
The monomer used to produce orlon is:
A.$C{{H}_{2}}=CHF$
B.$C{{H}_{2}}CC{{l}_{2}}$
C.$C{{H}_{2}}=CHCl$
D.$C{{H}_{2}}=CH-CN$
Answer
575.7k+ views
Hint: Orlon is also known as polyacrylonitrile(PAN). Orlon is used both commercially, and in industries which have rugged tasks. The monomer of orlon contains unsaturation in its carbon chain.
Complete step by step answer:
-A monomer could be a small molecule that reacts with an analogous molecule to create a bigger molecule. it's the littlest unit in an exceedingly polymer, which is usually
macromolecule with high mass. Monomers are the building blocks for biological macromolecules like DNA, RNA, proteins and carbohydrates.
-There are mainly four types of monomer which includes sugars, amino acids, fatty acids, and nucleotides.
-Polymers are a category of synthetic substances which composes of multiples of simpler units called monomers discussed above. Polymers are chains with an unspecified number of monomeric units. That is polymers are composed of monomers by joining them.
-A monomer could be a molecule that forms the fundamental unit for polymers, which are the building blocks of proteins. Monomers bind to other monomers to create repeating chain molecules through a process called polymerization.
-Orlon is created from polymerized acrylonitrile. The acrylic is dissolved in a very solvent, then extruded through spinnerets to supply long, continuous filaments. The smooth, thermoplastic fibers are proof against wrinkles, chemicals, UV light, weathering, insects, mildew, and moisture. Now let's come to the solution. Structure of orlon is:
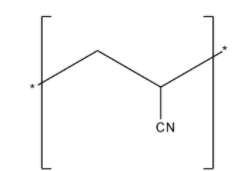
Acrylonitrile ( $C{{H}_{2}}=CH-CN$) is the monomeric unit of the polymer orlon . Orlon is also known as PAN (Polyacrylonitrile) as mentioned earlier.
So the correct option is D.
Note: The simplest technique to identify a monomer is to seem at its structure. It always contains different combinations of atoms that together form a singular molecule having a chemical formula in accordance with the overall formula of that class. for instance, the final formula for monomers of carbohydrates is ${{(C{{H}_{2}}O)}_{x}}$.
Complete step by step answer:
-A monomer could be a small molecule that reacts with an analogous molecule to create a bigger molecule. it's the littlest unit in an exceedingly polymer, which is usually
macromolecule with high mass. Monomers are the building blocks for biological macromolecules like DNA, RNA, proteins and carbohydrates.
-There are mainly four types of monomer which includes sugars, amino acids, fatty acids, and nucleotides.
-Polymers are a category of synthetic substances which composes of multiples of simpler units called monomers discussed above. Polymers are chains with an unspecified number of monomeric units. That is polymers are composed of monomers by joining them.
-A monomer could be a molecule that forms the fundamental unit for polymers, which are the building blocks of proteins. Monomers bind to other monomers to create repeating chain molecules through a process called polymerization.
-Orlon is created from polymerized acrylonitrile. The acrylic is dissolved in a very solvent, then extruded through spinnerets to supply long, continuous filaments. The smooth, thermoplastic fibers are proof against wrinkles, chemicals, UV light, weathering, insects, mildew, and moisture. Now let's come to the solution. Structure of orlon is:

Acrylonitrile ( $C{{H}_{2}}=CH-CN$) is the monomeric unit of the polymer orlon . Orlon is also known as PAN (Polyacrylonitrile) as mentioned earlier.
So the correct option is D.
Note: The simplest technique to identify a monomer is to seem at its structure. It always contains different combinations of atoms that together form a singular molecule having a chemical formula in accordance with the overall formula of that class. for instance, the final formula for monomers of carbohydrates is ${{(C{{H}_{2}}O)}_{x}}$.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




