
The formation of a double bond in an oxygen molecules is explained below. Arrange the given points in a sequence order.
(a)2${{p}_{y}}$orbitals of each oxygen atom overlap laterally/sidewise to form a pi-bond.
(b) thus, a double bond between two oxygen atoms in which one ${{p}_{Z}}$-${{p}_{Z}}$sigma bond and ${{p}_{y}}$-${{p}_{y}}$pi bond is formed.
(c) all the three 2p orbitals are perpendicular to each other. Hence, 2${{p}_{Z}}$orbitals of each oxygen atom overlap end to end to form a sigma bond.
(d) the electronic configuration of oxygen is: $\text{1}{{\text{s}}^{2}}\text{ 2}{{\text{s}}^{2}}\text{ 2p}_{x}^{2}\text{ 2p}_{y}^{1}\text{ 2}p_{Z}^{1}$.
(A) c a d b
(B) d c a b
(C) c d b a
(D) c d a b

Answer
569.7k+ views
Hint: Oxygen atom combines with another oxygen atom resulting in the formation of the oxygen molecule that contains the double out of which one is the sigma bond 9 (formed by the overlapping of $p_{z}^{1}$-$p_{z}^{1}$ orbitals) and other bond formed is called as the pi -bond (formed by the overlapping of the${{p}_{Z}}$-${{p}_{Z}}$ orbitals).
Complete step by step answer:
Oxygen is a non-metal belonging to the p-block elements and occupies the 16 th group in the periodic table and have the atomic number as 8 and molecular mass as 16 and has the general electronic configuration as $\text{1}{{\text{s}}^{2}}\text{ 2}{{\text{s}}^{2}}\text{ 2p}_{x}^{2}\text{ 2p}_{y}^{1}\text{ 2}p_{Z}^{1}$ and all the p-orbitals in the oxygen atoms are perpendicular to one another.
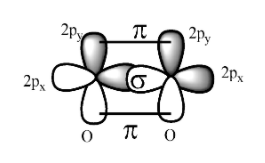
The formation of oxygen molecule is as;

While the formation of double bond between the two oxygen atoms the 2${{p}_{Z}}$ orbital of each atom overlaps with each other to form the bond and the resulting bond is called the sigma bond.
The remain $2p_{y}^{1}$ orbital of each oxygen atom overlap sidewise with each other to form the pi bond and thus, in all the oxygen molecule consists of one sigma bond and one pi bond i.e. there are total number of two bonds in it.
Hence, option (B) is correct.
Note: Sigma bonds are always formed between the s and p-orbitals by their end to end overlapping and the single covalent bonds between the atoms are mostly the covalent bonds. On the other hand, pi bonds are always formed between the p and d -orbitals by their sidewise overlapping and they are mostly found in the unsaturated compounds (i.e. the compound which contains the double bond).
Complete step by step answer:
Oxygen is a non-metal belonging to the p-block elements and occupies the 16 th group in the periodic table and have the atomic number as 8 and molecular mass as 16 and has the general electronic configuration as $\text{1}{{\text{s}}^{2}}\text{ 2}{{\text{s}}^{2}}\text{ 2p}_{x}^{2}\text{ 2p}_{y}^{1}\text{ 2}p_{Z}^{1}$ and all the p-orbitals in the oxygen atoms are perpendicular to one another.
The formation of oxygen molecule is as;

While the formation of double bond between the two oxygen atoms the 2${{p}_{Z}}$ orbital of each atom overlaps with each other to form the bond and the resulting bond is called the sigma bond.
The remain $2p_{y}^{1}$ orbital of each oxygen atom overlap sidewise with each other to form the pi bond and thus, in all the oxygen molecule consists of one sigma bond and one pi bond i.e. there are total number of two bonds in it.
Hence, option (B) is correct.
Note: Sigma bonds are always formed between the s and p-orbitals by their end to end overlapping and the single covalent bonds between the atoms are mostly the covalent bonds. On the other hand, pi bonds are always formed between the p and d -orbitals by their sidewise overlapping and they are mostly found in the unsaturated compounds (i.e. the compound which contains the double bond).
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




