
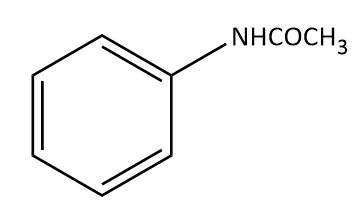
The major product obtained in the reaction of aniline with acetic anhydride is?
(A)
(B)
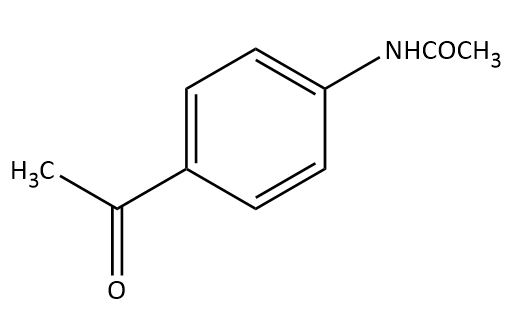
(C)
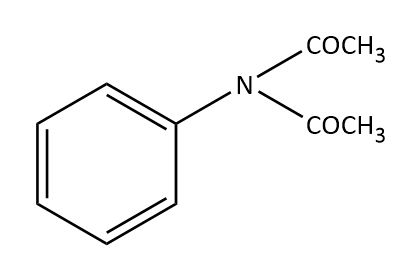
(D)
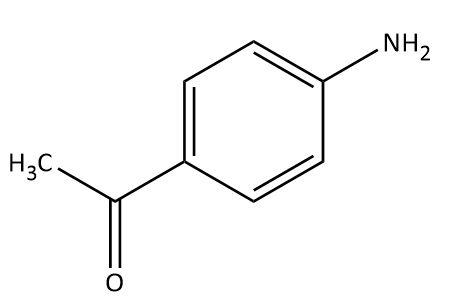




Answer
583.8k+ views
Hint: As we know that acetic anhydride contains two acetic groups bonded with oxygen and the carbonyl stretching frequency for this group is measured maximum. Therefore, it can be attacked by any group which is a Lewis base.
Complete step by step answer:
The aniline has amine group as a functional group which contains nitrogen bearing a lone pair of electrons due the amine group aniline is a very reactive for the halogenation. The nitrogen of amine has lone pair of electrons and delocalized its electron in the benzene ring by donating its electron to empty \[{\pi ^ * }\]orbital of benzene. Due to the delocalization the electron density on the benzene ring is increased at ortho and para positions which causes formation of trisubstituted product on benzene.
To decrease the delocalization effect on benzene, aniline reacts with acetic anhydride. The reaction is followed by an addition-elimination mechanism. The acetic anhydride group containing carbonyl carbon is very electrophilic in nature, so the amine group of aniline attacks readily on the acetic carbonyl carbon and eliminates a leaving group.
The mechanism is shown as-
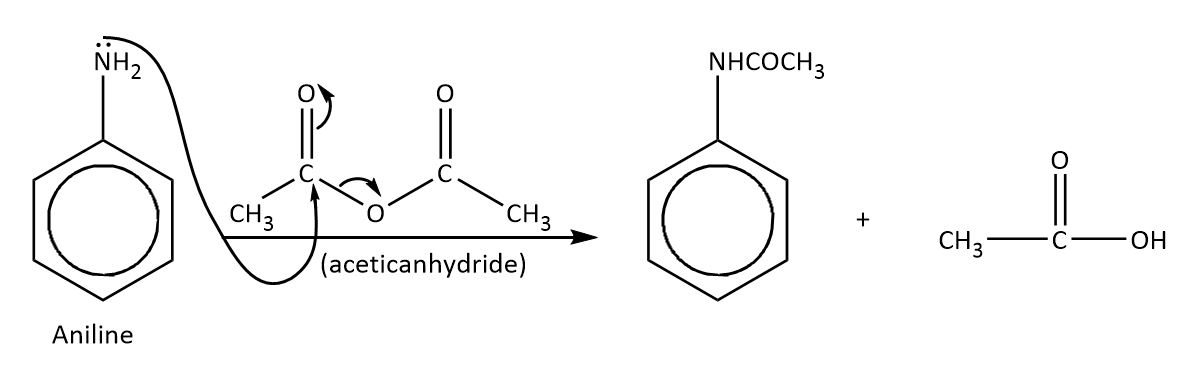
Thus, the correct option is A
Note:
Due to the partial delocalization of electron (resonance) in acetic anhydride the carbonyl group has maximum stretching frequency.
Complete step by step answer:
The aniline has amine group as a functional group which contains nitrogen bearing a lone pair of electrons due the amine group aniline is a very reactive for the halogenation. The nitrogen of amine has lone pair of electrons and delocalized its electron in the benzene ring by donating its electron to empty \[{\pi ^ * }\]orbital of benzene. Due to the delocalization the electron density on the benzene ring is increased at ortho and para positions which causes formation of trisubstituted product on benzene.
To decrease the delocalization effect on benzene, aniline reacts with acetic anhydride. The reaction is followed by an addition-elimination mechanism. The acetic anhydride group containing carbonyl carbon is very electrophilic in nature, so the amine group of aniline attacks readily on the acetic carbonyl carbon and eliminates a leaving group.
The mechanism is shown as-

Thus, the correct option is A
Note:
Due to the partial delocalization of electron (resonance) in acetic anhydride the carbonyl group has maximum stretching frequency.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




