
The manganate and permanganate ions are tetrahedral, due to:
A: The $\pi$ bonding involves overlap of p-orbitals of oxygen with d-orbitals of manganese.
B: There is no $\pi$ – bonding.
C: The $\pi$ bonding involves overlap of p-orbitals of oxygen with p-orbitals of manganese.
D: The $\pi$ bonding involves overlap of d-orbitals of oxygen with d-orbitals of manganese.
Answer
579.9k+ views
Hint: The permanganate ion is not neutral but negatively charged having a -1 charge. The “per” prefix in permanganate is a part of the naming system in case of oxo-anions referring to the oxidation state of the Manganese in the anion. For simplicity, always remember that the prefix “per”, meaning is “above” or “higher” and we should also remember that the oxidation state of manganese in permanganate ion is higher (i.e. more positive) in comparison to manganate.
Complete step by step answer:
Manganate ion:
The manganate ion possesses a negative charge.
The molecular formula of manganate is \[Mn{O_4}^{2 - }\]
The chemical structure of manganate is shown below:
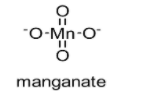
In this manganate ion, two oxygen atoms are having a double bond with the manganese atom while remaining two oxygen atoms are having a single bond.
In this manganate ion, $\pi$ bonds belong to p-orbitals of oxygen and with d-orbitals of manganese (d$\pi$ – p$\pi$).
Permanganate ion:
The permanganate ion possesses a negative charge.
The molecular formula of permanganate is \[Mn{O_4}^ - \].
The chemical structure of permanganate is shown below:
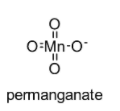
In this permanganate ion, three oxygen atoms are having a double bond with manganese atom and one oxygen atom is having a single bond with manganese atom.
In this permanganate ion, $\pi$ bonds belong to p-orbitals of oxygen and with d-orbitals of manganese (d$\pi$ – p$\pi$).
As a result, the manganate and permanganate ions are tetrahedral, due to the $\pi$ bonding involving overlap of p-orbitals of oxygen with d-orbitals of manganese.
Thus, the correct option is (A).
Note: Manganate consists of manganese in +6 oxidation state while permanganate consists of manganese in +7 oxidation state. Manganate is green in color whereas permanganate is pink in color.
Complete step by step answer:
Manganate ion:
The manganate ion possesses a negative charge.
The molecular formula of manganate is \[Mn{O_4}^{2 - }\]
The chemical structure of manganate is shown below:

In this manganate ion, two oxygen atoms are having a double bond with the manganese atom while remaining two oxygen atoms are having a single bond.
In this manganate ion, $\pi$ bonds belong to p-orbitals of oxygen and with d-orbitals of manganese (d$\pi$ – p$\pi$).
Permanganate ion:
The permanganate ion possesses a negative charge.
The molecular formula of permanganate is \[Mn{O_4}^ - \].
The chemical structure of permanganate is shown below:

In this permanganate ion, three oxygen atoms are having a double bond with manganese atom and one oxygen atom is having a single bond with manganese atom.
In this permanganate ion, $\pi$ bonds belong to p-orbitals of oxygen and with d-orbitals of manganese (d$\pi$ – p$\pi$).
As a result, the manganate and permanganate ions are tetrahedral, due to the $\pi$ bonding involving overlap of p-orbitals of oxygen with d-orbitals of manganese.
Thus, the correct option is (A).
Note: Manganate consists of manganese in +6 oxidation state while permanganate consists of manganese in +7 oxidation state. Manganate is green in color whereas permanganate is pink in color.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




