
The genotypic ratio of a monohybrid cross will be
(a) 3:1
(b) 1:1:1
(c) 1:2:1
(d) 2:1
Answer
586.2k+ views
Hint: Monohybrid crosses are between two subjects with homozygous genotype or genotype with completely dominant or recessive traits. Gregor Mendel made monohybrid crosses for seven traits and followed their alternative forms and in all cases, the dominant form appeared in ${{F}_{1}}$ generation, and in ${{F}_{2}}$ both dominant and recessive appeared.
Complete step by step answer:
Monohybrid cross is a cross when only one trait and its two alternative forms are considered during hybridization experiment: The purple- flowered male plant is crossed with the white- flowered female plant. Tall male plant is crossed with the dwarf female plant.
Steps in Monohybrid cross: Trait: Height of plant: TallVs Dwarf Testing of parental plants for purity.
Monohybrid Cross between tall male plant and female dwarf plant and Vice Versa
${{F}_{1}}$ Generation – All plants were tall (Dwarfness disappeared) .
${{F}_{2}}$ Generation – Tall and dwarf plants both appeared in a ratio of approximately 3:1.
${{F}_{3}}$ Generation – Of the tall plants of ${{F}_{2}}$ some plants gave tall and some segregated again into Tall and Dwarf in 3:1 ratio and dwarf plant gave only dwarf plant.
${{F}_{4}}$ Generation – Some tall plants of ${{F}_{3}}$ generation given tall only and some again segregated in 3:1 ratio.
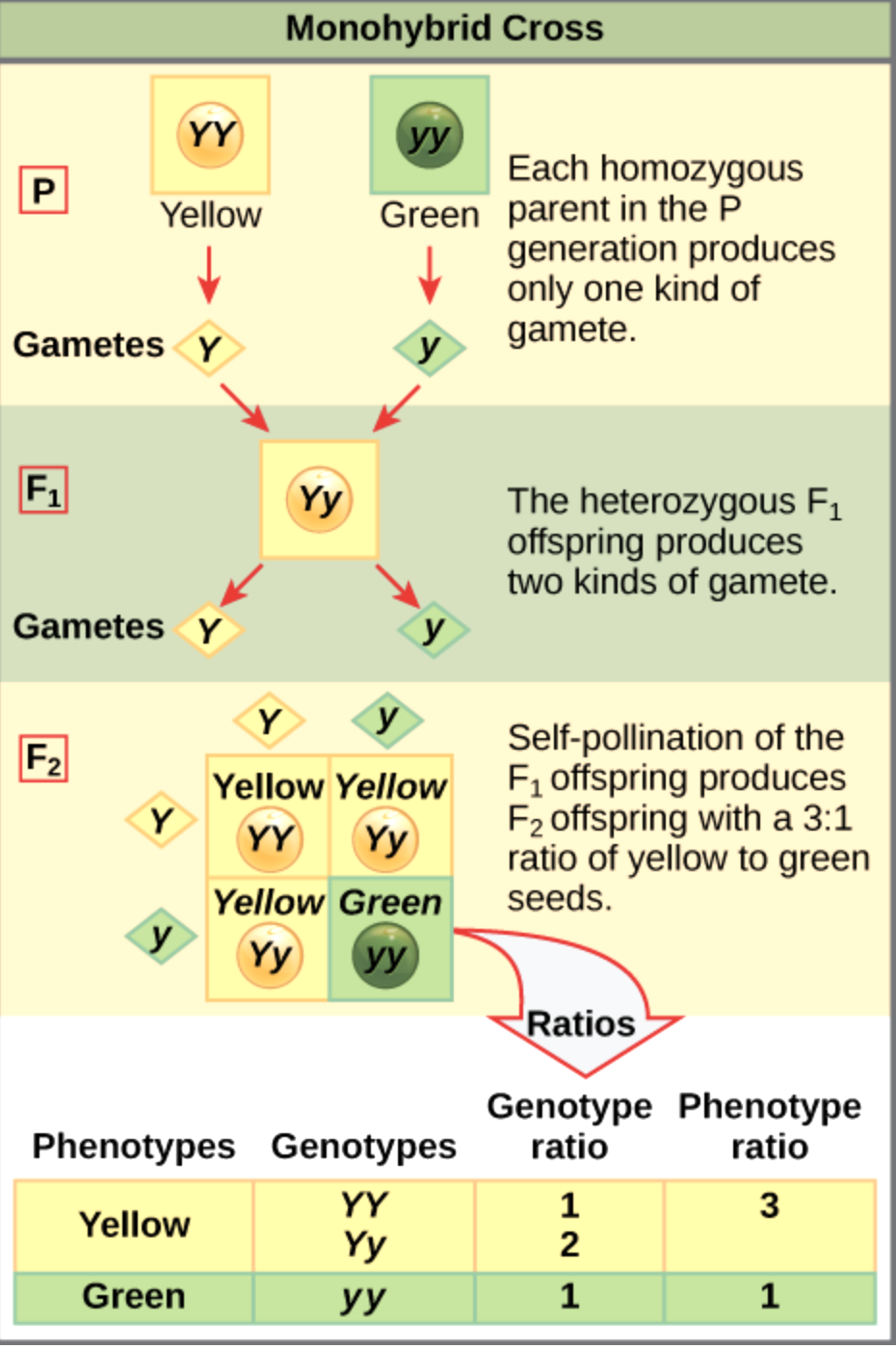
Mendel’s conclusion based on monohybrid cross:
Something is transferred from one generation to another, which carries information for expression of the trait. This something is particulate in nature. Mendel called this particulate thing as Factor or DeterminerMendelian factor is now termed as a gene.
