at $5m{s^{ - 1}}$ an angle $\theta = {\tan ^{ - 1}}\left( {\dfrac{1}{3}} \right)$ to y axis in y-z plane then we need to find the velocity of B wrt A.
According to the condition the figure will be.
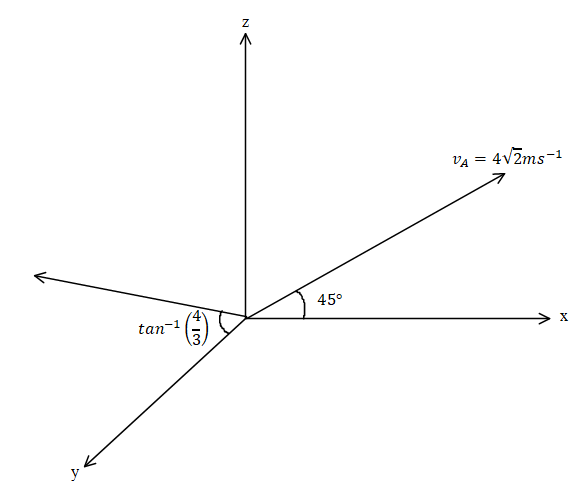
The velocity of particle A is ${v_A} = 4\hat i + 4\hat k$ and the velocity of particle B is equal to ${v_B} = 3\hat j + 4\hat k$.
The relative velocity of the particle B with respect to particle A is equal to,
$ \Rightarrow {v_B} - {v_A} = \left( {3\hat j + 4\hat k} \right) - \left( {4\hat i + 4\hat k} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow {v_B} - {v_A} = 3\hat j + 4\hat k - 4\hat i - 4\hat k$
$ \Rightarrow {v_B} - {v_A} = 3\hat j + 4\hat k - 4\hat i - 4\hat k$
$ \Rightarrow {v_B} - {v_A} = 3\hat j - 4\hat i$
The magnitude of the velocity is equal to,
$ \Rightarrow {v_B} - {v_A} = \sqrt {{3^2} + {4^2}} $
$ \Rightarrow {v_B} - {v_A} = \sqrt {9 + 16} $
$ \Rightarrow {v_B} - {v_A} = \sqrt {25} $
$ \Rightarrow {v_B} - {v_A} = 5m{s^{ - 1}}$
Which means option A is correct. The magnitude of the acceleration will not change with time and therefore the option B is wrong.
The relative velocity is ${v_B} - {v_A} = 3\hat j - 4\hat i$ which means it is in the x-y plane, the option C is also correct. The angle of the initially equal to,
$ \Rightarrow \theta = {\tan ^{ - 1}}\left( { - \dfrac{4}{3}} \right)$
As the angle is negative and therefore we add $\dfrac{\pi }{2}$ so the angle becomes $\theta + \dfrac{\pi }{2}$, so the option D is correct.
The wrong option is option B, so the answer for this problem is option B.
Note: The students are advised to remember the formula of the relative velocity and also the diagram of the velocity of the particle A and particle B should be drawn very carefully as the answer is very dependent on the diagram.
Formula used:
The relative velocity of the two particles is given by,
$ \Rightarrow {v_B} - {v_A}$
Where the velocity of particle B is ${v_B}$ and the velocity of particle A is${v_A}$.
Complete step by step solution:
In this problem it is given that a particle ‘A’ is projected with velocity $4\sqrt 2 m{s^{ - 1}}$ making an angle $45^\circ $ to the horizontal. Particle B is projected at $5m{s^{ - 1}}$ an angle $\theta = {\tan ^{ - 1}}\left( {\dfrac{1}{3}} \right)$ to y axis in y-z plane then we need to find the velocity of B wrt A.
According to the condition the figure will be.

The velocity of particle A is ${v_A} = 4\hat i + 4\hat k$ and the velocity of particle B is equal to ${v_B} = 3\hat j + 4\hat k$.
The relative velocity of the particle B with respect to particle A is equal to,
$ \Rightarrow {v_B} - {v_A} = \left( {3\hat j + 4\hat k} \right) - \left( {4\hat i + 4\hat k} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow {v_B} - {v_A} = 3\hat j + 4\hat k - 4\hat i - 4\hat k$
$ \Rightarrow {v_B} - {v_A} = 3\hat j + 4\hat k - 4\hat i - 4\hat k$
$ \Rightarrow {v_B} - {v_A} = 3\hat j - 4\hat i$
The magnitude of the velocity is equal to,
$ \Rightarrow {v_B} - {v_A} = \sqrt {{3^2} + {4^2}} $
$ \Rightarrow {v_B} - {v_A} = \sqrt {9 + 16} $
$ \Rightarrow {v_B} - {v_A} = \sqrt {25} $
$ \Rightarrow {v_B} - {v_A} = 5m{s^{ - 1}}$
Which means option A is correct. The magnitude of the acceleration will not change with time and therefore the option B is wrong.
The relative velocity is ${v_B} - {v_A} = 3\hat j - 4\hat i$ which means it is in the x-y plane, the option C is also correct. The angle of the initially equal to,
$ \Rightarrow \theta = {\tan ^{ - 1}}\left( { - \dfrac{4}{3}} \right)$
As the angle is negative and therefore we add $\dfrac{\pi }{2}$ so the angle becomes $\theta + \dfrac{\pi }{2}$, so the option D is correct.
The wrong option is option B, so the answer for this problem is option B.
Note: The students are advised to remember the formula of the relative velocity and also the diagram of the velocity of the particle A and particle B should be drawn very carefully as the answer is very dependent on the diagram.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




