
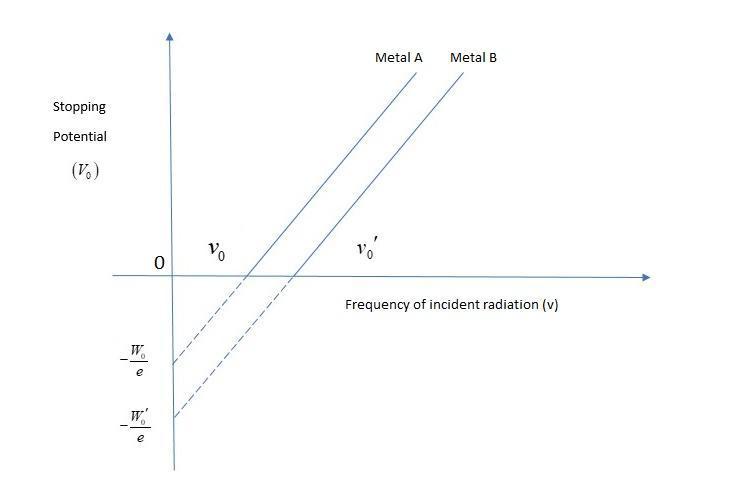
The graph shows variation of stopping potential \[{V_0}\] versus frequency of incident radiation for two photosensitive metals A and B. Which of the two metals has higher threshold frequency and why?

Answer
529.9k+ views
- Hint: Here we will proceed by defining the term threshold frequency and then we will be discussing which metal has high threshold frequency by using the given graph and explaining the exact reasons.
Complete step-by-step solution -
Threshold frequency: The threshold frequency is defined as the minimum frequency of incident radiation below which the photoelectric emission is not possible completely, irrespective of the incident radiation i.e., this frequency is just able to eject electrons without giving them additional energy.
Also stopping potential is the potential necessary to stop any electron from reaching the outside.
As the frequency increases stopping potential also increases. At zero stopping potential the frequency of incident radiation is more to metal A. Both the metals have the same stopping potential at different frequencies and this frequency is more than metal A. So, metal A has a higher threshold frequency.
Thus, metal A has high threshold frequency.
Note: Stopping potential is defined as the potential required to stop ejection of electrons from a metal surface to stop ejection of electrons from a metal surface when an incident beam of energy greater than the work potential of metal is directed on it.
Complete step-by-step solution -
Threshold frequency: The threshold frequency is defined as the minimum frequency of incident radiation below which the photoelectric emission is not possible completely, irrespective of the incident radiation i.e., this frequency is just able to eject electrons without giving them additional energy.
Also stopping potential is the potential necessary to stop any electron from reaching the outside.
As the frequency increases stopping potential also increases. At zero stopping potential the frequency of incident radiation is more to metal A. Both the metals have the same stopping potential at different frequencies and this frequency is more than metal A. So, metal A has a higher threshold frequency.
Thus, metal A has high threshold frequency.
Note: Stopping potential is defined as the potential required to stop ejection of electrons from a metal surface to stop ejection of electrons from a metal surface when an incident beam of energy greater than the work potential of metal is directed on it.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




