
The hybridization state of C atom in butenedioic acid is:
(A) $s{{p}^{2}}$
(B) $s{{p}^{3}}$
(C) both A and B
(D) sp
Answer
538.5k+ views
Hint: Butenedioic acid is an organic compound containing two carboxyl functional groups (-COOH). It has the chemical formula ${{C}_{4}}{{H}_{4}}{{O}_{4}}$. It can also be written as $H{{O}_{2}}CCH=CHC{{O}_{2}}H$. Butendioic acid has two isomers, cis and trans. Cis-butendioic acid is known as maleic acid and trans-butendioic acid is known as fumaric acid. The structure of butenedioic acid can help us figure out the hybridization of carbon atoms present in it.
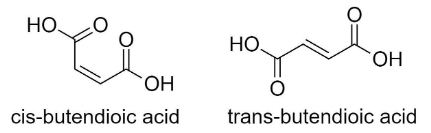
Complete step by step solution:
The concept of making new hybrid orbitals by mixing atomic orbitals is known as hybridization or orbital hybridization. These new hybrid orbitals are suitable to form chemical bonds and have completely different shapes, energies, etc. than the original atomic orbitals.
There are three types of $s{{p}^{x}}$ hybridization, $s{{p}^{3}}$, $s{{p}^{2}}$, and sp.
When one s orbital and three p orbitals hybridize, they form four $s{{p}^{3}}$ orbitals. This is known as $s{{p}^{3}}$ hybridization. In each $s{{p}^{3}}$ orbital, there is 25% of s character and 75% of p character. These usually have a tetrahedral shape.
When one s orbital and two p orbitals hybridize, they form three $s{{p}^{2}}$ orbitals. This is known as $s{{p}^{2}}$ hybridization. In each $s{{p}^{2}}$ orbital, there is 33% of s character and 67% of p character. These usually have trigonal planar shape.
When one s orbital and one p orbital hybridize, they form two sp orbitals. This is known as sp hybridization. In each sp orbital, there is 50% of s character and 50% of p character. These usually have linear shape.
Hybridization of an atom can be found out using these simple steps:
Step 1: Write down the Lewis structure of the molecule as this helps us clearly see the bonding pattern.
Here is the Lewis structure of butenedioic acid.
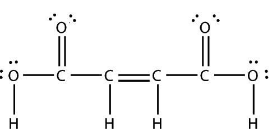
Step 2: Calculate the number of sigma $(\sigma )$ bonds.
We can see that in butenedioic acid each carbon atom has three sigma $\sigma $ bonds.
Step 3: Calculate the number of lone pairs.
Lone pairs can be calculated using the formula
\[\text{number of lone pairs = }\dfrac{v-b-c}{2}\]
Where v is the number of valence electrons of the atom before bond formation,
b is the total number of bonds formed by the atoms. These include both sigma $\sigma $ and pi $\pi $ bonds,
and c is the charge on the particular atom (not the entire molecule).
We know that a carbon atom has 4 valence electrons. So, v = 4.
As we can see from the Lewis structure in step 1, each carbon atom forms 4 bonds, three sigma $\sigma $ bonds and one pi $\pi $ bond. So, b = 4.
Since there is no charge on any of the carbon atoms, c = 0.
So, by using these values, we can find out the number of lone pairs of each carbon atom in the butenedioic acid.
\[\text{number of lone pairs = }\dfrac{4-4-0}{2}=0\]
Step 4: Calculate the steric number using the formula
\[\text{steric number = number of }\sigma \text{ bonds + number of lone pairs}\]
So, using the data from step 2 and step 3, we can find out that
\[\text{steric number = 3 + 0 = 3}\]
Step 5: Find hybridization and shape of the molecule using steric number using the following table
For $s{{p}^{x}}$ hybridization
As we have calculated in step 4, the steric number for each carbon atom in butenedioic acid is 3, so the hybridization of each carbon atom is $s{{p}^{2}}$ and has trigonal planar shape.
