
The acidity of ortho-nitrophenol is -----that of the ortho- methoxyphenol.
(A) More than
(B) Similar
(C) Less than
(D) None of these
Answer
565.5k+ views
Hint: Electron withdrawing group has \[\text{-I}\](negative inductive effect) or negative mesomeric effect while electron donating group has \[\text{+I}\](positive inductive effect) or positive mesomeric effect.
Acidic strength of a compound depends on the stability of the conjugate base.
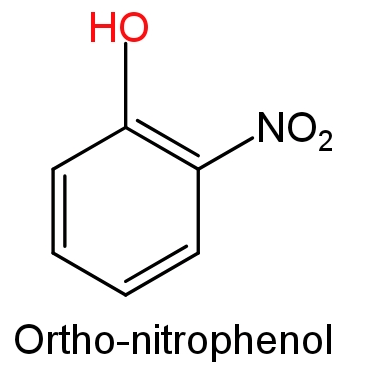
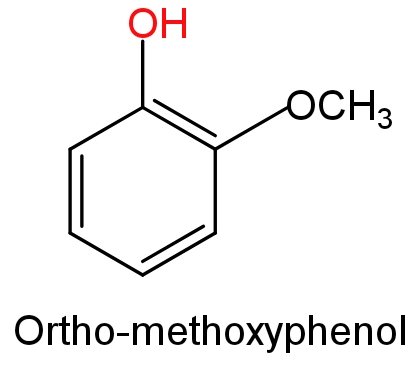
In ortho-nitrophenol a nitro$\text{(-N}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\text{)}$group is attached to the ortho position (1, 2 –position) of phenol, while in ortho-methoxyphenol a methoxy$\text{(-OC}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\text{)}$group is attached to the ortho position (1, 2 –position) of phenol.
Complete answer:
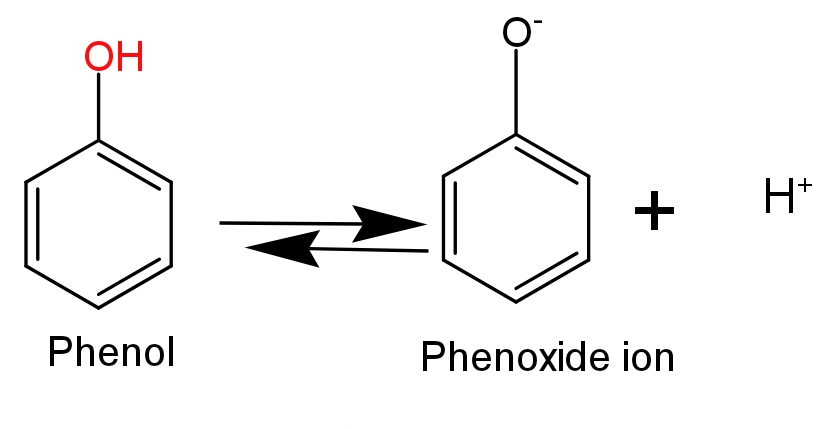
The stability of phenoxide ion determines the acidic nature of the compounds.
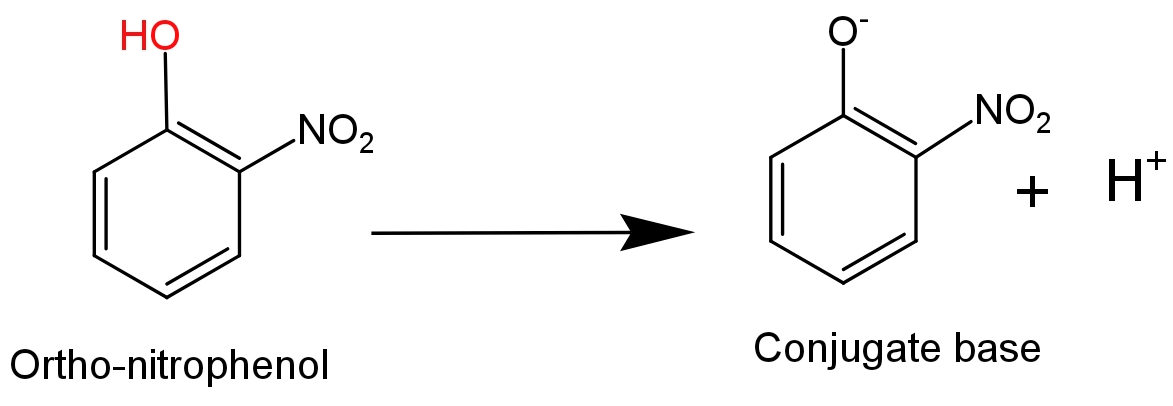
-Ortho-nitrophenol is more acidic in nature because, in ortho-nitrophenol an electron withdrawing nitro$\text{(-N}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\text{)}$group is attached to the ortho position which helps in stabilising the negative charge on the oxygen atom of phenoxide ion. Hence, due to the stabilization of conjugate base of phenol acidic nature of phenol will increase
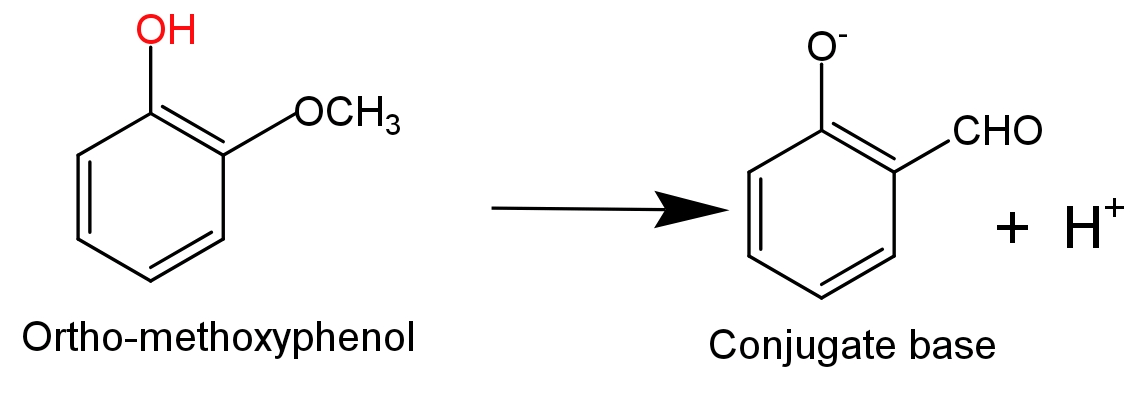
- While in case of ortho-methoxyphenol an electron donating methoxy$\text{(-OC}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\text{)}$group is attached to the ortho position which destabilise the phenoxide ion by increasing the charge density on the oxygen atom of phenoxide ion. So, it will decrease the acidity of phenol.
Hence, option (A) will be the correct answer.
Note:
