
The main function of cerebrospinal fluid is
(a) Nourishment of brain and spinal cord
(b) Functioning as a cushion against shocks
(c) Keeping the central nervous system moist
(d) All of the above
Answer
574.8k+ views
Hint: Generally, it is a clear and colorless bodily liquid that occupies the subarachnoid space and the ventricular system around and inside the brain and spinal cord. For the cortex, it acts as a buffer and it gives an essentially mechanical and immunological assurance to the brain inside the skull and serves a fundamental function in cerebral autoregulation of the cerebral bloodstream.
Complete answer:
The cavities of the central nervous system are represented as the ventricles that are lined with the choroid plexus. The choroid plexus is formed by the inserted pia mater, blood vessels, the ependymal cells. It is responsible for the production of the extracellular fluid called the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) which drains the ventricles of the brain and spinal cord. The cerebrospinal fluid is responsible for gathering the waste from the interstitial space, distribution of nutrients to the cerebrum and spinal cord, going about as a shock collector during wound and moistening of the central nervous system.
Additional information:
Glymphatic system: It is the system in which, the functional waste clearance pathway for the vertebrate central nervous system (CNS) that comprises of a para-arterial influx route for CSF to enter the cerebrum coupled to a clearance mechanism for the evacuation of interstitial fluid and extracellular solutes from the interstitial compartments of the brain and spinal cord.
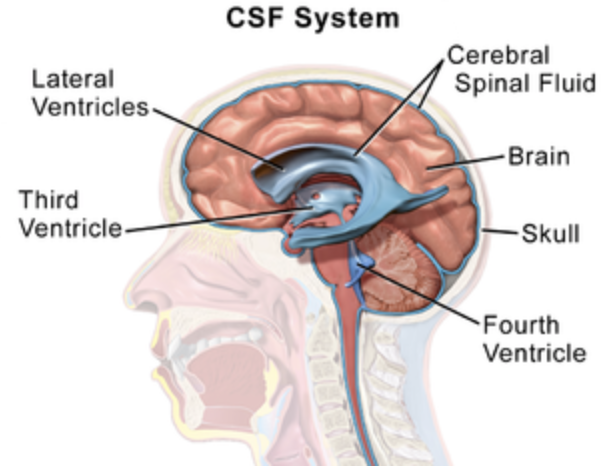
Choroid plexus: It is the structure in the ventricles of the brain where CSF is produced.
Lumbar puncture: The distinguishing at time of therapeutic strategy which performed to collect cerebrospinal fluid for biochemical, cytological analysis, and microbiological, or rarely to assure increased intracranial pressure.
So the correct answer to the above question is ‘All of the above’.
Note: CSF is produced at a rate of 500 ml/day. Since the subarachnoid space around the cerebrum and spinal cord can contain just 135 to 150 ml, enormous amounts are drained into the blood with the help of arachnoid granulations in the prevalent sagittal sinus. In this manner, the CSF turns over about 3.7 times each day.
Complete answer:
The cavities of the central nervous system are represented as the ventricles that are lined with the choroid plexus. The choroid plexus is formed by the inserted pia mater, blood vessels, the ependymal cells. It is responsible for the production of the extracellular fluid called the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) which drains the ventricles of the brain and spinal cord. The cerebrospinal fluid is responsible for gathering the waste from the interstitial space, distribution of nutrients to the cerebrum and spinal cord, going about as a shock collector during wound and moistening of the central nervous system.
Additional information:
Glymphatic system: It is the system in which, the functional waste clearance pathway for the vertebrate central nervous system (CNS) that comprises of a para-arterial influx route for CSF to enter the cerebrum coupled to a clearance mechanism for the evacuation of interstitial fluid and extracellular solutes from the interstitial compartments of the brain and spinal cord.

Choroid plexus: It is the structure in the ventricles of the brain where CSF is produced.
Lumbar puncture: The distinguishing at time of therapeutic strategy which performed to collect cerebrospinal fluid for biochemical, cytological analysis, and microbiological, or rarely to assure increased intracranial pressure.
So the correct answer to the above question is ‘All of the above’.
Note: CSF is produced at a rate of 500 ml/day. Since the subarachnoid space around the cerebrum and spinal cord can contain just 135 to 150 ml, enormous amounts are drained into the blood with the help of arachnoid granulations in the prevalent sagittal sinus. In this manner, the CSF turns over about 3.7 times each day.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




