
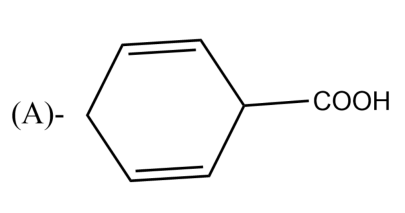
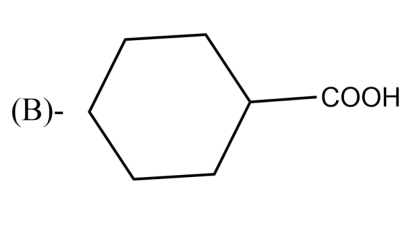
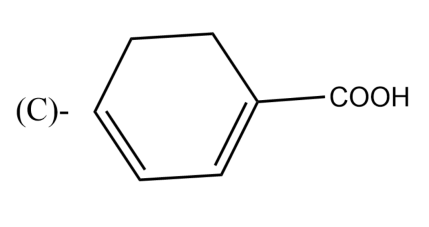
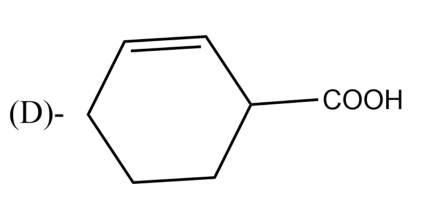
The Birch reduction of benzoic acid gives:




Answer
588k+ views
Hint: The Birch reduction is an organic reaction which converts arenes into cyclohexadiene. Arenes are the aromatic hydrocarbons.
Complete step by step answer:
-Birch reduction is named after the Australian chemist Arthur Birch. In this reaction, reduction of aromatic rings occurs in liquid ammonia with sodium, lithium or potassium and alcohol like ethanol or tert-butanol.
-Birch reduction mechanism starts with the formation of the radical anion by the addition of solvated electrons to the aromatic ring. The alcohol gives a proton to the radical anion and to the next to the last carbocation.
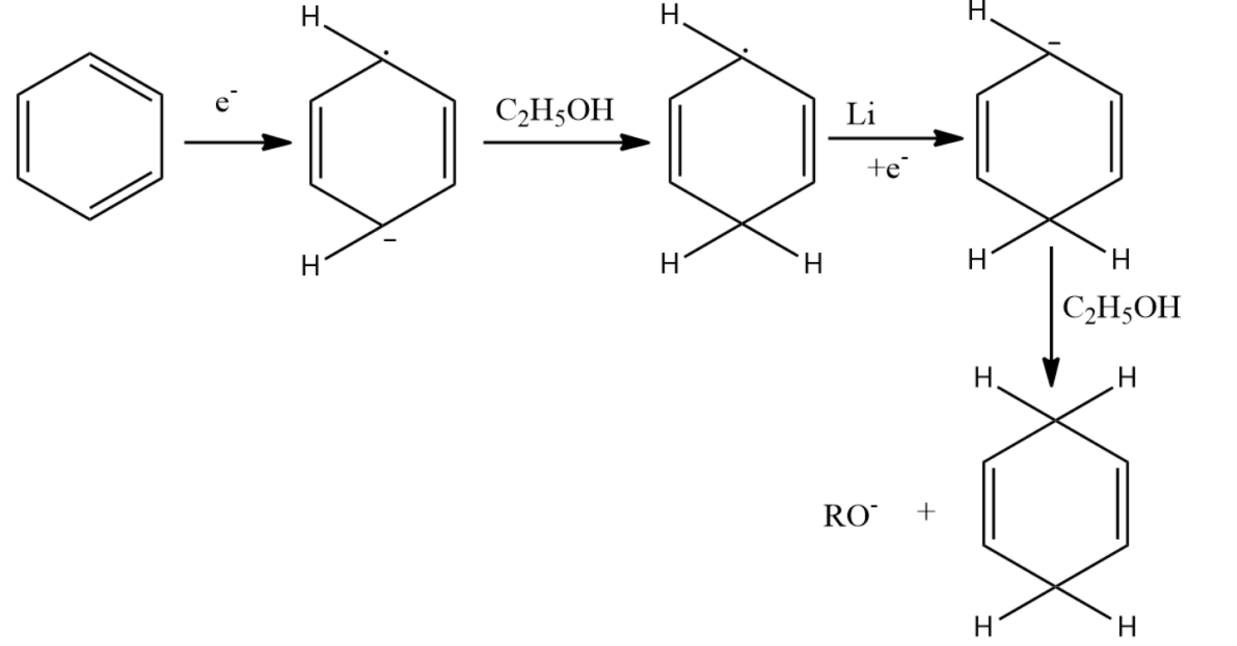
-Birch reduction offers a substitution to arene at 1,4-cyclohexadiene.
-The presence of electron-withdrawing groups causes variations in the Birch reduction mechanisms. The reaction of the different electron-withdrawing group gives different effects. For example, the reaction of benzoic acid on benzene leads to the formation of 2,5-cyclohexadiene carboxylic acid, which can be rationalized on the basis of the carboxylic acid stabilizing an adjacent anion.
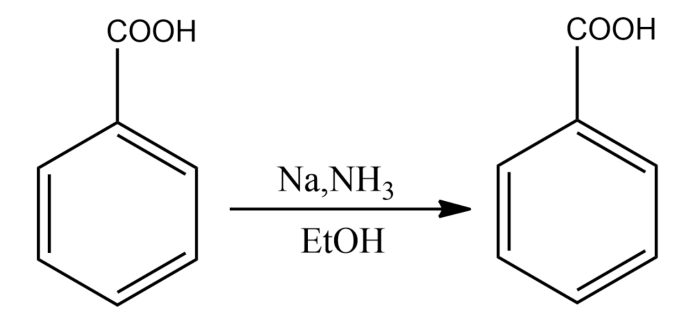
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note: Birch reduction has the ability to selectively reduce certain bonds in a molecule. Birch reduction is sometimes the only key for the reduction of several naturally occurring compounds. This reaction is also very important for the reduction of aromatic and non-aromatic moieties. The selective reduction of aromatic and non-aromatic moieties makes it useful for multi-step total synthesis processes. When electron-withdrawing groups are used, the protonation is more favoured for the para position. When electron-donating groups are used, protonation is more favoured for ortho or meta positions. The structure of the product formed in the Birch reduction is determined by the position where the protonation has occurred.
Complete step by step answer:
-Birch reduction is named after the Australian chemist Arthur Birch. In this reaction, reduction of aromatic rings occurs in liquid ammonia with sodium, lithium or potassium and alcohol like ethanol or tert-butanol.
-Birch reduction mechanism starts with the formation of the radical anion by the addition of solvated electrons to the aromatic ring. The alcohol gives a proton to the radical anion and to the next to the last carbocation.

-Birch reduction offers a substitution to arene at 1,4-cyclohexadiene.
-The presence of electron-withdrawing groups causes variations in the Birch reduction mechanisms. The reaction of the different electron-withdrawing group gives different effects. For example, the reaction of benzoic acid on benzene leads to the formation of 2,5-cyclohexadiene carboxylic acid, which can be rationalized on the basis of the carboxylic acid stabilizing an adjacent anion.

So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note: Birch reduction has the ability to selectively reduce certain bonds in a molecule. Birch reduction is sometimes the only key for the reduction of several naturally occurring compounds. This reaction is also very important for the reduction of aromatic and non-aromatic moieties. The selective reduction of aromatic and non-aromatic moieties makes it useful for multi-step total synthesis processes. When electron-withdrawing groups are used, the protonation is more favoured for the para position. When electron-donating groups are used, protonation is more favoured for ortho or meta positions. The structure of the product formed in the Birch reduction is determined by the position where the protonation has occurred.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