Inductive effect $\text{(I-effect)}$ is the permanent effect on sigma electrons. It involves the partial electron displacement along the chain of saturated carbon atoms due to the presence of covalent bonds at one end of the chain. While in mesomeric effect ($\text{(M-effect)}$involves the complete transfer of a pie- electron or lone pair of electrons to the adjacent atom or covalent bond.
Acidic strength of a compound depends on the stability of the conjugate base.
In ortho-nitrophenol a nitro$\text{(-N}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\text{)}$group is attached to the ortho position (1, 2 –position) of phenol, while in ortho-methoxyphenol a methoxy$\text{(-OC}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\text{)}$group is attached to the ortho position (1, 2 –position) of phenol.


Complete answer:
The stability of phenoxide ion determines the acidic nature of the compounds.

-Ortho-nitrophenol is more acidic in nature because, in ortho-nitrophenol an electron withdrawing nitro$\text{(-N}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\text{)}$group is attached to the ortho position which helps in stabilising the negative charge on the oxygen atom of phenoxide ion. Hence, due to the stabilization of conjugate base of phenol acidic nature of phenol will increase

- While in case of ortho-methoxyphenol an electron donating methoxy$\text{(-OC}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\text{)}$group is attached to the ortho position which destabilise the phenoxide ion by increasing the charge density on the oxygen atom of phenoxide ion. So, it will decrease the acidity of phenol.

Hence, option (A) will be the correct answer.
Note:
Inductive effect $\text{(I-effect)}$ is the permanent effect on sigma electrons. It involves the partial electron displacement along the chain of saturated carbon atoms due to the presence of covalent bonds at one end of the chain. While in mesomeric effect ($\text{(M-effect)}$involves the complete transfer of a pie- electron or lone pair of electrons to the adjacent atom or covalent bond.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




