
The ground state electronic configuration of $CO$ molecule is:
A: $1{\sigma ^2}2{\sigma ^2}1{\Pi ^4}3{\sigma ^2}$
B: $1{\sigma ^2}2{\sigma ^2}3{\sigma ^2}1{\Pi ^2}2{\Pi ^2}$
C: $1{\sigma ^2}2{\sigma ^2}1{\Pi ^2}3{\sigma ^2}2{\Pi ^2}$
D: $1{\sigma ^2}1{\Pi ^4}2{\sigma ^2}3{\sigma ^2}$
Answer
585.9k+ views
Hint: Electronic configuration is the distribution of electrons of an atom or molecule in atomic or molecular orbitals. Carbon monoxide is isoelectronic with nitrogen. Isoelectronic species are those species which have the same number of electrons.
Complete step by step answer:
In this question we have to find the ground state electronic configuration of $CO$ molecule. $CO$ Molecule is composed of two atoms of different elements. Such molecules are called heteroatomic molecules. In heteroatomic molecules intermixing of atomic orbitals only occurs when electronegativity value is similar to the two atoms. $CO$ is composed of oxygen and carbon.
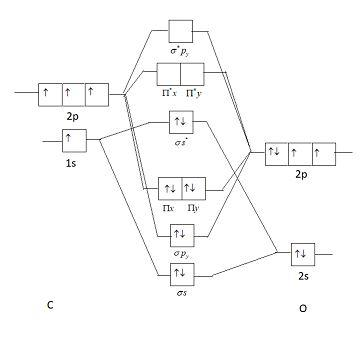
This picture shows a molecular orbital diagram of $CO$.
Oxygen is an electronegative element due to which it is stable and lower in energy. As energy of oxygen is lower than that of carbon, the energy difference of $2s$ orbital of oxygen and carbon is very high. As in heteroatomic molecules electronegativity difference should be low, electronic configuration of $2s$ orbital will not be considered as their mixing will be low (explained above). Electronic configuration of $CO$ molecules is similar to nitrogen (as the number of electrons is the same in both species).
Electronic configuration of ${N_2}$ is: ${\left( {\sigma 1s} \right)^2}{\left( {{\sigma ^*}1s} \right)^2}{\left( {\sigma 2s} \right)^2}{\left( {{\sigma ^*}2s} \right)^2}{\left( {\Pi 2{p_x}} \right)^2}{\left( {\Pi 2{p_y}} \right)^2}{\left( {\sigma 2{p_z}} \right)^2}$
Electronic configuration of $CO$ it is $1{\sigma ^2}2{\sigma ^2}1{\Pi ^4}3{\sigma ^2}$.
Therefore the correct answer is option A.
Additional information: Bond length is approximately equal to the average distance between the nuclei of two bonded atoms. More will be the bond order more will be the pull between electrons of two atoms and less will be the bond length.
Note:
Molecules which have unpaired electrons have net magnetic moment and are called paramagnetic. A molecule which doesn’t have unpaired electrons that molecule does not have net magnetic moment and are called diamagnetic.
Complete step by step answer:
In this question we have to find the ground state electronic configuration of $CO$ molecule. $CO$ Molecule is composed of two atoms of different elements. Such molecules are called heteroatomic molecules. In heteroatomic molecules intermixing of atomic orbitals only occurs when electronegativity value is similar to the two atoms. $CO$ is composed of oxygen and carbon.

This picture shows a molecular orbital diagram of $CO$.
Oxygen is an electronegative element due to which it is stable and lower in energy. As energy of oxygen is lower than that of carbon, the energy difference of $2s$ orbital of oxygen and carbon is very high. As in heteroatomic molecules electronegativity difference should be low, electronic configuration of $2s$ orbital will not be considered as their mixing will be low (explained above). Electronic configuration of $CO$ molecules is similar to nitrogen (as the number of electrons is the same in both species).
Electronic configuration of ${N_2}$ is: ${\left( {\sigma 1s} \right)^2}{\left( {{\sigma ^*}1s} \right)^2}{\left( {\sigma 2s} \right)^2}{\left( {{\sigma ^*}2s} \right)^2}{\left( {\Pi 2{p_x}} \right)^2}{\left( {\Pi 2{p_y}} \right)^2}{\left( {\sigma 2{p_z}} \right)^2}$
Electronic configuration of $CO$ it is $1{\sigma ^2}2{\sigma ^2}1{\Pi ^4}3{\sigma ^2}$.
Therefore the correct answer is option A.
Additional information: Bond length is approximately equal to the average distance between the nuclei of two bonded atoms. More will be the bond order more will be the pull between electrons of two atoms and less will be the bond length.
Note:
Molecules which have unpaired electrons have net magnetic moment and are called paramagnetic. A molecule which doesn’t have unpaired electrons that molecule does not have net magnetic moment and are called diamagnetic.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