- Genes are present in a linear fashion on specific loci(position) on homologous chromosomes in pairs each gene exist in two forms or alleles and govern the expression of alternative phenotypes (Allelomorphs ) such as Tall and Dwarf
In conclusion, the basic probability as it relates to Mendelian genetics. Mendel’s Law of segregation states that monohybrid cross for genotypic ratio 1:2:1 and phenotypic ratio is 3: 1.
Besides that Mendel’s Law Of Independent Assortment describes the outcome of dihybrid crosses for phenotypic ratio 9:3:3:1.
So, the correct answer is, ‘(c) 1:2:1.’
Note:
- Monohybrid cross is a cross that involves individuals and the examination of a single physical character in the next generation.
- Chi- square test is used to predict the monohybrid and dihybrid crosses by collecting and analysing the square test fitness. The most important step to reach accurate and precise outcomes of monohybrid and dihybrid crosses is to use the same types of objects in probability tests.
Complete step by step answer:
Monohybrid cross is a cross when only one trait and its two alternative forms are considered during hybridization experiment: The purple- flowered male plant is crossed with the white- flowered female plant. Tall male plant is crossed with the dwarf female plant.
Steps in Monohybrid cross: Trait: Height of plant: TallVs Dwarf Testing of parental plants for purity.
Monohybrid Cross between tall male plant and female dwarf plant and Vice Versa
${{F}_{1}}$ Generation – All plants were tall (Dwarfness disappeared) .
${{F}_{2}}$ Generation – Tall and dwarf plants both appeared in a ratio of approximately 3:1.
${{F}_{3}}$ Generation – Of the tall plants of ${{F}_{2}}$ some plants gave tall and some segregated again into Tall and Dwarf in 3:1 ratio and dwarf plant gave only dwarf plant.
${{F}_{4}}$ Generation – Some tall plants of ${{F}_{3}}$ generation given tall only and some again segregated in 3:1 ratio.

Mendel’s conclusion based on monohybrid cross:
Something is transferred from one generation to another, which carries information for expression of the trait. This something is particulate in nature. Mendel called this particulate thing as Factor or DeterminerMendelian factor is now termed as a gene.
- Genes are present in a linear fashion on specific loci(position) on homologous chromosomes in pairs each gene exist in two forms or alleles and govern the expression of alternative phenotypes (Allelomorphs ) such as Tall and Dwarf
In conclusion, the basic probability as it relates to Mendelian genetics. Mendel’s Law of segregation states that monohybrid cross for genotypic ratio 1:2:1 and phenotypic ratio is 3: 1.
Besides that Mendel’s Law Of Independent Assortment describes the outcome of dihybrid crosses for phenotypic ratio 9:3:3:1.
So, the correct answer is, ‘(c) 1:2:1.’
Note:
- Monohybrid cross is a cross that involves individuals and the examination of a single physical character in the next generation.
- Chi- square test is used to predict the monohybrid and dihybrid crosses by collecting and analysing the square test fitness. The most important step to reach accurate and precise outcomes of monohybrid and dihybrid crosses is to use the same types of objects in probability tests.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




