
The basicity of phosphoric acid is:-
(a)- 1
(b)- 2
(c)- 3
(d)- 4
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: For checking the basicity of a compound the structure is drawn. The type of bonds the central metal atom forms and the group joined to the metal atom is to be found out. Electronegativity of the atom is also checked.
Complete step by step answer:
When oxoacids of phosphorus are formed, it shows basic character.
This basic character is because of the presence of an OH group present in the compound.
The OH group present is ionizable because the H atom is attached to a highly electronegative atom O (oxygen). When dissolved in water the hydrogen ions get separated which tells the basicity of the compound.
So, to check the basicity of the compound we have to count the number of OH group present which are directly attached to the central atom
Phosphoric acid has a formula \[{{H}_{3}}P{{O}_{4}}\].
In this, the phosphorus has a +5 oxidation state.
Let us now see the structure of the phosphoric acid \[{{H}_{3}}P{{O}_{4}}\].
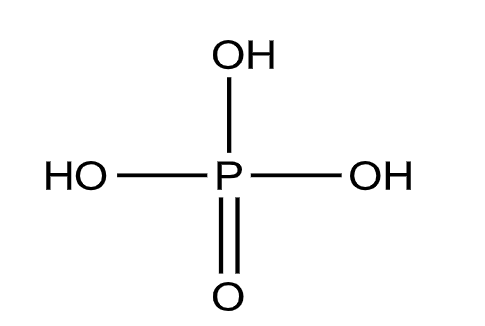
From the structure, we can see that there are three P-OH bonds and one P=O bond.
So, due to the presence of three P-OH bonds, it can give 3 hydrogen ions when dissolved in water.
Hence the correct option is (c)- 3.
Additional information:
The basicity of some oxoacids of phosphorus are:
The phosphinic acid (\[{{H}_{3}}P{{O}_{2}}\]) has basicity 1
The hypophosphoric acid (\[{{H}_{4}}{{P}_{2}}{{O}_{6}}\]) has basicity 4.
The peroxodiphosphoric acid (\[{{H}_{4}}{{P}_{2}}{{O}_{8}}\]) has basicity 4.
Note:
The chemical properties of the members of a homologous series similar though the first member may vary considerably from the rest of the members. The successive members of a homologous series differ by a \[C{{H}_{2}}\] group or by 14 mass units.
Complete step by step answer:
When oxoacids of phosphorus are formed, it shows basic character.
This basic character is because of the presence of an OH group present in the compound.
The OH group present is ionizable because the H atom is attached to a highly electronegative atom O (oxygen). When dissolved in water the hydrogen ions get separated which tells the basicity of the compound.
So, to check the basicity of the compound we have to count the number of OH group present which are directly attached to the central atom
Phosphoric acid has a formula \[{{H}_{3}}P{{O}_{4}}\].
In this, the phosphorus has a +5 oxidation state.
Let us now see the structure of the phosphoric acid \[{{H}_{3}}P{{O}_{4}}\].

From the structure, we can see that there are three P-OH bonds and one P=O bond.
So, due to the presence of three P-OH bonds, it can give 3 hydrogen ions when dissolved in water.
Hence the correct option is (c)- 3.
Additional information:
The basicity of some oxoacids of phosphorus are:
The phosphinic acid (\[{{H}_{3}}P{{O}_{2}}\]) has basicity 1
The hypophosphoric acid (\[{{H}_{4}}{{P}_{2}}{{O}_{6}}\]) has basicity 4.
The peroxodiphosphoric acid (\[{{H}_{4}}{{P}_{2}}{{O}_{8}}\]) has basicity 4.
Note:
The chemical properties of the members of a homologous series similar though the first member may vary considerably from the rest of the members. The successive members of a homologous series differ by a \[C{{H}_{2}}\] group or by 14 mass units.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