So, hybridization state of C atom in butenedioic acid is option (A) $s{{p}^{2}}$.
Note: A very common mistake that can be made while calculating the number of bonds of an atom is missing or forgetting to count the C-H bonds, as H atoms are not usually depicted in the structure of a molecule. This is why it is very important to draw the Lewis structure of a molecule before calculating the number of sigma $\sigma $ or pi $\pi $ bonds.

Complete step by step solution:
The concept of making new hybrid orbitals by mixing atomic orbitals is known as hybridization or orbital hybridization. These new hybrid orbitals are suitable to form chemical bonds and have completely different shapes, energies, etc. than the original atomic orbitals.
There are three types of $s{{p}^{x}}$ hybridization, $s{{p}^{3}}$, $s{{p}^{2}}$, and sp.
When one s orbital and three p orbitals hybridize, they form four $s{{p}^{3}}$ orbitals. This is known as $s{{p}^{3}}$ hybridization. In each $s{{p}^{3}}$ orbital, there is 25% of s character and 75% of p character. These usually have a tetrahedral shape.
When one s orbital and two p orbitals hybridize, they form three $s{{p}^{2}}$ orbitals. This is known as $s{{p}^{2}}$ hybridization. In each $s{{p}^{2}}$ orbital, there is 33% of s character and 67% of p character. These usually have trigonal planar shape.
When one s orbital and one p orbital hybridize, they form two sp orbitals. This is known as sp hybridization. In each sp orbital, there is 50% of s character and 50% of p character. These usually have linear shape.
Hybridization of an atom can be found out using these simple steps:
Step 1: Write down the Lewis structure of the molecule as this helps us clearly see the bonding pattern.
Here is the Lewis structure of butenedioic acid.

Step 2: Calculate the number of sigma $(\sigma )$ bonds.
We can see that in butenedioic acid each carbon atom has three sigma $\sigma $ bonds.
Step 3: Calculate the number of lone pairs.
Lone pairs can be calculated using the formula
\[\text{number of lone pairs = }\dfrac{v-b-c}{2}\]
Where v is the number of valence electrons of the atom before bond formation,
b is the total number of bonds formed by the atoms. These include both sigma $\sigma $ and pi $\pi $ bonds,
and c is the charge on the particular atom (not the entire molecule).
We know that a carbon atom has 4 valence electrons. So, v = 4.
As we can see from the Lewis structure in step 1, each carbon atom forms 4 bonds, three sigma $\sigma $ bonds and one pi $\pi $ bond. So, b = 4.
Since there is no charge on any of the carbon atoms, c = 0.
So, by using these values, we can find out the number of lone pairs of each carbon atom in the butenedioic acid.
\[\text{number of lone pairs = }\dfrac{4-4-0}{2}=0\]
Step 4: Calculate the steric number using the formula
\[\text{steric number = number of }\sigma \text{ bonds + number of lone pairs}\]
So, using the data from step 2 and step 3, we can find out that
\[\text{steric number = 3 + 0 = 3}\]
Step 5: Find hybridization and shape of the molecule using steric number using the following table
For $s{{p}^{x}}$ hybridization
| STERIC NUMBER | HYBRIDIZATION | STRUCTURE |
| 2 | sp | Linear |
| 3 | $s{{p}^{2}}$ | Trigonal planar |
| 4 | $s{{p}^{3}}$ | Tetrahedral |
As we have calculated in step 4, the steric number for each carbon atom in butenedioic acid is 3, so the hybridization of each carbon atom is $s{{p}^{2}}$ and has trigonal planar shape.
So, hybridization state of C atom in butenedioic acid is option (A) $s{{p}^{2}}$.
Note: A very common mistake that can be made while calculating the number of bonds of an atom is missing or forgetting to count the C-H bonds, as H atoms are not usually depicted in the structure of a molecule. This is why it is very important to draw the Lewis structure of a molecule before calculating the number of sigma $\sigma $ or pi $\pi $ bonds.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




