
The mature infective stages of the malarial parasite which are transferred from mosquito to man are:
(a) Trophozoites
(b) Sporozoites
(c) Gametocytes
(d) Merozoites
Answer
583.2k+ views
Hint: The human-infective stage which is a motile spore-like stage in the life cycle of parasitic sporozoans (e.g. the malaria organism), and is carried by the female Anopheles mosquito in the salivary gland is introduced to a healthy human after bitten by the infected mosquito. They grow and multiply in the liver to become merozoites which then invade the erythrocytes (RBCs) to form trophozoites, schizonts, and gametocytes, during which the symptoms of malaria are produced.
Complete answer:
The blood-stage parasites i.e Plasmodium are those that cause the symptoms of malaria. During the blood meal by a female Anopheles mosquito certain forms of blood-stage parasites (gametocytes, which occur in male and female forms) are ingested. Now those parasites mate and reproduce in the gut of the mosquito and begin a cycle of growth and multiplication in the mosquito. Then sporozoite migrates to the mosquito’s salivary glands after 10-18 days. When a healthy human is bitten, anticoagulant saliva is injected together with the sporozoites, which migrate to the liver, thereby beginning a new cycle.
The malarial parasite goes through various stages in the life cycle. Some of the stages are completed in the mosquito and some are completed in humans. The parasite form in the salivary glands of the infected mosquito is known as sporozoites. while feeding on human blood, the infective stage, the sporozoites are transferred from mosquito to man. The sporozoites go to the human liver for multiplication which turns into merozoites and attacks human RBC.
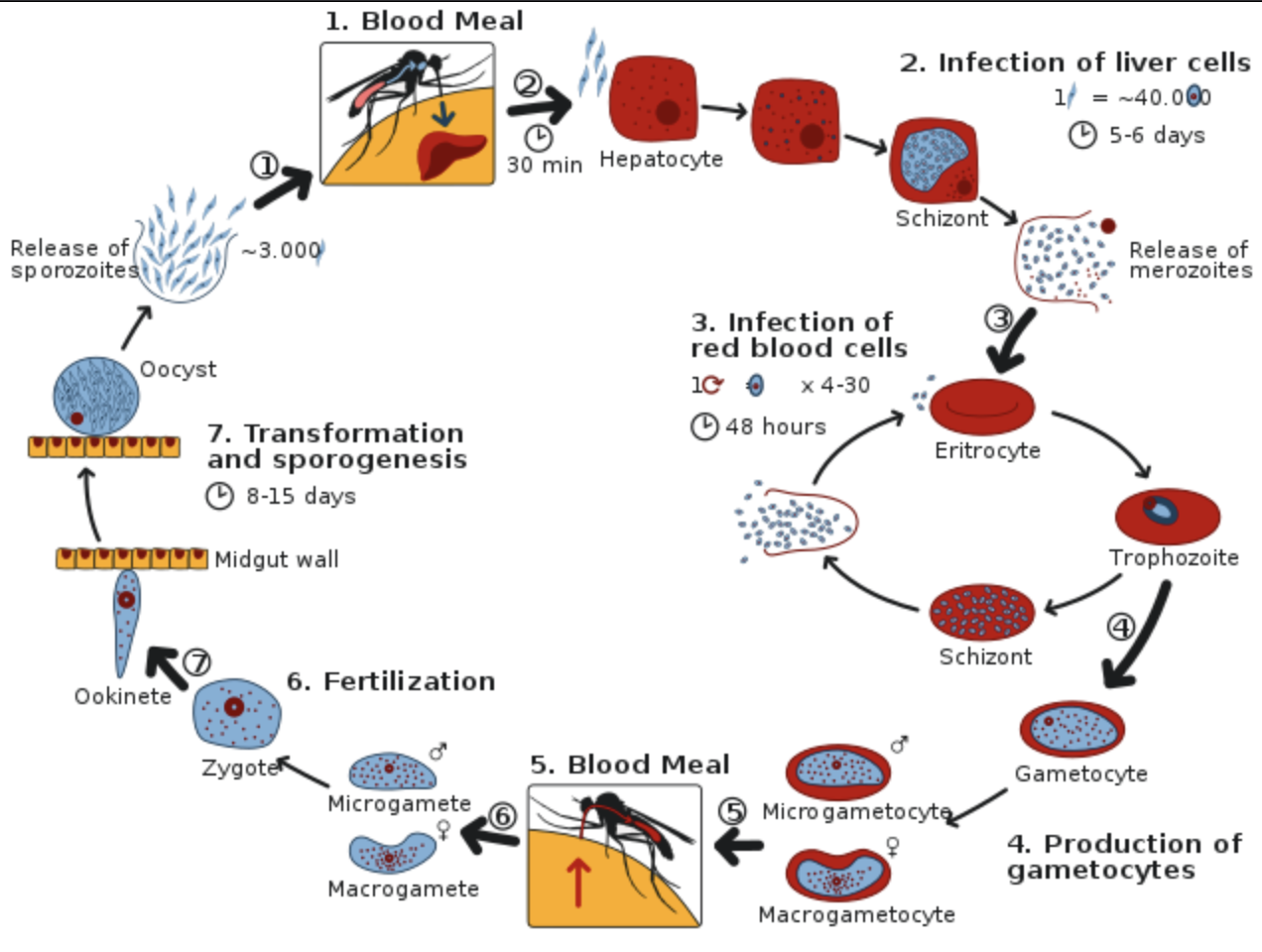
So, the correct answer is, ‘sporozoites’.
