
The enthalpy of hydrogenation of cyclohexene is $ - 119.5kJ/mol$ . If enthalpy of hydrogenation of benzene is $ - 208.1kJ/mol$ , find the resonance energy of benzene.
A.$ - 150.4kJ/mol$
B.$ - 208kJ/mol$
C.$ - 508.9kJ/mol$
D.$ - 269.9kJ/mol$
Answer
559.5k+ views
Hint: Resonance energy of a molecule is the theoretical difference between the energies of resonance hybrid and the most stable structure of the molecule. It is a measure of extra stability gained by a molecule as a result of resonance.
Complete step by step answer:
Hydrogenation is a chemical reaction between a molecule and hydrogen. Usually an unsaturated compound reacts with molecular hydrogen in order to saturate the compound. The enthalpy change during this reaction is called enthalpy of hydrogenation.
It is given in the question that the enthalpy of hydrogenation of cyclohexene is $ - 119.5kJ/mol$ . The corresponding reaction is shown below.
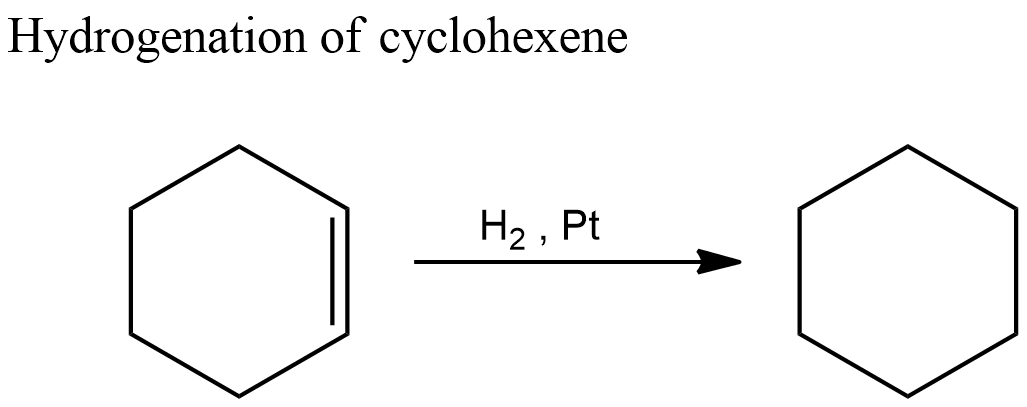
Cyclohexene contains one double bond. Hydrogenation reaction of cyclohexene involves breaking this double bond and adding two hydrogen atoms and thereby saturating the compound. $ - 119.5kJ/mol$ is the energy involved in the breaking of one double bond.
Benzene also contains a cyclohexane ring. But it contains three double bonds. We have seen that energy involved in breaking one double bond and adding two hydrogens is $ - 119.5kJ/mol$ . So, in order to break three double bonds and add six hydrogens, the energy involved will be three times the value of enthalpy of hydrogenation of cyclohexene.
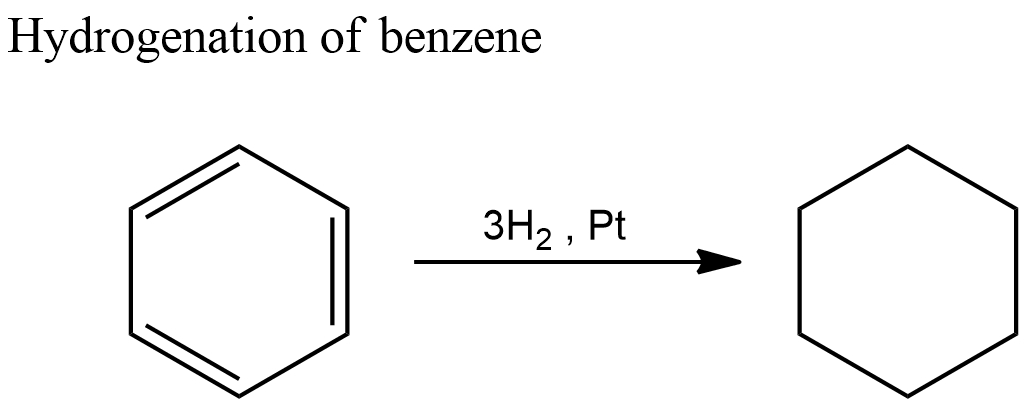
Hence the expected value of enthalpy of hydrogenation of benzene $ = 3 \times \left( { - 119.5} \right) = - 358.5kJ/mol$
But it is given that enthalpy of hydrogenation of benzene is $ - 208.1kJ/mol$ . Hence the resonance energy of benzene will be different between the calculated value and observed value.
Resonance energy of benzene $ = \left( { - 358.5} \right) - \left( { - 208.1} \right) = - 150.4kJ/mol$
Hence resonance energy of benzene is $ - 150.4kJ/mol$ .
Therefore, the correct option is A.
Note:
Observed value of enthalpy of hydrogenation does not match with the calculated value. This is because of the extra stability of benzene gained by resonance. If benzene is just three alkenes formed in a ring, the observed and calculated values may match. But there are different resonance structures possible for benzene which makes it more stable.
Complete step by step answer:
Hydrogenation is a chemical reaction between a molecule and hydrogen. Usually an unsaturated compound reacts with molecular hydrogen in order to saturate the compound. The enthalpy change during this reaction is called enthalpy of hydrogenation.
It is given in the question that the enthalpy of hydrogenation of cyclohexene is $ - 119.5kJ/mol$ . The corresponding reaction is shown below.

Cyclohexene contains one double bond. Hydrogenation reaction of cyclohexene involves breaking this double bond and adding two hydrogen atoms and thereby saturating the compound. $ - 119.5kJ/mol$ is the energy involved in the breaking of one double bond.
Benzene also contains a cyclohexane ring. But it contains three double bonds. We have seen that energy involved in breaking one double bond and adding two hydrogens is $ - 119.5kJ/mol$ . So, in order to break three double bonds and add six hydrogens, the energy involved will be three times the value of enthalpy of hydrogenation of cyclohexene.

Hence the expected value of enthalpy of hydrogenation of benzene $ = 3 \times \left( { - 119.5} \right) = - 358.5kJ/mol$
But it is given that enthalpy of hydrogenation of benzene is $ - 208.1kJ/mol$ . Hence the resonance energy of benzene will be different between the calculated value and observed value.
Resonance energy of benzene $ = \left( { - 358.5} \right) - \left( { - 208.1} \right) = - 150.4kJ/mol$
Hence resonance energy of benzene is $ - 150.4kJ/mol$ .
Therefore, the correct option is A.
Note:
Observed value of enthalpy of hydrogenation does not match with the calculated value. This is because of the extra stability of benzene gained by resonance. If benzene is just three alkenes formed in a ring, the observed and calculated values may match. But there are different resonance structures possible for benzene which makes it more stable.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




