
The electronic configuration of Cu is:
[A] $\left[ Ne \right]3{{s}^{2}}3{{p}^{6}}3{{d}^{9}}4{{s}^{2}}$
[B] $\left[ Ne \right]3{{s}^{2}}3{{p}^{6}}3{{d}^{10}}4{{s}^{1}}$
[C] $\left[ Ne \right]3{{s}^{2}}3{{p}^{6}}3{{d}^{3}}4{{s}^{2}}4{{p}^{6}}$
[D] $\left[ Ne \right]3{{s}^{2}}3{{p}^{6}}3{{d}^{5}}4{{s}^{2}}4{{p}^{4}}$
Answer
592.8k+ views
Hint: We know that the atomic number of copper is 29 and we can use it to write its electronic configuration. Copper will exist with a full-filled d-orbital, one electron from the last orbital will move to the inner 3d-orbital.
Complete answer: We know that the atomic number of copper is 29 and we can use it to write its electronic configuration. Copper will exist with a full-filled d-orbital, one electron from the last orbital will move to the inner 3d-orbital.
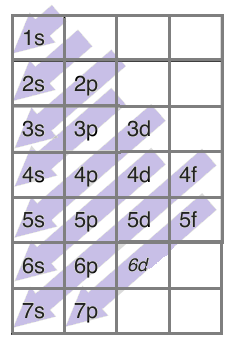
Now, following the above trend, the electronic configuration of copper should be $1{{s}^{2}}2{{s}^{2}}2{{p}^{6}}3{{s}^{2}}3{{p}^{6}}4{{s}^{2}}3{{d}^{9}}$.
But as we know, half-filled and full-filled d-orbitals gain extra stability therefore, one electron from the 4s-orbital moves to the 3d-orbitals and gains more stability. Therefore, the actual configuration of copper is $1{{s}^{2}}2{{s}^{2}}2{{p}^{6}}3{{s}^{2}}3{{p}^{6}}3{{d}^{10}}4{{s}^{1}}$
We can write the electronic configuration for any atom in terms of the nearest noble gas too. We can use argon for writing the configuration of copper but here, in the option we have neon so we will use that.
We know that the atomic number of neon is 10. Therefore, its electronic configuration will be$1{{s}^{2}}2{{s}^{2}}2{{p}^{6}}$. Therefore, in the electronic configuration of copper, in place of $1{{s}^{2}}2{{s}^{2}}2{{p}^{6}}$we can write [Ne].
Therefore, the electronic configuration of copper is $\left[ Ne \right]3{{s}^{2}}3{{p}^{6}}3{{d}^{10}}4{{s}^{1}}$.
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note: Half-filled and full-filled p-orbitals and d-orbitals gain extra stability due to their symmetry. It is also due to the fact that this arrangement helps them gain higher stability due to higher exchange energy. Exchange energy is the energy which is released when two electrons with the same spin exchange their positions in the same energy orbital.
Complete answer: We know that the atomic number of copper is 29 and we can use it to write its electronic configuration. Copper will exist with a full-filled d-orbital, one electron from the last orbital will move to the inner 3d-orbital.

Now, following the above trend, the electronic configuration of copper should be $1{{s}^{2}}2{{s}^{2}}2{{p}^{6}}3{{s}^{2}}3{{p}^{6}}4{{s}^{2}}3{{d}^{9}}$.
But as we know, half-filled and full-filled d-orbitals gain extra stability therefore, one electron from the 4s-orbital moves to the 3d-orbitals and gains more stability. Therefore, the actual configuration of copper is $1{{s}^{2}}2{{s}^{2}}2{{p}^{6}}3{{s}^{2}}3{{p}^{6}}3{{d}^{10}}4{{s}^{1}}$
We can write the electronic configuration for any atom in terms of the nearest noble gas too. We can use argon for writing the configuration of copper but here, in the option we have neon so we will use that.
We know that the atomic number of neon is 10. Therefore, its electronic configuration will be$1{{s}^{2}}2{{s}^{2}}2{{p}^{6}}$. Therefore, in the electronic configuration of copper, in place of $1{{s}^{2}}2{{s}^{2}}2{{p}^{6}}$we can write [Ne].
Therefore, the electronic configuration of copper is $\left[ Ne \right]3{{s}^{2}}3{{p}^{6}}3{{d}^{10}}4{{s}^{1}}$.
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note: Half-filled and full-filled p-orbitals and d-orbitals gain extra stability due to their symmetry. It is also due to the fact that this arrangement helps them gain higher stability due to higher exchange energy. Exchange energy is the energy which is released when two electrons with the same spin exchange their positions in the same energy orbital.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




