
The kernel color of wheat is determined by _______ gene-
a. One
b. Two
c. Three
d. Five
Answer
594.9k+ views
Hint: Polygenic inheritance traces the inheritance of characteristics that are determined by more than one gene. The kernel colour of wheat is determined through a combination of few genes by considering the red and white color of the wheat.
Complete answer:
The inheritance of traits that are determined by two or more genes is known as polytechnic inheritance. The kernel colour of wheat is determined by two genes that are R1 and R2.
The Scientists Nilsson and Ehle performed several crosses between varieties of wheat plants having red and white seeds. In maximum of the crosses, the F2 generation gave a ratio of 3 red to 1 white.
The red colour of wheat was determined by homozygous dominant R1R2R1R2 gene. While the expression of heterozygous dominant gene was determined by R1r2R1r2 gene expression.
The intensity of the red colour wheat obtained was determined by the number of R genes in the F2 generation. Hence, the option (b) two is the correct answer.
The crossing is done as follows:
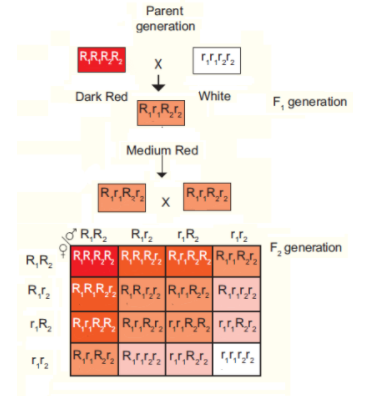
Additional information:
The Polygenic inheritance occurs when one characteristic of an organism or plant is controlled by two or more genes. Polygenes exist in other organisms and plants, as well. The few main examples of polygenic Inheritance other than the kernel color of wheat, in both plants and animals are-
- The height, skin color, eye color, weight in humans- The functioning of these genes greatly depends on environmental factors. They control the functioning of the pituitary and thus controlling growth.
- Ear length in maize – Scientists Emerson and East, observed many quantitative variations in ear size in maize plants. They worked on two varieties of maize which are long eared black Mexican sweet corn and short eared Tom Thumb popcorn.
- Ray Size in Flower Heads of Compositae- It was seen in Bidens Pilosa of Compositae. It was carried out between a normal plant and a recessive mutant. Both showed different characters.
Note: The true breeding wheat plants are white and red. They are crossed to create an F1 of intermediate colour, then the F1 are then crossed to produce the range of colours. The phenotype ratio obtained is 1 : 2 : 1, that is, very red, red and pink respectively.
Complete answer:
The inheritance of traits that are determined by two or more genes is known as polytechnic inheritance. The kernel colour of wheat is determined by two genes that are R1 and R2.
The Scientists Nilsson and Ehle performed several crosses between varieties of wheat plants having red and white seeds. In maximum of the crosses, the F2 generation gave a ratio of 3 red to 1 white.
The red colour of wheat was determined by homozygous dominant R1R2R1R2 gene. While the expression of heterozygous dominant gene was determined by R1r2R1r2 gene expression.
The intensity of the red colour wheat obtained was determined by the number of R genes in the F2 generation. Hence, the option (b) two is the correct answer.
The crossing is done as follows:

Additional information:
The Polygenic inheritance occurs when one characteristic of an organism or plant is controlled by two or more genes. Polygenes exist in other organisms and plants, as well. The few main examples of polygenic Inheritance other than the kernel color of wheat, in both plants and animals are-
- The height, skin color, eye color, weight in humans- The functioning of these genes greatly depends on environmental factors. They control the functioning of the pituitary and thus controlling growth.
- Ear length in maize – Scientists Emerson and East, observed many quantitative variations in ear size in maize plants. They worked on two varieties of maize which are long eared black Mexican sweet corn and short eared Tom Thumb popcorn.
- Ray Size in Flower Heads of Compositae- It was seen in Bidens Pilosa of Compositae. It was carried out between a normal plant and a recessive mutant. Both showed different characters.
Note: The true breeding wheat plants are white and red. They are crossed to create an F1 of intermediate colour, then the F1 are then crossed to produce the range of colours. The phenotype ratio obtained is 1 : 2 : 1, that is, very red, red and pink respectively.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




