
The central cavity of sponges, the paragastric cavity, is made of ____ cells.
A. Choanocyte
B. Chromocyte
C. Amoebocyte
D. Pinacocyte
Answer
573.3k+ views
Hint: The perigastric cavity is the void within the stomach which is the sponge cavity or one of the sponge cavities through which the radial canals expand and which pass through the cloaca externally. They are multicellular organisms with bodies full of pores and channels that allow the movement of water through them.
Complete answer:
Any type of cell, such as a red blood cell, that encloses a pigment is known as a chromocyte.
An amebocyte is a dense cell in the body of invertebrates that counts sponges, echinoderms, mollusks, tunicates, and several chelicerates (moving like an ameba).
Pinacocytes are slim cells found on the outermost layer of a sponge (phylum Porifera).
The core gastric cavity of sponges is the spongocoel. The paragastric cavity of the sponges is often pointed to as the spongocoel. It is largely lined with flagella by choanocytes that are specialized digestion cells. Via Ostia, water joins the spongocoel and exits it through the osculum.
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
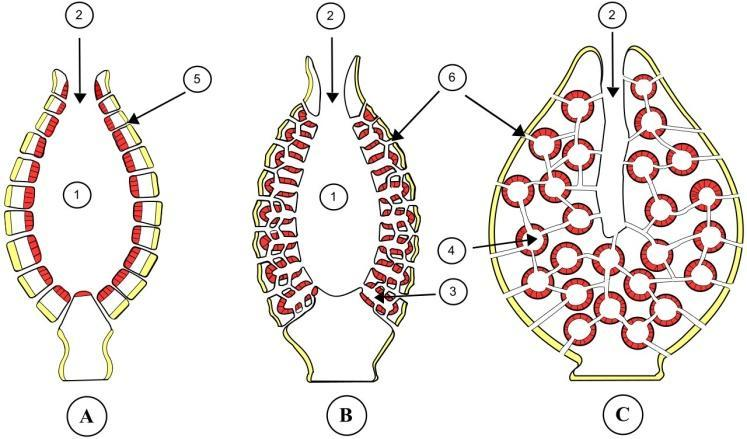
Note:
Cells that line the core of sponges having a central flagellum, or cilium, enclosed by a collar of microvilli joined by a thin membrane, are often known as collar cells. The choanoderm, a sort of cell layer set up in sponges, is prepared up of them. The cell has the nearest similarity to the choanoflagellates, the animal kingdom's (metazoans) closest related single-celled protists. Regularly, the flagellar beat, causing a water rush through the microvilli that can then separate nutrients from the water drawn from the sponge collar.
Complete answer:
Any type of cell, such as a red blood cell, that encloses a pigment is known as a chromocyte.
An amebocyte is a dense cell in the body of invertebrates that counts sponges, echinoderms, mollusks, tunicates, and several chelicerates (moving like an ameba).
Pinacocytes are slim cells found on the outermost layer of a sponge (phylum Porifera).
The core gastric cavity of sponges is the spongocoel. The paragastric cavity of the sponges is often pointed to as the spongocoel. It is largely lined with flagella by choanocytes that are specialized digestion cells. Via Ostia, water joins the spongocoel and exits it through the osculum.
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.

Note:
Cells that line the core of sponges having a central flagellum, or cilium, enclosed by a collar of microvilli joined by a thin membrane, are often known as collar cells. The choanoderm, a sort of cell layer set up in sponges, is prepared up of them. The cell has the nearest similarity to the choanoflagellates, the animal kingdom's (metazoans) closest related single-celled protists. Regularly, the flagellar beat, causing a water rush through the microvilli that can then separate nutrients from the water drawn from the sponge collar.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




