
The magnetic flux through loop is shown in the fig. It increases according to the relation${{\phi }_{B}}=6{{t}^{2}}+7t$, where ${{\phi }_{B}}$ is in milliwebers and t is in seconds.
(a). What is the magnitude of the emf induced in the loop when $t=2s$.
(b). What is the direction of current through R?
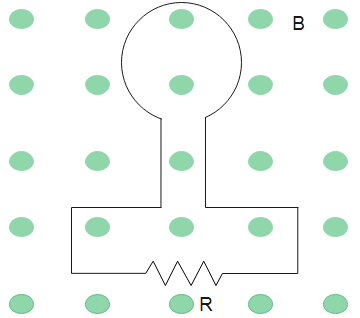

Answer
528.9k+ views
Hint: Given, a loop is kept in a magnetic field such that the flux through it is changing by the given relation. The negative rate of change of magnetic flux is equal to the emf induced. The rate can be calculated by differentiating the change in flux with respect to time. The right hand rule represents the right hand rule.
Formulas used:
$e=-\dfrac{d\phi }{dt}$
Complete step by step answer:
Given, magnetic flux varies according to the relation ${{\phi }_{B}}=6{{t}^{2}}+7t$.
When the magnetic flux through a fixed area varies continuously, an emf is induced. The rate of change of magnetic flux is equal to the emf induced. Therefore,
$e=-\dfrac{d\phi }{dt}$
Here, $e$ is the emf induced
$\dfrac{d\phi }{dt}$ is represented by the rate of change of flux
${{\phi }_{B}}=6{{t}^{2}}+7t$
We differentiate the above equation with respect to time to get,
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{d{{\phi }_{B}}}{dt}=6(2t)+7 \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{d{{\phi }_{B}}}{dt}=12t+7 \\
\end{align}$
When $t=2s$, substituting in the above equation, we get,
$\begin{align}
& e=-\dfrac{d{{\phi }_{B}}}{dt}=-(12\times 2+7) \\
& \Rightarrow e=-31V \\
\end{align}$
Therefore, the emf induced in the loop is $-31V$.
The right hand rule is used to determine the direction of current in the loop. According to the right hand rule the fingers are curled in the direction of magnetic field then the thumb gives the direction of current. Therefore, the direction of current is shown in the figure below.
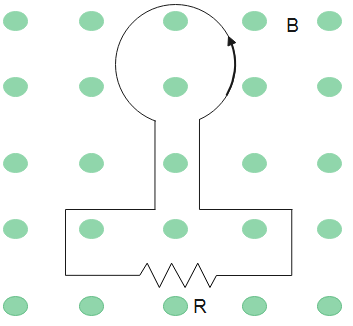
Therefore, the emf induced in the loop is $-31V$ and the direction of current is anticlockwise.
Note: The negative sign in the emf indicates that the emf induced is opposite to the direction of change in flux. This is in accordance with the law of conservation of energy. The current in the loop depends on the emf induced and the resistance in the circuit. The flux can be changed by either moving the loop in a uniform magnetic field or by continuously changing the magnetic field. Dot means that the direction of the magnetic field is in the plane of the paper.
Formulas used:
$e=-\dfrac{d\phi }{dt}$
Complete step by step answer:
Given, magnetic flux varies according to the relation ${{\phi }_{B}}=6{{t}^{2}}+7t$.
When the magnetic flux through a fixed area varies continuously, an emf is induced. The rate of change of magnetic flux is equal to the emf induced. Therefore,
$e=-\dfrac{d\phi }{dt}$
Here, $e$ is the emf induced
$\dfrac{d\phi }{dt}$ is represented by the rate of change of flux
${{\phi }_{B}}=6{{t}^{2}}+7t$
We differentiate the above equation with respect to time to get,
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{d{{\phi }_{B}}}{dt}=6(2t)+7 \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{d{{\phi }_{B}}}{dt}=12t+7 \\
\end{align}$
When $t=2s$, substituting in the above equation, we get,
$\begin{align}
& e=-\dfrac{d{{\phi }_{B}}}{dt}=-(12\times 2+7) \\
& \Rightarrow e=-31V \\
\end{align}$
Therefore, the emf induced in the loop is $-31V$.
The right hand rule is used to determine the direction of current in the loop. According to the right hand rule the fingers are curled in the direction of magnetic field then the thumb gives the direction of current. Therefore, the direction of current is shown in the figure below.

Therefore, the emf induced in the loop is $-31V$ and the direction of current is anticlockwise.
Note: The negative sign in the emf indicates that the emf induced is opposite to the direction of change in flux. This is in accordance with the law of conservation of energy. The current in the loop depends on the emf induced and the resistance in the circuit. The flux can be changed by either moving the loop in a uniform magnetic field or by continuously changing the magnetic field. Dot means that the direction of the magnetic field is in the plane of the paper.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




