
The alkene that exhibits geometrical isomerism is:
A.propane
B.2-methylpropene
C.2-butene
D.2-methyl-2-butene
Answer
578.1k+ views
Hint: To answer this question, you should recall the concept of geometrical isomerism. Geometrical isomerism is defined as the type of stereoisomerism having the same molecular formula and same structure but differ in the relative arrangement of atoms.
Complete step by step solution:
We know that isomers are defined as the molecules with the same molecular formula but possess a different arrangement of the atoms in space or different connectivity of atoms. The phenomenon in which the molecules in which the atoms that form the isomers are connected differently is known as structural isomerism. The phenomenon in which the connectivity of atoms is the same in isomers but a different spatial arrangement is a stereoisomerism.
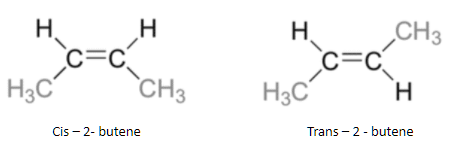
2-Butene can exist as cis and trans isomers because of the double bond that leads to the restricted rotation. The cis-isomer has the two methyl groups on the same side and the trans-isomer has the two methyl groups on opposite sides.
2-methyl propene and 2-methyl-2-butene contain a double bond but the groups attached to one of the C of the double bond are the same. Hence, all the geometric isomers of these respective compounds will be identical.
Hence, it can be concluded that the correct option is option C.
Note: Geometric isomerism is one of the forms of stereoisomerism. The key point in geometrical isomers is the restricted rotation of a bond present somewhere in a molecule. At the most basic level of organic chemistry, carbon-carbon double bond is one of the examples leading to a restricted rotation.
Complete step by step solution:
We know that isomers are defined as the molecules with the same molecular formula but possess a different arrangement of the atoms in space or different connectivity of atoms. The phenomenon in which the molecules in which the atoms that form the isomers are connected differently is known as structural isomerism. The phenomenon in which the connectivity of atoms is the same in isomers but a different spatial arrangement is a stereoisomerism.
2-Butene can exist as cis and trans isomers because of the double bond that leads to the restricted rotation. The cis-isomer has the two methyl groups on the same side and the trans-isomer has the two methyl groups on opposite sides.
2-methyl propene and 2-methyl-2-butene contain a double bond but the groups attached to one of the C of the double bond are the same. Hence, all the geometric isomers of these respective compounds will be identical.
Hence, it can be concluded that the correct option is option C.

Note: Geometric isomerism is one of the forms of stereoisomerism. The key point in geometrical isomers is the restricted rotation of a bond present somewhere in a molecule. At the most basic level of organic chemistry, carbon-carbon double bond is one of the examples leading to a restricted rotation.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




