
The distance between the chords of contact of tangents to the circle ${{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}{\text{ + }}{{\text{y}}^{\text{2}}}{\text{ + 2gx + 2fy + c = 0}}$ from the origin and from the point (g,f) is-
Answer
612.9k+ views
Hint: To solve this question, we use the basic theory of circles. As given circle having equation: ${{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}{\text{ + }}{{\text{y}}^{\text{2}}}{\text{ + 2gx + 2fy + c = 0}}$. First, we write the equation of tangent and chord to this circle and then after the tangent passes through origin, we put (0, 0) in this.
Complete step-by-step answer:
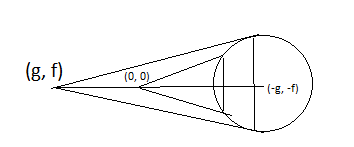
given equation of circle,
${{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}{\text{ + }}{{\text{y}}^{\text{2}}}{\text{ + 2gx + 2fy + c = 0}}$.
Tangent to this circle at (p,q)
⇒xp+yq+g(x+p)+f(y+q)+c=0 …….... (1)
equations of chord of contact of tangents from origin (0,0) and point (g,f) given circle are,
⇒x(0)+y(0)+g(x+0)+f(y+0)+c=0
⇒gx+fy+c=0 ………... (2)
⇒xg+yf+g(x+g)+f(y+f)+c=0
⇒gx+fy+$\dfrac{{\text{1}}}{{\text{2}}}\left( {{{\text{g}}^{\text{2}}}{\text{ + }}{{\text{f}}^{\text{2}}}{\text{ + c}}} \right)$=0 ………. (3)
From (2) and (3) it's clear that equations are parallel.
Distance between these chords is given by,
= $\dfrac{{\dfrac{{\text{1}}}{{\text{2}}}\left( {{{\text{g}}^{\text{2}}}{\text{ + }}{{\text{f}}^{\text{2}}}{\text{ + c}}} \right){\text{ - c}}}}{{\sqrt {{{\text{g}}^{\text{2}}}{\text{ + }}{{\text{f}}^{\text{2}}}} }}$
= $\dfrac{{\left( {{{\text{g}}^{\text{2}}}{\text{ + }}{{\text{f}}^{\text{2}}}{\text{ + c}}} \right)}}{{2\sqrt {{{\text{g}}^{\text{2}}}{\text{ + }}{{\text{f}}^{\text{2}}}} }}$is the distance.
Therefore, The distance between the chords of contact of tangents to the circle ${{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}{\text{ + }}{{\text{y}}^{\text{2}}}{\text{ + 2gx + 2fy + c = 0}}$ from the origin and from the point (g,f) is $\dfrac{{\left( {{{\text{g}}^{\text{2}}}{\text{ + }}{{\text{f}}^{\text{2}}}{\text{ + c}}} \right)}}{{2\sqrt {{{\text{g}}^{\text{2}}}{\text{ + }}{{\text{f}}^{\text{2}}}} }}$.
Note- Here are some basic properties of circles. For example, the outer line of a circle is at equidistant from the center. The diameter of the circle divides it into two equal parts. Circles which have equal radii are congruent to each other.
Complete step-by-step answer:

given equation of circle,
${{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}{\text{ + }}{{\text{y}}^{\text{2}}}{\text{ + 2gx + 2fy + c = 0}}$.
Tangent to this circle at (p,q)
⇒xp+yq+g(x+p)+f(y+q)+c=0 …….... (1)
equations of chord of contact of tangents from origin (0,0) and point (g,f) given circle are,
⇒x(0)+y(0)+g(x+0)+f(y+0)+c=0
⇒gx+fy+c=0 ………... (2)
⇒xg+yf+g(x+g)+f(y+f)+c=0
⇒gx+fy+$\dfrac{{\text{1}}}{{\text{2}}}\left( {{{\text{g}}^{\text{2}}}{\text{ + }}{{\text{f}}^{\text{2}}}{\text{ + c}}} \right)$=0 ………. (3)
From (2) and (3) it's clear that equations are parallel.
Distance between these chords is given by,
= $\dfrac{{\dfrac{{\text{1}}}{{\text{2}}}\left( {{{\text{g}}^{\text{2}}}{\text{ + }}{{\text{f}}^{\text{2}}}{\text{ + c}}} \right){\text{ - c}}}}{{\sqrt {{{\text{g}}^{\text{2}}}{\text{ + }}{{\text{f}}^{\text{2}}}} }}$
= $\dfrac{{\left( {{{\text{g}}^{\text{2}}}{\text{ + }}{{\text{f}}^{\text{2}}}{\text{ + c}}} \right)}}{{2\sqrt {{{\text{g}}^{\text{2}}}{\text{ + }}{{\text{f}}^{\text{2}}}} }}$is the distance.
Therefore, The distance between the chords of contact of tangents to the circle ${{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}{\text{ + }}{{\text{y}}^{\text{2}}}{\text{ + 2gx + 2fy + c = 0}}$ from the origin and from the point (g,f) is $\dfrac{{\left( {{{\text{g}}^{\text{2}}}{\text{ + }}{{\text{f}}^{\text{2}}}{\text{ + c}}} \right)}}{{2\sqrt {{{\text{g}}^{\text{2}}}{\text{ + }}{{\text{f}}^{\text{2}}}} }}$.
Note- Here are some basic properties of circles. For example, the outer line of a circle is at equidistant from the center. The diameter of the circle divides it into two equal parts. Circles which have equal radii are congruent to each other.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




