
The line integral of an electric field along the circumference of a circle of radius r drawn with a point Q at the centre will be
A. $\dfrac{1}{{4{\pi ^2}{\varepsilon _0}}}\dfrac{Q}{r}$
B. $\dfrac{Q}{{2\pi {\varepsilon _0}r}}$
C. Zero
D. $2\pi Qr$
Answer
543.6k+ views
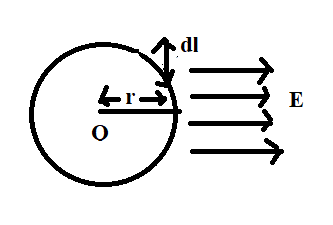
Hint: Here, electric field (E) is flowing along the circumference of the circle whose radius is ‘r’ and centre of the circle is O. A small integral of length ‘’dl’’ is drawn perpendicular to the direction of the electric field. The integral drawn on the circumference of the circle.
Complete step by step answer: To calculate, $\phi \mathop E\limits^ \to .\mathop {dl}\limits^ \to $
According to the above figure, the integral ($\mathop {dl}\limits^ \to $) and electric field ($\mathop E\limits^ \to $) are perpendicular to each other.
Therefore, $\mathop E\limits^ \to .\mathop {dl}\limits^ \to $= $Edl\cos {90^o}$= 0
Or $\mathop E\limits^ \to .\mathop {dl}\limits^ \to $= 0
Thus, $\phi \mathop E\limits^ \to .\mathop {dl}\limits^ \to $ is also zero everywhere along the integral will be zero.
Or $\phi \mathop E\limits^ \to .\mathop {dl}\limits^ \to $= 0
Hence, option (C) is the correct option.
Additional information:
Gauss’s law states that the total of the electric flux out of a closed surface is equal to the charge enclosed divided by the permittivity and also, the total electric flux through a closed surface is zero if no charge is enclosed by the surface.
$\phi = \dfrac{q}{{{\varepsilon _0}}}$
Where q= total charge.
${\varepsilon _0}$= permittivity of the air.
Note: In this question you are asked to find the line integral of an electric field along the circumference of a circle. Students must remember the concept of gauss’s law in which the electric field inside the uniformly charged sphere is zero. Here, we simply use the dot product between the integral and electric field that is perpendicular to each other and get the answer as zero.
Complete step by step answer: To calculate, $\phi \mathop E\limits^ \to .\mathop {dl}\limits^ \to $
According to the above figure, the integral ($\mathop {dl}\limits^ \to $) and electric field ($\mathop E\limits^ \to $) are perpendicular to each other.
Therefore, $\mathop E\limits^ \to .\mathop {dl}\limits^ \to $= $Edl\cos {90^o}$= 0
Or $\mathop E\limits^ \to .\mathop {dl}\limits^ \to $= 0
Thus, $\phi \mathop E\limits^ \to .\mathop {dl}\limits^ \to $ is also zero everywhere along the integral will be zero.
Or $\phi \mathop E\limits^ \to .\mathop {dl}\limits^ \to $= 0

Hence, option (C) is the correct option.
Additional information:
Gauss’s law states that the total of the electric flux out of a closed surface is equal to the charge enclosed divided by the permittivity and also, the total electric flux through a closed surface is zero if no charge is enclosed by the surface.
$\phi = \dfrac{q}{{{\varepsilon _0}}}$
Where q= total charge.
${\varepsilon _0}$= permittivity of the air.
Note: In this question you are asked to find the line integral of an electric field along the circumference of a circle. Students must remember the concept of gauss’s law in which the electric field inside the uniformly charged sphere is zero. Here, we simply use the dot product between the integral and electric field that is perpendicular to each other and get the answer as zero.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




