
What is the TCA cycle? Describe its different steps
Answer
591.3k+ views
Hint: Various biochemical processes and cycles are carried out within the body of organisms. The TCA cycle is one such cycle. TCA stands for the chemical compound that is the first product of this reaction. It is used to generate the energy currency of the cells.
Complete answer:
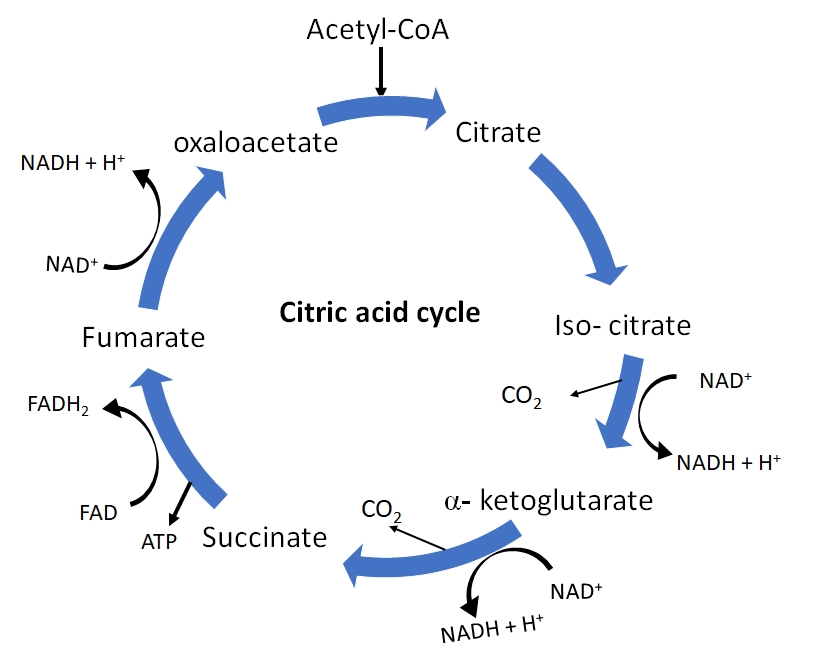
TCA cycle or the tricarboxylic acid cycle is also known as the citric acid cycle (CAC) or the Krebs cycle is a series of chemical reactions used which occurs within all aerobic organisms to release stored energy through the oxidation of acetyl $\text{CoA}$ which is derived from carbohydrates, fats, and proteins.
There are 8 steps in the TCA cycle. They are:
- Step 1: Acetyl $\text{CoA}$ joins with a four- carbon molecule, oxaloacetate, releasing $\text{CoA}$ group and forming a six- carbon compound called citric acid.
- Step 2: Citric acid is converted into its isomeric form, isocitric acid, or isocitrate. It is actually a two- step process, first involving the removal and then the addition of a water molecule. Due to this, sometimes the TCA cycle is said to have 9 steps, however, this whole reaction is considered to be one step.
- Step 3: Isocitrate is oxidized to release a molecule of carbon dioxide, leaving a five- carbon α- ketoglutarate molecule. During this step, $\text{NAD}^+$ is reduced to form $\text{NADH}$. The enzyme isocitrate dehydrogenase catalyzes this reaction is very important in rate determination of the cycle.
- Step 4: Here α- ketoglutarate is oxidized, reducing $\text{NAD}^+$ to $\text{NADH}$ and releasing a molecule of carbon dioxide. The remaining four- carbon molecule picks up the Coenzyme A, forming an unstable succinyl $\text{CoA}$. This step is also a rate- determining step.
- Step 5: The $\text{CoA}$ of succinyl $\text{CoA}$ is replaced by a phosphate group, which is later transferred to $\text{ADP}$ to make $\text{ATP}$. In some cells, guanosine diphosphate ($\text{GDP}$)is used, forming $\text{GTP}$. Four- carbon succinate is produced as a product of this reaction.