Additional information:
1) Five species of Plasmodium (single-celled parasites) can infect humans and cause illness: Plasmodium falciparum, Plasmodium malariae, Plasmodium vivax, Plasmodium ovale, Plasmodium knowlesi..
2) Chloroquine is the preferred treatment for any parasite that is sensitive to the drug. But the parasites that cause malaria are resistant to chloroquine in many parts of the world, and the drug is no longer an effective treatment.
3) Beyond the brain, the lungs are the most affected organ in severe malaria. Lung dysfunction occurs in 20% of all cases of adults with falciparum or vivax severe malaria.
4) A severe epidemic of falciparum malaria began in 1986. At that time over the next 2 years, high death rates occurred in all age groups.
Note: Antimalarial immunity is lost over the last period of time. It probably varies from host to host. It is found that while remaining protected from severe disease, African expatriates (for example, graduate students attending European universities) lose some immunity over 2 to 3 years. Ironically, whole populations become vulnerable to epidemic malaria, when malaria control in a previously high-transmission area proves successful.
Complete answer:
The blood-stage parasites i.e Plasmodium are those that cause the symptoms of malaria. During the blood meal by a female Anopheles mosquito certain forms of blood-stage parasites (gametocytes, which occur in male and female forms) are ingested. Now those parasites mate and reproduce in the gut of the mosquito and begin a cycle of growth and multiplication in the mosquito. Then sporozoite migrates to the mosquito’s salivary glands after 10-18 days. When a healthy human is bitten, anticoagulant saliva is injected together with the sporozoites, which migrate to the liver, thereby beginning a new cycle.
The malarial parasite goes through various stages in the life cycle. Some of the stages are completed in the mosquito and some are completed in humans. The parasite form in the salivary glands of the infected mosquito is known as sporozoites. while feeding on human blood, the infective stage, the sporozoites are transferred from mosquito to man. The sporozoites go to the human liver for multiplication which turns into merozoites and attacks human RBC.

So, the correct answer is, ‘sporozoites’.
Additional information:
1) Five species of Plasmodium (single-celled parasites) can infect humans and cause illness: Plasmodium falciparum, Plasmodium malariae, Plasmodium vivax, Plasmodium ovale, Plasmodium knowlesi..
2) Chloroquine is the preferred treatment for any parasite that is sensitive to the drug. But the parasites that cause malaria are resistant to chloroquine in many parts of the world, and the drug is no longer an effective treatment.
3) Beyond the brain, the lungs are the most affected organ in severe malaria. Lung dysfunction occurs in 20% of all cases of adults with falciparum or vivax severe malaria.
4) A severe epidemic of falciparum malaria began in 1986. At that time over the next 2 years, high death rates occurred in all age groups.
Note: Antimalarial immunity is lost over the last period of time. It probably varies from host to host. It is found that while remaining protected from severe disease, African expatriates (for example, graduate students attending European universities) lose some immunity over 2 to 3 years. Ironically, whole populations become vulnerable to epidemic malaria, when malaria control in a previously high-transmission area proves successful.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




