
Tertiary alkyl halides are practically inert to substitution by ${{S}_{N}}2$ mechanism because:
(A) insolubility
(B) instability
(C) steric hindrance
(D) inductive effect
Answer
591.3k+ views
Hint: Recall substitution by ${{S}_{N}}2$ mechanism. You will understand the conditions needed for the reaction to take place. As there are no ions involved in this mechanism, less branching is preferred for the reaction to take place.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us draw the structure of a simple tertiary alkyl halide to form a clear idea about the reactant.
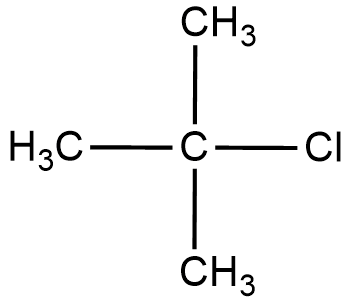
We will now define the ${{S}_{N}}2$ mechanism to understand the reaction.
-${{S}_{N}}2$ stands for Substitution Nucleophilic bimolecular.
-It is a type of reaction mechanism commonly found in organic chemistry. In this mechanism one bond is broken and one bond is formed at the same time.
-Since two reacting molecules are involved in the rate determining step , it is called ${{S}_{N}}2$.
Factors affecting the rate of reaction are:
- Substrate
- Nucleophile
- Solvent
- Leaving group
In this question we will discuss only the first factor as the remaining three are not applicable.
-The substrate plays an important role in the reaction as the nucleophile attacks the substrate from behind. At the same time the leaving group has to break the bond.
-The hindrance caused by surrounding groups reduces the rate of the reaction. This is called steric hindrance.
In tertiary alkyl halide, there are 3 $-C{{H}_{3}}$ groups attached to the central carbon hence increasing the hindrance.
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note: Do not get confused between steric hindrance and instability. The reason why tertiary alkyl halides are inert to ${{S}_{N}}2$ mechanism is because of hindrance offered by attached groups. It is due to this reason that the intermediate is highly unstable and does not yield any product.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us draw the structure of a simple tertiary alkyl halide to form a clear idea about the reactant.

We will now define the ${{S}_{N}}2$ mechanism to understand the reaction.
-${{S}_{N}}2$ stands for Substitution Nucleophilic bimolecular.
-It is a type of reaction mechanism commonly found in organic chemistry. In this mechanism one bond is broken and one bond is formed at the same time.
-Since two reacting molecules are involved in the rate determining step , it is called ${{S}_{N}}2$.
Factors affecting the rate of reaction are:
- Substrate
- Nucleophile
- Solvent
- Leaving group
In this question we will discuss only the first factor as the remaining three are not applicable.
-The substrate plays an important role in the reaction as the nucleophile attacks the substrate from behind. At the same time the leaving group has to break the bond.
-The hindrance caused by surrounding groups reduces the rate of the reaction. This is called steric hindrance.
In tertiary alkyl halide, there are 3 $-C{{H}_{3}}$ groups attached to the central carbon hence increasing the hindrance.
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note: Do not get confused between steric hindrance and instability. The reason why tertiary alkyl halides are inert to ${{S}_{N}}2$ mechanism is because of hindrance offered by attached groups. It is due to this reason that the intermediate is highly unstable and does not yield any product.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