- Step 6: Succinate is oxidized, forming another four- carbon molecule fumarate. Two hydrogen atoms are transferred to $\text{FAD}$ producing $\text{FADH}_2$.
- Step 7: Water is added to the four- carbon molecule fumarate, converting it into malate.
- Step 8: Oxaloacetate is regenerated by oxidation of malate. Another molecule of $\text{NAD}^+$ is reduced to $\text{NADH}$ in the process.
One TCA cycle "turn" yields 1 $\text{GTP}$, 3 $\text{NADH}$, 1 $FAD{ H }_{ 2 }$ , 2 $CO_{ 2 }$ and based on the oxidation pathway they can produce 15 to 18ATP and since one glucose yields 2 Acetyl $\text{CoA}$, per glucose 30 to 38ATP are obtained.
Note: The Acetyl $\text{CoA}$ that is required for this reaction can be obtained from the breakdown of either glucose, fats, or proteins and then enter this common pathway for the synthesis of ATP. Apart from all these products, the TCA cycle intermediate products are used for biosynthesis of other important compounds like amino acids, nitrogenous bases, etc.
Complete answer:
TCA cycle or the tricarboxylic acid cycle is also known as the citric acid cycle (CAC) or the Krebs cycle is a series of chemical reactions used which occurs within all aerobic organisms to release stored energy through the oxidation of acetyl $\text{CoA}$ which is derived from carbohydrates, fats, and proteins.
There are 8 steps in the TCA cycle. They are:
- Step 1: Acetyl $\text{CoA}$ joins with a four- carbon molecule, oxaloacetate, releasing $\text{CoA}$ group and forming a six- carbon compound called citric acid.
- Step 2: Citric acid is converted into its isomeric form, isocitric acid, or isocitrate. It is actually a two- step process, first involving the removal and then the addition of a water molecule. Due to this, sometimes the TCA cycle is said to have 9 steps, however, this whole reaction is considered to be one step.
- Step 3: Isocitrate is oxidized to release a molecule of carbon dioxide, leaving a five- carbon α- ketoglutarate molecule. During this step, $\text{NAD}^+$ is reduced to form $\text{NADH}$. The enzyme isocitrate dehydrogenase catalyzes this reaction is very important in rate determination of the cycle.
- Step 4: Here α- ketoglutarate is oxidized, reducing $\text{NAD}^+$ to $\text{NADH}$ and releasing a molecule of carbon dioxide. The remaining four- carbon molecule picks up the Coenzyme A, forming an unstable succinyl $\text{CoA}$. This step is also a rate- determining step.
- Step 5: The $\text{CoA}$ of succinyl $\text{CoA}$ is replaced by a phosphate group, which is later transferred to $\text{ADP}$ to make $\text{ATP}$. In some cells, guanosine diphosphate ($\text{GDP}$)is used, forming $\text{GTP}$. Four- carbon succinate is produced as a product of this reaction.
- Step 6: Succinate is oxidized, forming another four- carbon molecule fumarate. Two hydrogen atoms are transferred to $\text{FAD}$ producing $\text{FADH}_2$.
- Step 7: Water is added to the four- carbon molecule fumarate, converting it into malate.
- Step 8: Oxaloacetate is regenerated by oxidation of malate. Another molecule of $\text{NAD}^+$ is reduced to $\text{NADH}$ in the process.
One TCA cycle "turn" yields 1 $\text{GTP}$, 3 $\text{NADH}$, 1 $FAD{ H }_{ 2 }$ , 2 $CO_{ 2 }$ and based on the oxidation pathway they can produce 15 to 18ATP and since one glucose yields 2 Acetyl $\text{CoA}$, per glucose 30 to 38ATP are obtained.

Note: The Acetyl $\text{CoA}$ that is required for this reaction can be obtained from the breakdown of either glucose, fats, or proteins and then enter this common pathway for the synthesis of ATP. Apart from all these products, the TCA cycle intermediate products are used for biosynthesis of other important compounds like amino acids, nitrogenous bases, etc.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




