
The halogen atom in aryl halide is-
A.O-and p-directing
B.M-directing
C.O, m and p-directing
D.O- and m- directing
Answer
582.3k+ views
Hint When mono-substituted benzene reacts with an electrophile, the electrophile can get attached to ortho, para or meta position on benzene. The electrophile if gets attached to the ortho or para position, it is called ortho and para directing group. If it gets attached to the meta position it is called a meta directing group.
Step-by-Step solution
Halo-arene or aryl halide$\left( {Ph - X} \right)$ is compound containing one benzene ring with halogen group attached in with the ring. Its structure is given as-
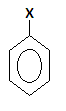
In this structure the ring represents the phenyl group and X is halide.
We know that ortho and para directing groups are electron donating groups and the meta directing groups are electron withdrawing groups. But Halides are the exception to this rule because even when they are electron withdrawing groups they are still ortho and para directing.
1.The halogens are highly electronegative which means they are an electron withdrawing group.
2.But because of their strong –I effect they are highly deactivating due to which the electron density on the benzene ring decreases.
3.But halogens donate their lone pair of electrons in the resonance form which increases the density at ortho and para- position. The resonance structure of aryl halide is shown as-
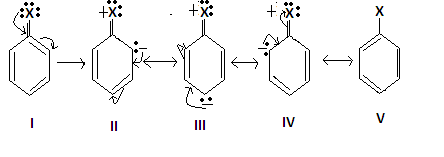
4.Due to this reason the halogen in aryl halide are considered ortho and para- directing.
Answer-Hence the correct answer is A.
Note:I effect is actually an inductive effect which arises when an electron withdrawing group is attached to a carbon chain Halogen shows negative inductive I effect because it has more electron accepting capacity than hydrogen. Here we can also explain this question on basis of resonance effect-
1.Halogen shows positive resonance effect as they have a tendency to donate electrons to double bond or conjugated systems (alternate double bond system).
2.Since benzene has a conjugated system hence halogen donates its electron in the ring acquiring a positive charge. Hence it acts as an ortho and para directing group.
Step-by-Step solution
Halo-arene or aryl halide$\left( {Ph - X} \right)$ is compound containing one benzene ring with halogen group attached in with the ring. Its structure is given as-

In this structure the ring represents the phenyl group and X is halide.
We know that ortho and para directing groups are electron donating groups and the meta directing groups are electron withdrawing groups. But Halides are the exception to this rule because even when they are electron withdrawing groups they are still ortho and para directing.
1.The halogens are highly electronegative which means they are an electron withdrawing group.
2.But because of their strong –I effect they are highly deactivating due to which the electron density on the benzene ring decreases.
3.But halogens donate their lone pair of electrons in the resonance form which increases the density at ortho and para- position. The resonance structure of aryl halide is shown as-

4.Due to this reason the halogen in aryl halide are considered ortho and para- directing.
Answer-Hence the correct answer is A.
Note:I effect is actually an inductive effect which arises when an electron withdrawing group is attached to a carbon chain Halogen shows negative inductive I effect because it has more electron accepting capacity than hydrogen. Here we can also explain this question on basis of resonance effect-
1.Halogen shows positive resonance effect as they have a tendency to donate electrons to double bond or conjugated systems (alternate double bond system).
2.Since benzene has a conjugated system hence halogen donates its electron in the ring acquiring a positive charge. Hence it acts as an ortho and para directing group.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




