
The graph of the hyperbolic tangent function for all real values is:
A. Strictly increasing
B. Strictly decreasing
C. Strictly increasing in the interval $\left[ {0,\infty } \right)$ and strictly decreasing in the interval $\left( { - \infty ,0} \right]$
D. Strictly increasing in the interval $\left( { - \infty ,0} \right]$ and Strictly decreasing in the interval $\left[ {0,\infty } \right)$
Answer
577.8k+ views
Hint:
We will write the value of $\tanh x$ as the ratio of hyperbolic sine function to hyperbolic cosine function. We will then draw a corresponding graph of the given function. Then, check the nature of the graph, that is where the graph is increasing or where the graph is decreasing.
Complete step by step solution:
The hyperbolic tangent function is the ratio of hyperbolic sine function to hyperbolic cosine function.
That is, $\tanh x = \dfrac{{\sinh x}}{{\cosh x}}$
Now, the value of $\sinh x = \dfrac{{{e^x} - {e^{ - x}}}}{2}$ and the value of $\cosh x = \dfrac{{{e^x} + {e^{ - x}}}}{2}$
Then, we can write the hyperbolic function of tangent as
$\tanh x = \dfrac{{\dfrac{{{e^x} - {e^{ - x}}}}{2}}}{{\dfrac{{{e^x} + {e^{ - x}}}}{2}}} = \dfrac{{{e^x} - {e^{ - x}}}}{{{e^x} + {e^{ - x}}}}$
We will plot the graph of $\tanh x$ to identify the nature of the function.
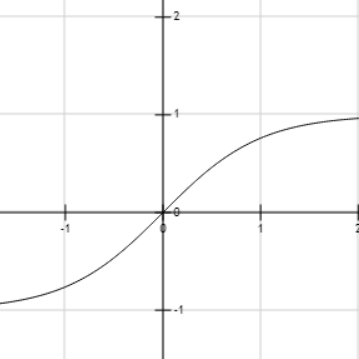
We can see that as the value of $x$ increases, then the value of $\tanh x$ also increases.
Therefore, the graph of the hyperbolic tangent function for all real values is strictly increasing.
Note:
The value of $\tanh x = \dfrac{{{e^x} - {e^{ - x}}}}{{{e^x} + {e^{ - x}}}}$. When $x$tends to infinity, $\tanh x$ tends to 1 such as
$
\mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to \infty } \tanh x = \mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to \infty } \dfrac{{{e^x} - {e^{ - x}}}}{{{e^x} + {e^{ - x}}}} \\
= \mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to \infty } \dfrac{{\left( {1 - {e^{ - 2x}}} \right)}}{{\left( {1 + {e^{ - 2x}}} \right)}} \\
= \dfrac{{1 - \mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to \infty } {e^{ - 2x}}}}{{1 + \mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to \infty } {e^{ - 2x}}}} \\
= 1 \\
$
Similarly, when $x$ tends to $ - \infty $, the value of $\tanh x$ tends to $ - 1$. Then, we can say that the value becomes almost the same for higher or lower values of $x$.
We will write the value of $\tanh x$ as the ratio of hyperbolic sine function to hyperbolic cosine function. We will then draw a corresponding graph of the given function. Then, check the nature of the graph, that is where the graph is increasing or where the graph is decreasing.
Complete step by step solution:
The hyperbolic tangent function is the ratio of hyperbolic sine function to hyperbolic cosine function.
That is, $\tanh x = \dfrac{{\sinh x}}{{\cosh x}}$
Now, the value of $\sinh x = \dfrac{{{e^x} - {e^{ - x}}}}{2}$ and the value of $\cosh x = \dfrac{{{e^x} + {e^{ - x}}}}{2}$
Then, we can write the hyperbolic function of tangent as
$\tanh x = \dfrac{{\dfrac{{{e^x} - {e^{ - x}}}}{2}}}{{\dfrac{{{e^x} + {e^{ - x}}}}{2}}} = \dfrac{{{e^x} - {e^{ - x}}}}{{{e^x} + {e^{ - x}}}}$
We will plot the graph of $\tanh x$ to identify the nature of the function.

We can see that as the value of $x$ increases, then the value of $\tanh x$ also increases.
Therefore, the graph of the hyperbolic tangent function for all real values is strictly increasing.
Note:
The value of $\tanh x = \dfrac{{{e^x} - {e^{ - x}}}}{{{e^x} + {e^{ - x}}}}$. When $x$tends to infinity, $\tanh x$ tends to 1 such as
$
\mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to \infty } \tanh x = \mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to \infty } \dfrac{{{e^x} - {e^{ - x}}}}{{{e^x} + {e^{ - x}}}} \\
= \mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to \infty } \dfrac{{\left( {1 - {e^{ - 2x}}} \right)}}{{\left( {1 + {e^{ - 2x}}} \right)}} \\
= \dfrac{{1 - \mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to \infty } {e^{ - 2x}}}}{{1 + \mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to \infty } {e^{ - 2x}}}} \\
= 1 \\
$
Similarly, when $x$ tends to $ - \infty $, the value of $\tanh x$ tends to $ - 1$. Then, we can say that the value becomes almost the same for higher or lower values of $x$.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers




